GDPR violations can result in severe consequences. In its first year, over 89,000 data breaches were reported, leading to fines totaling €56 million. In 2019, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) imposed record fines on British Airways (€183 million) and Marriott International (€110 million) for breaches affecting millions of customers.
Organizations that do not comply with GDPR face various sanctions and penalties. The most severe penalty includes fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Additionally, organizations may face sanctions such as bans on data processing activities, orders to delete or correct data, and other restrictions.
The impact of GDPR violations can be significant, affecting both finances and operations. Organizations may face legal actions from individuals due to data mishandling, resulting in high legal fees and reputational damage. In this blog, we will explore the impact of the violation of GDPR policy.
Table of Contents
What Constitutes GDPR Violations?
GDPR violations can occur in various ways, depending on which parts of the regulation are not followed. These breaches can also be complex, depending on the specific circumstances and types of data processing involved. The following are examples of actions that may be considered GDPR violations:
- Using personal data for different purposes than originally intended, collecting excessive data, or retaining it beyond what is necessary.
- Processing personal data without obtaining clear, informed, and explicit consent from the data subject.
- Failing to offer clear, accessible privacy notices or neglecting to inform data subjects about how their information will be used.
- Failing to report GDPR data breaches in accordance with compliance requirements.
- Not respecting the rights of data subjects, including their right to access or request the deletion of their data.
- Transferring personal data outside the EU to countries or organizations lacking adequate data protection measures or without proper safeguards in place.
- Failing to implement suitable technical and organizational measures to maintain a level of security that matches the risk.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Recent GDPR Violation Incident In Uber For Data Transfer
Dutch regulators have levied a hefty fine of €290 million against Uber following revelations that the company failed to report a significant data breach that occurred in 2016. The breach compromised the sensitive personal information of approximately 57 million users and drivers, including names, email addresses, and phone numbers. Despite the severity of the incident, Uber did not disclose the breach to regulators or affected individuals until 2018, a delay that has been deemed a serious violation of data protection laws. This fine reflects the increasing scrutiny on companies to adhere to stringent data protection regulations and emphasizes the critical need for prompt and transparent reporting. Regulatory actions remind organizations of their duty to protect user data and the risks of non-compliance.
Types of GDPR Violations & Penalties
Various types of GDPR violations can lead to penalties, with some of the most common offenses including:
Failure to Obtain Consent
Under the GDPR, organizations are required to secure explicit and informed consent from individuals before collecting or processing their personal data. Failure to do so can lead to substantial fines.
Data Breaches
Companies must report data breaches to the relevant authorities within 72 hours of discovery. Failure to comply can lead to fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Insufficient Data Protection Policies
Companies must implement robust data protection policies and procedures to safeguard personal data. Failure to comply can result in fines up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Failure to Comply with Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants individuals several rights regarding their personal data, such as the right to access, correct, and delete their information. Companies that fail to uphold these rights may face fines of up to 4% of their annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater.
Breaches Concerning Data Transfers Outside the EU/EEA
Under the GDPR, personal data may only be transferred outside the EU/EEA if specific conditions are fulfilled. These include obtaining the data subject’s explicit consent, and implementing safeguards like binding corporate rules or standard contractual clauses.
Calculation of Fines
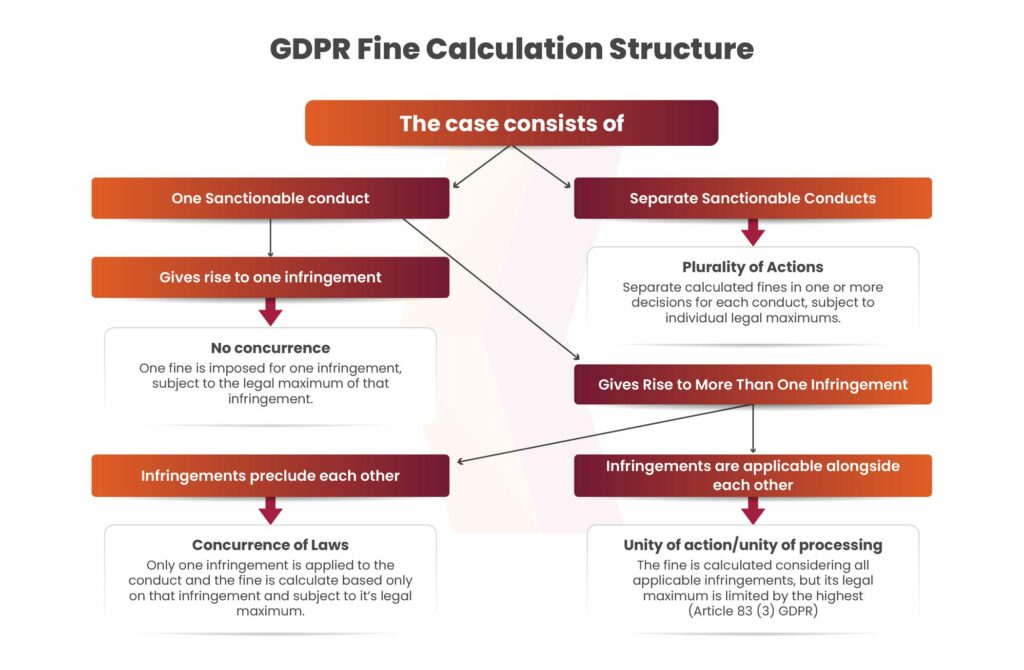
GDPR imposes two-tier fines, with penalties based on infringement type
Under the GDPR, fines follow a two-tiered system. The first tier, for less severe violations, can lead to fines up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher. The second tier, for more serious breaches, can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue, whichever is higher. The fine tier depends on the severity of the violation.
Fines are determined on a case-by-case basis, considering factors like the nature, gravity, and duration of the breach, the number of affected data subjects, and the company’s level of responsibility.
Factors used to determine fine amounts
Article 83 of the GDPR outlines factors for determining fine levels, including the nature, gravity, and duration of the infringement, the number of affected data subjects, cooperation with the supervisory authority, and any prior violations by the controller or processor.
The European Data Protection Board (EDPB) has also issued guidelines for calculating administrative fines. These guidelines emphasize that fines should be effective, proportionate, and deterrent. They include a step-by-step approach: identifying the number of infringements, setting an initial fine amount, evaluating mitigating and aggravating factors, ensuring compliance with legal limits, and assessing the fine’s effectiveness, deterrence, and proportionality.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
How Can Kratikal Help You With GDPR Compliance?
Kratikal provides comprehensive solutions to help organizations achieve GDPR compliance, minimizing the risk of penalties and maintaining customer trust. Our services include conducting data protection audits to identify gaps, implementing robust breach management strategies to meet the reporting requirement, and establishing clear processes for obtaining explicit user consent. We also assist in developing strong data protection policies, ensuring compliance with GDPR mandates for data subject rights, including access, correction, and deletion of personal data. Additionally, we support organizations in managing international data transfers by implementing safeguards like standard contractual clauses and binding corporate rules. With Kratikal’s expertise, your organization can effectively navigate GDPR requirements and stay compliant.
FAQs
- What is considered a GDPR violation?
A personal data breach is a security incident that affects the availability, confidentiality, or integrity of your personal information. A UK GDPR breach may result in the accidental or unlawful destruction, unauthorized disclosure, or compromise of your personal data.
- What data falls under GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies only when data processing involves personal data, as defined in Article 4(1). Personal data refers to any information related to an identified or identifiable natural person.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *