We all know how crucial NBFCs are in encouraging inclusive growth in the country. Micro, small, and medium-sized businesses benefit from NBFCs’ innovative financial services. Furthermore, NBFCs contribute to the development of an economy by creating wealth, giving bank credit to rural sectors, and offering financial assistance to the poor.
Before we get into the classification of NBFCs, let’s first define what they are. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates NBFCs, and they must be registered under the Companies Act of 2013. It is characterized as a financial institution that provides banking services but does not hold a banking license.
NBFCs are financial intermediaries that accept deposits and deliver credits, and they play a critical role in directing scarce financial resources toward capital production.
Table of Contents
Reasons why NBFCs are vital to the economy:
- Growth – Customers in both urban and rural locations are served by NBFCs. They fund small-business ventures, which are critical for rural development. Small-ticket financing for affordable housing developments is also available. These factors all contribute to the country’s inclusive growth.
- Infrastructure Lending – NBFCs provide a significant contribution to the economy by financing infrastructure projects, which are critical in a developing country like India. These are risky ventures since they demand a significant sum of money and only produce profits over a long period of time, which discourages banks from lending. NBFCs have lent more money to infrastructure than banks in recent years.
- Cost Effective – Because they have fewer costs, NBFCs are more profitable than banks. Customers can benefit from lower-cost loans because of this. As a result, NBFC credit growth outpaces that of the banking industry, with more clients choosing NBFCs.
The Reserve Bank of India published the Master Direction – Information Technology Framework for the NBFC Sector this year, in response to the growing importance of NBFCs in the Indian economy. The NBFC IT Framework is designed to improve safety, security, and operational efficiency, resulting in benefits for NBFCs and their clients. The new “recommendations” will be followed by NBFCs with assets above 500 crores. Developing basic IT systems, mostly for database maintenance, is recommended for smaller NBFCs with less than 500 crores in assets.
Classification of NBFCs based on their asset size:
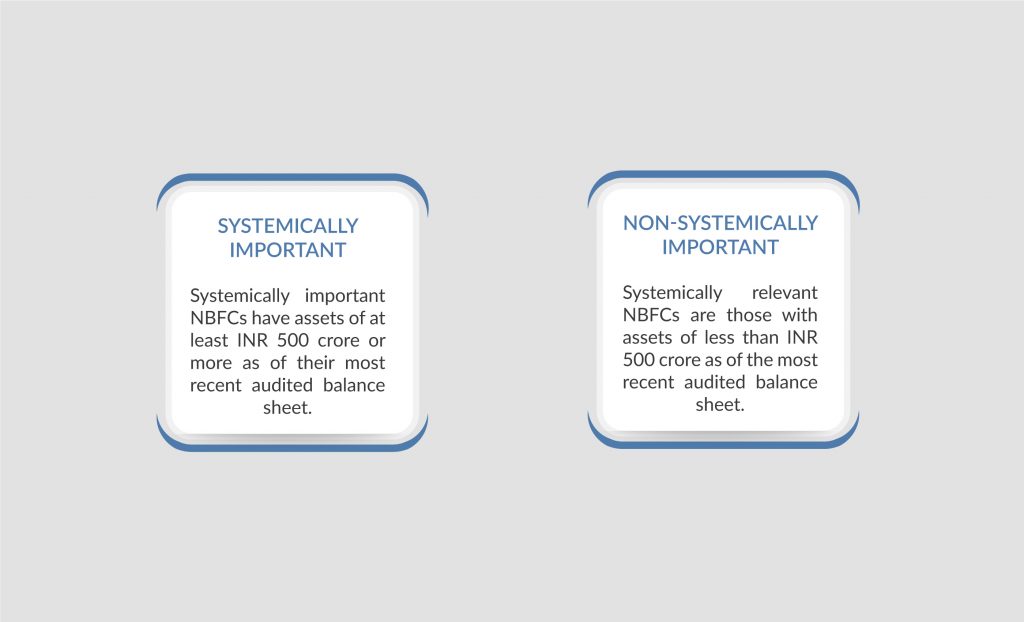
- Systemically Important – Systemically important NBFCs have assets of at least INR 500 crore or more as of their most recent audited balance sheet.
- Non-systemically Important – Systemically relevant NBFCs are those with assets of less than INR 500 crore as of the most recent audited balance sheet.
Let’s discuss them in detail to have a proper understanding of the above two categories as per DNBS PPD No 04/66 15 001/2016-17 released on 8th June 2017.
Section A applies to assets worth more than 500 crores
Corporate governance includes IT governance. This would entail executive support, organizational structure, and processes to ensure that the NBFC’s IT supports and extends its business strategy and objectives. Further IT governance is divided into basic principles like – IT Strategy committee, IT Policy, Information and Cyber Security, IT Operations, IS Audit Business community Planning.
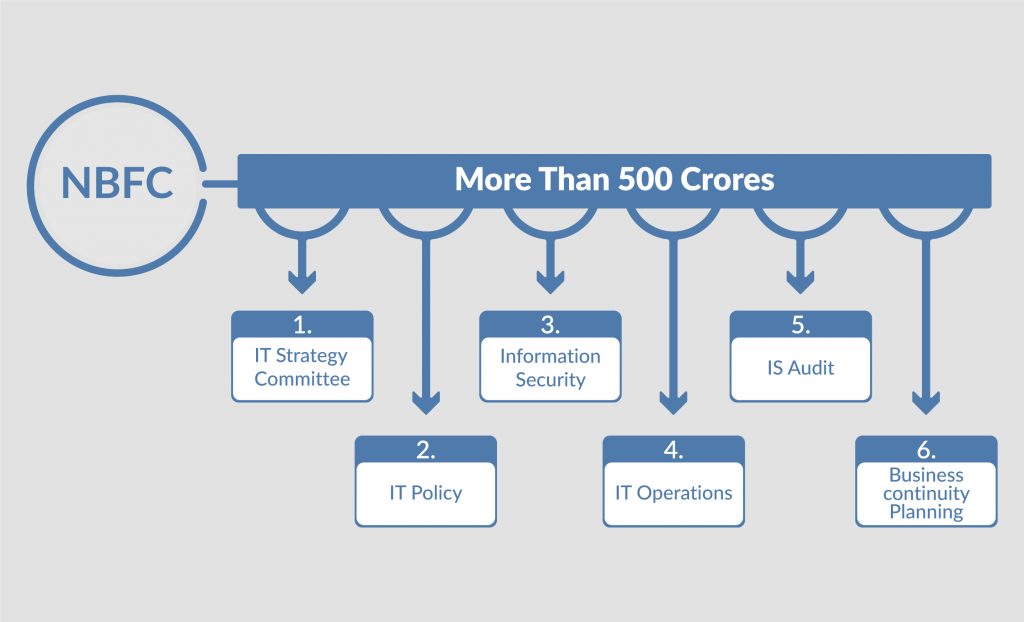
- IT Strategy Committee
An IT Strategy Committee is needed for all NBFCs. The group should have an impartial chairman and include the CIO and CTO. The IT Strategy Committee should convene at least once every six months. It will also assess and revise IT strategies to align with company strategies, as well as conduct Board Policy reviews, cyber security arrangements, and other IT Governance-related tasks. Its decisions could be made public.
The role and responsibilities of IT strategy –
- Approval of IT strategy and policy documents, as well as confirming that management has implemented an efficient strategic planning process
- Guarantee that management has put in place policies and practices to ensure that IT adds value to the company.
- Assuring that IT investments are balanced in terms of risks and rewards, as well as those budgets are within acceptable limits.
2. IT Policy –
An IT policy must be formulated by NBFCs which will be approved by the board with the following objectives –
- An IT organizational structure that is proportional to the size, scope, and nature of the NBFC’s business activities.
- Periodic assessments of IT training requirements should be created to guarantee that sufficient, competent, and capable human resources are available to ensure technical competency at senior/middle-level management of NBFC.
3. Information Security –
All NBFCs have information assets, and Information Security (IS) refers to the safeguarding of these assets to meet organizational objectives. The goal of IS is to limit access to sensitive data and ensure that only authorized individuals can access it, guaranteeing that data cannot be viewed or compromised without permission. NBFCs must have an IS Policy with the following essential principles that have been authorized by the board of directors –
- Authenticity – It is required for IS to assure the authenticity of data, transactions, communications, and documents.
- Availability – Ensuring that consumers have continuous access to data when they need it.
- Integrity – Guarantee the accuracy and reliability of data by ensuring that no changes are made without permission.
- Confidentiality – Access to sensitive data should only be granted to authorized individuals.
4. IT Operations –
Information processing and storage should be supported by IT operations so that the essential data is available in a timely, reliable, secure, and resilient manner. The Board or Senior Management should assess the risk associated with current and anticipated IT operations, as well as the risk tolerance, before establishing and monitoring risk management policies.
5. IS Audit –
The IS Audit’s goal is to assess the effectiveness of controls in place to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the organization’s IT infrastructure. IS Audit will identify risks and mitigation strategies related to IT infrastructure, such as server architecture, local and wide area networks, physical and information security, telecommunications, and so on.
6. Business Continuity Planning
To create a thorough Business Impact Analysis, NBFCs must first identify essential business verticals, locations, and shared resources. The procedure would consider the effects of any natural or man-made calamities on the NBFC’s operations. The vulnerabilities associated with interrelationships between multiple systems, departments, and business processes must be properly understood by NBFCs.
Section B applies to assets worth Less than 500 crores-
Smaller NBFCs are advised to begin by implementing basic IT systems, mostly for database maintenance. A Board-approved Information Technology policy/Information System policy is required for NBFCs with assets of less than 500 crores. The following fundamental standards may be used to develop this policy –
- Physical/logical access controls, as well as a well-defined password policy, are all basic security features.
- User roles that are well-defined.
- Cybersecurity and information security are two terms that are often used interchangeably.
- Compliance with the RBI’s regulatory returns (COSMOS Returns);
- Data backup and testing plan.
- A Board-approved BCP policy that ensures the Board’s regular oversight through periodic reports (at least once a year);
- To limit the possibility of error and misuse while also ensuring data/information reliability, a maker-checker idea was developed.
What can be the solution?
Given the amount of complexity of business and acceptable levels of risk, NBFCs with more than or less than 500 crores should put in place a cyber security policy explaining the strategy comprising an appropriate approach to combat cyber threats, officially approved by their Board. NBFCs should assess their organizational structures to ensure that security risks are recognized, given enough attention, and escalated to suitable levels in the hierarchy for prompt action.
Kratikal being a CERT-In Empanelled company deals with cyber security solutions. NBFCs should be well equipped to deal with rising cyber risks such as “zero-day” attacks, remote access threats, and targeted attacks. NBFCs should, among other things, adopt the required preventive and corrective steps in dealing with various forms of cyber risks, such as denial of service (DoS), ransomware/crypto ware, destructive malware, and business email fraud.
The scope of expansion in this market is exponential, with every public entity focusing on changing its cyber security methods. Stay up to date on the newest cyber security trends and news by following the Kratikal blogs.
Let us know what you think in the comments section below!









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *