आज का संकल्प, कल की सुरक्षा
India is among the fastest-growing countries in the world in terms of digitization and technological advancement. Over the past few years, the Indian government has employed several programs and schemes to ensure the proper fulfillment of the infrastructural requirements to facilitate such growth. However, with rapid technological development and increased use of the internet comes the growing risk of cybercrimes. This has generated a huge demand for a proper cybersecurity framework.
The two most important growth parameters that determine the strength of cybersecurity infrastructure are security and sustainability. The current cybersecurity landscape of India needs to evolve in tandem with the increasing rate of cybercrimes. Recognizing this need, the Indian government has rolled out initiatives such as Cyber Surakhsit Bharat, Cyber Jagrukta Divas, Cyber Suraksha Kendra, etc., to support the growth and development of the country’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
The government also observed that 60% of cybercrime complaints are related to financial fraud. To address the situation, the MHA launched the Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting & Management System (CFCFRMS), which will act as an immediate response mechanism for stopping and preventing the theft of funds by threat actors. In addition, the government recognizes the fact that human negligence and lack of awareness among employees are the prominent causes of cybercrimes in the country. To address this issue, the Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative was launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
So, here is all you need to know about this promising initiative.
Table of Contents
What is Cyber Jagrukta Divas?
Cyber Jagrukta Divas is a government initiative that has been brought under the I4C scheme to raise cybersecurity awareness among public sector undertakings (PSUs), panchayat raj institutions (PRIs), universities, schools, etc. The exact guidelines relayed by the Home Ministry are that the above-mentioned institutions must carry out an awareness campaign on the first Wednesday of each month for at least an hour.
The MHA has asked the offices and branches of all the states and union territories to observe Cyber Jagrukta Divas and prepare a comprehensive “Annual Action Plan“ that will act as a nodal guideline for year-round awareness campaigns. The Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative will be administered by the MHA under the purview of the I4C scheme.
The government has also made provisions in its budgetary proposal for the acknowledgment of 5-10 employees from each organization, who have made exceptional contributions to generating cybersecurity awareness against cybercrimes. The Ministries are also asked to recognize the officials as “Cyber Star of the Month” as a reward and motivation to appreciate their effort.
What is the I4C Scheme?
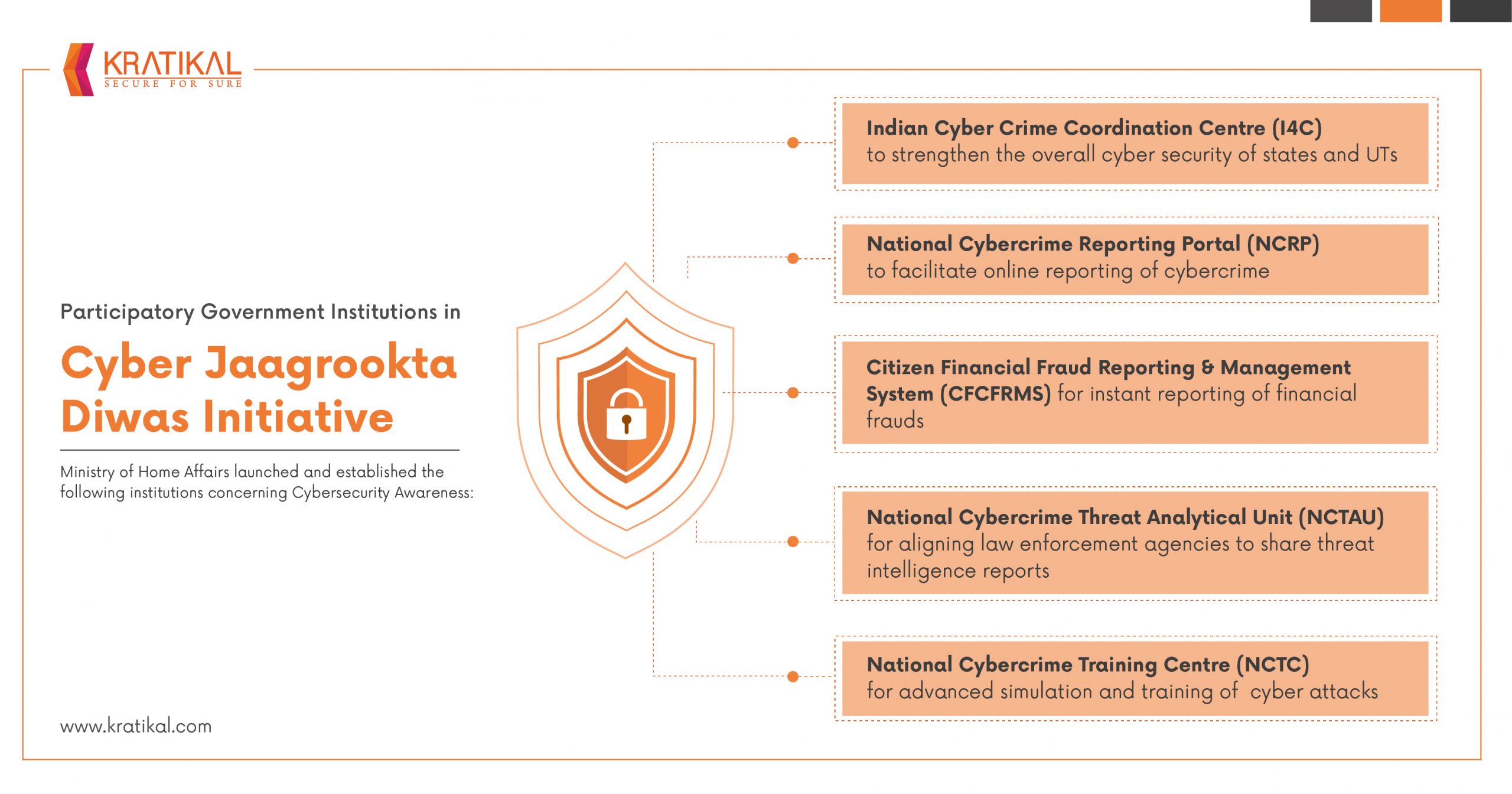
The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) was incorporated and established by the Ministry of Home Affairs to empower and strengthen the capabilities of regulatory and law enforcement agencies. The I4C scheme is responsible for acting as a nodal point in the fight against cyber attacks. The departments under this scheme are provided with the responsibility of conducting research and development to identify the needs and problems of law enforcement agencies, incorporating the forensic tools and techniques developed in collaboration with research or academic institutions.
Topics to be Covered Under Cyber Jagrukta Divas
The Ministry of Home Affairs has suggested a set of topics that must be covered under the annual action plan for generating cybersecurity awareness in organizations. These topics are divided into four major units. The annual action plan that is required to be prepared by every organization must comprise these four units. However, each of the institutions has the flexibility to choose amongst the given topics for developing their action plan.
Unit 1: Cyber Crimes and Safety
The topics covered in the first unit are:
- Introduction to cybercrimes
- Kinds of cybercrimes: phishing, identity theft, cyberstalking, cyber obscenity, computer vandalism, ransomware, identity theft
- Spotting fake apps and fake news on social media and the internet (fake email messages, fake post, fake WhatsApp messages, fake customer care/toll-free numbers, fake jobs)
- Internet ethics, internet addiction, ATM scams, online shopping threats, lottery emails/SMS, debit/credit card fraud, email security, mobile phone security
- Mobile apps security, USB storage device security
- Mobile connectivity security attacks (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Mobile as USB)
- Preventive measures to be taken in cyberspace, reporting of cybercrime
- Forgery and fraud from mobile devices
- The cyber risk associated with varied online activities and protection therefrom
- Work on different digital platforms safely
- Online cyber crimes against women and impersonation scams
- Safety in online financial transactions
Unit 2: Concept and Use of Cyber Hygiene in Daily Life
- Browser security, desktop security, UPI security, juice jacking, Google map security, OTP fraud
- IoT security, Wi-Fi security, spotting fake apps on social media and the internet (fake email messages, fake post, fake WhatsApp messages, fake customer care/toll-free numbers, fake jobs)
- Internet ethics, internet addiction, ATM scams, online shopping threats, lottery emails/SMS, loan frauds
- How to avoid social engineering attacks, debit/credit card fraud, email security, mobile phone security, mobile apps security, USB storage device security, data security
- Mobile connectivity security attacks (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi), mobile as USB, broadband internet security
- Preventive measures to be taken in cyberspace, reporting of cybercrime
Unit 3: Introduction to Social Networks
- Social networks and its contents like blogs
- Safe and proper use of social networks, inappropriate content on social networks
- Flagging and reporting of inappropriate content
Unit 4: Electronic Payments and Safeguard Therein
- Concept of e-payments, ATMs, and telebanking
- Immediate payment systems, Mobile money transfers, and e-wallets
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI)
- Cybercrimes in electronic payments
- KYC: Concept, cases, and safeguards

Why did the Home Ministry Launch this Initiative?
There are several factors that encouraged the ministry to launch this cybersecurity initiative. Some of the major ones are:
Rising Number of Cyber Attacks in the Country
- In May 2021, Air India suffered a data breach (through a supply chain attack) and the personal data of 4.5 million passengers was compromised.
- In the same month, test results and personally identifiable information (PII) of 190,000 CAT applicants were leaked on the dark web.
- The personally identifiable information (PII) of 500,000 Indian police officers was leaked and sold in February 2021.
- In January 2021, the COVID-19 test results of at least 1500 patients were leaked with all their personal information, which was regarded as a breach of the Indian healthcare system.
- Recently, over 70 Indian government and private websites were hacked by a hacktivist group named “DragonForce Malaysia” and religious extremist messages were displayed.
Growing Intensity of Hybrid Warfare
In early 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine and the war is still going on. However, the war is being fought not only on the battlefield but also in cyberspace. This has raised alarms for all countries to not only prepare themselves against their enemies through weapons but also incorporate robust cyber security infrastructure to defend against cyber attacks. In hybrid warfare, state-sponsored threat actors can cripple the digital system of the target country. So, India needs to establish a robust cyber security framework to protect its critical infrastructure.
Laying Foundation of the Nation’s Cyber Security Strategy
The government of India is still far from establishing a clear National Cyber Security Strategy. In addition to the introduction of the Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative, the government has put into place several ongoing initiatives and policies to address the issue of rising cybercrimes. The government, through its various ministries, is looking to transform the reactive mechanism for responding to cyber crimes into a proactive approach toward cyber security. The government is working on transforming cybersecurity best practices and guidelines into strategies through various initiatives and regulatory bodies.
Securing Government Organisations
State and central PSUs are the organizations primarily targeted by the Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative. The motive of the initiative is to secure government institutions and to prevent any kind of damage to these organizations. The initiative will prepare organizations to defend themselves against prominent cyber threats such as ransomware attacks, DDoS attacks, phishing, spoofing, BEC attacks, etc. The primary goal of the Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative is to raise cyber awareness among the employees of government organizations as employees serve as the first line of defence against cyber attacks.
“Cyber Hygiene” is the Goal of Cyber Jagrukta Divas
The Home Ministry has come up with the Cyber Jagrukta Divas initiative to improve the cyber hygiene of the country’s institutions, especially those regulated by the government. This initiative will facilitate the capacity building of government organizations and their employees to handle the issues related to cybercrime. The MHA is also looking into this initiative as an opportunity to spread cybersecurity awareness regarding how to report cybercrime. The government has established a couple of cybercrime portals to address fraud and breaches in a systematic manner. In the long run, this initiative will make the employees of government organizations vigilant and cyber aware.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *