
Operational technology (OT) systems are essential in various sectors, including manufacturing, energy, and transportation, in the current digital era. Real-time monitoring and control of physical processes and devices are the responsibility of these systems. However, there is a higher danger of security breaches and attacks when OT solutions are used more frequently.
It is important to think about the security threats that come with technology as it develops and becomes more ingrained in our daily lives. This is particularly true for operational technology (OT) systems, which are used to manage and control vital infrastructure, including factories and power plants.
An OT system’s attack surface describes the different ways that it might be accessed or used by cybercriminals. A security breach could have disastrous results because of the growing reliance on OT technologies.
In this article, we will examine the various facts of the OT security attack surface, including typical flaws and recommended defense strategies. Additionally, we’ll talk about the significance of taking preventative action to lower risk and the function that cybersecurity experts have in protecting OT systems.
Table of Content
What is an OT Security surface attack?
The whole region of a system or organization that is vulnerable to hacking is known as the “attack surface.” It consists of all the points of entry that a stranger could utilize to access the system. Once connected to your network, the user could alter or download information to damage your system. It is simpler to defend your organization to reduce your attack surface.
A smart initial step to lowering or defending your attack surface is to perform a surface analysis.
A wide attack surface has numerous areas where an unauthorized individual would be able to access sensitive data, including financial records, personally identifiable information (PII) for employees and customers, secret product or sales information, and more.
The greatest strategies to improve your security posture and reduce risk include limiting external access points, limiting digital footprints, and tightening authentication requirements.
Let us quickly Brief the Different Types of Attack Surfaces
Modern cybersecurity discussions frequently revolve around one specific attack surface: the digital attack surface of your firm. However, if your security staff is just monitoring the digital footprint of your company, you could be leaving yourself up to unforeseen security hazards.
Below is the list of 5 types of attack surfaces –
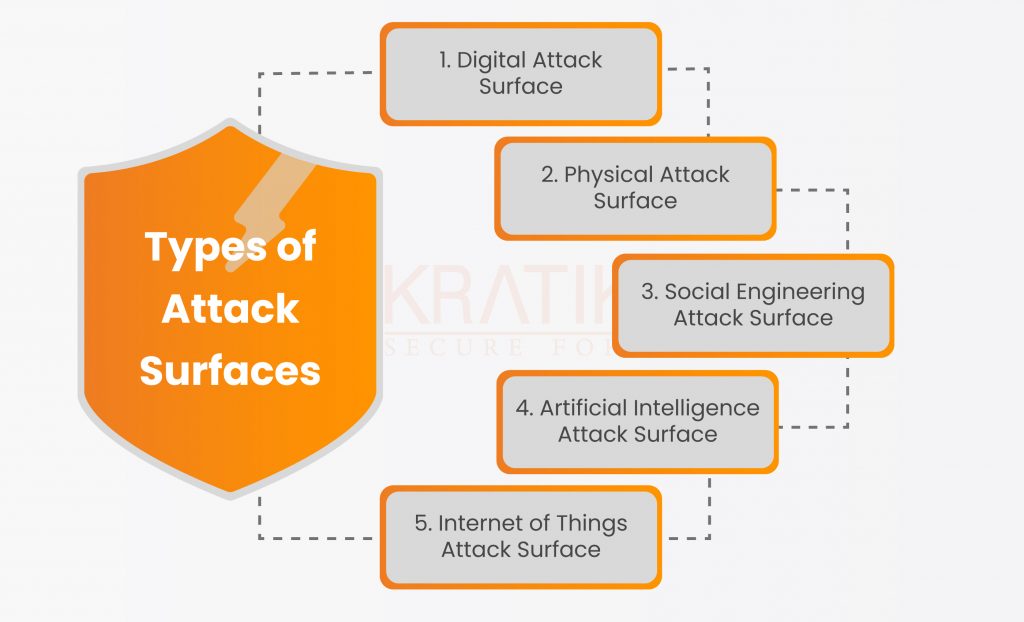
- Digital Attack Surface – Any digital touchpoints that could be used as a gateway for unauthorized access to your systems and network are referred to as your network’s “attack surface.” These consist of codes, servers, programs, ports, websites, and unapproved system access points. The digital attack surface includes any vulnerabilities brought on by poor coding, exposed APIs, poorly maintained software, or weak passwords.
- Physical Attack Surface – A physical attack surface includes every piece of hardware and physical endpoint equipment, including computers, tablets, laptops, printers, switches, routers, security cameras, USB ports, and mobile phones. A physical attack surface, then, is a security flaw within a system that is physically reachable by an attacker who wants to conduct a security attack and access your systems and networks.
- Social Engineering Attack Surface – Protecting both physical and digital attack surfaces can be difficult when social engineering is used by attackers to persuade people to reveal passwords or sensitive information. This can involve criminals impersonating employees to obtain information, seizing login details through phishing, or sending contaminated files to a worker. The social engineering attack surface includes external risks preying on personnel with little security awareness as well as malicious insider threats.
- Artificial Intelligence Attack Surface – AI algorithms are susceptible to adversarial machine learning, which can reveal flaws that businesses may not have known existed. It is more difficult to defend against possible threats because attacks of this nature cannot be patched like conventional software. Additionally, a malicious actor only needs to submit dangerous data in order to trick an AI system; they do not even require credentials to do so. AI technologies, according to experts, are even simpler to exploit than traditional IT systems.
- Network Attack Surface – It refers to a vulnerability in a network that an attacker can exploit to gain access to an organization’s internal system or sensitive data. For example, open ports, weak or default passwords, and misconfigured devices.
Reducing Attack Surface –
With a deep understanding of the types of attack surfaces, we need to focus on how to reduce these attack surfaces. Below are the steps for the reduction of the attack surface.
- Zero Trust – Before gaining access to your resources, a user must establish their identity and device security. Although it’s simpler to relax these restrictions and let everyone view everything, putting security first will make your business safer.
- Strong Authentication Policies – Prior to establishing their identification and the security of their device, a user should not be granted access to your resources. Although it would be simpler to relax these restrictions and let everyone access everything, doing so would put your company’s safety at risk.
- Segment your network– Hackers will find it more difficult to quickly access the core of your company the more firewalls you erect. If you do it well, security controls can be reduced to just one user or computer.
- Strong Access User Protocol – Each user must have access to your network in order to carry out their duties, but as soon as they leave your company, those privileges should be revoked. To firmly establish password policies, collaborate with Human Resources.
- Train employees: Employees are essential in protecting against cyberattacks. By providing them with regular cybersecurity awareness training, they can learn how to identify and prevent attacks through phishing emails and social engineering. This training will help them understand and follow best practices for keeping the organization secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reducing the attack surface is an essential step in securing an OT (Operational Technology) environment. By identifying and inventorying all assets, assessing vulnerabilities, implementing security controls, removing unnecessary assets, monitoring and reviewing the system, and staying up to date, organizations can effectively reduce the risk of attacks and protect their OT systems and networks.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that their OT environment is secure and can continue to operate smoothly.
Kratikal Tech a CERT-IN Empanelled organization ensures reducing the attack surface by performing rigorous testing, meaning full protection from any prospective damages caused by these devices.
We use cutting-edge technologies, full-fledged tools, and the best practices to perform pen-testing over the IT infrastructure of companies. Our effective and futuristic approach makes sure to keep businesses protected against several cyber crimes.
Write your thoughts on OT security in the comment section below


