To bring or not to ‘bring your own device’ to work, that is the question!
During COVID-19, when organizations were abruptly forced to shift to a remote work model, BYOD became a novelty, and now, as the use of personal computing devices – especially smartphones – has expanded, the BYOD model has developed likewise.
A study by IndustryArc suggests that the BYOD market will reach $485.5 billion by 2025 pertaining to the increasing acceptance of BYOD policies to catch up to the growing demand for work flexibility.
Before too long, BYOD was a welcomed concept following its unique qualities – reduction of capital expenditures and up-to-date devices to name some – but its advantages also brought some special security challenges which ended up expanding an organization’s attack surface.
Let’s further examine the concept of BYOD to better understand what it has in store for the employers and employees alike.
Table of Contents
BYOD Security: The Challenges
BYOD, or Bring Your Own Device, allows employees to use personal devices – Laptops, Smartphones, USB Drives – for official business. Since these devices are connected to the company’s internal network, they can access organizational systems, including the sensitive information stored in them.
2022 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report states that the components of a business exposed to the internet are the components most targeted by cyber criminals, who exploit these vulnerabilities due to their technological misconfiguration and misuse.
BYOD, though beneficial, exposes many elements of an organization to such risks, which can result in –
- Potential Data Leakage
Usage of personal devices by the employees to even perform mundane tasks, like logging into their work account, can pose a great risk to a corporate network. The data stored on personal devices can be accessed by an attacker in case the device is stolen or lost.
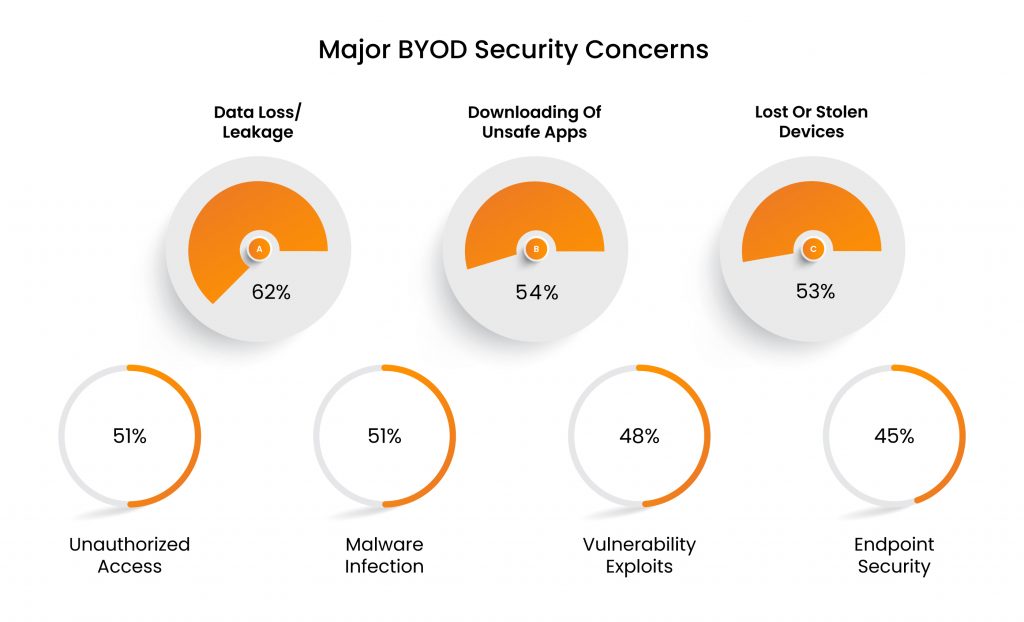
Bitglass’s 2021 BYOD Security Report revealed that security professionals’ main security concern about BYOD employment remains data leakage (62%), while concerns related to users downloading unsafe apps or content (54%), and lost or stolen devices (53%) follows closely behind.
- Lacking Endpoint Security
Employee devices may be up-to-date most of the time, but there is a chance that they may be poorly managed in terms of security. They may lack firewalls, antivirus or other significant on-device security solutions.
These depleted security measures increase the likelihood of an attacker exploiting a vulnerability and accessing the organization’s network and business applications.
The above mentioned report by Bitglass disclosed that around 45% security professionals are concerned about their inability to control endpoint security.
- Attack Surface Expansion
BYOD policy implementation has left an organization’s security team protecting a wide range of devices. This lands IT teams in a difficult position as different devices contain their own fair share of unique vulnerabilities and attack vectors.
- Blending Personal And Business Life
With BYOD, the possibility of employees using their personal devices to perform both the work related tasks and their personal tasks will only increase. Organizations will have no means to know whether the websites visited or the applications installed, some of which may be malicious, by the employees are for work or personal use.
Devices may also be used to connect to unsecured wireless networks which will put the organizational information stored on those devices in jeopardy.
BYOD Security: The Mitigation

- Educating employees is important!
Design a detailed BYOD policy and take the time to school the employees about it. Users should be aware of what they can and cannot do on their personal devices, why these security measures are vital and the consequences they will have to face in case they violate the policy.
Employees should undergo security training, and gain awareness of all the potential threats to themselves and the organization to help them prevent security incidents – major and minor alike – in the future.
- Segregate your personal and business data!
An employee’s personal device can contain information that the employee does not wish to share with their workplace, at the same time, the sensitive business information should not be shared with others. A BYOD security policy should clearly state how to bifurcate personal and official data to prevent unwanted exposure.
- Have a solution in place for lost/stolen devices!
A stolen or lost device should immediately be reported to the management or the IT department so the necessary action can be taken, such as employing remote device lock, wipe the data, reset the password, and initiate auto-wipe for critical applications.
- A Secured Network Connectivity is the key!
Since attackers can easily eavesdrop and pry on business activities in case an employee connects to a public network, they should be educated to connect their devices to a secure network, not only in the office, but also at their leisure. They should only connect to a secured network via an encrypted Virtual Private Network (VPN).
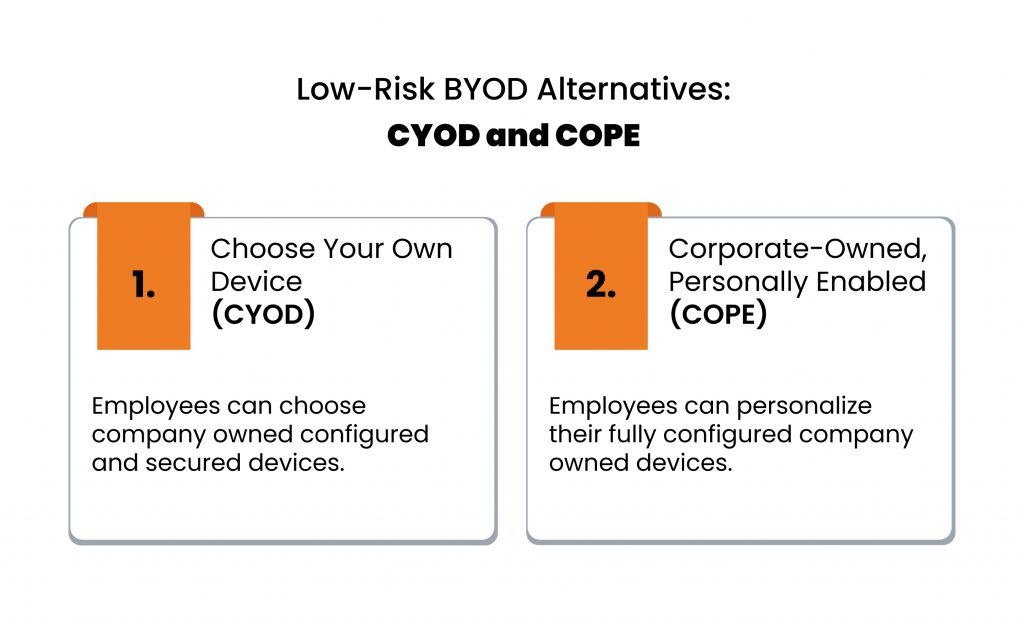
Low-Risk BYOD Alternatives: CYOD and COPE
BYOD, with its compelling pros and cons, has two potential alternative models which are adopted by countless organizations.
- Choose Your Own Device (CYOD)
This policy permits businesses to let their employees choose their own equipment from a set of pre-approved devices that the company owns. These devices are configured and secured beforehand.
CYOD gives employees freedom to select their own device to promote compatibility and enforce a certain level of security on all the devices.
- Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled (COPE)
COPE provides employees with equipment which are completely owned by the organization, which maintains the device and pays its preservation costs, but allows users to personalize them. With some restrictions, the users are permitted to download applications and software which may not be work related, and customize the interface as per their own convenience.
This policy gives the highest level of device control to the company so the devices can be pre-configured for security reasons and made compatible with the organization’s systems and networks. It authorizes the owner to harden and lock the device in advance to enhance its security.
Up Your BYOD Security With Kratikal
With remote work taking the stage in recent time, BYOD security policies have been adopted by numerous companies.
Kratikal, a CERT-In empanelled security solutions firm, provides the necessary services to ensure the security of an organization’s IT assets, as well as their employees’ safety, through security testing. The complete suite of VAPT services, including Network Penetration Testing, Application Penetration Testing, Cloud Penetration Testing, and many more, is designed to evaluate the vulnerabilities in various devices and their networks so they can be dealt with beforehand.
BYOD policy, along with its benefits, has put forth various challenges for cyberspace! What are your thoughts on the matter? Share your thoughts about remote work and BYOD in the comment section below!










Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *