Red teaming is like staging a realistic rehearsal for a potential cyber attack to check an organization’s security resilience before they become actual problems. The exercise has three key phases: getting inside the system, maintaining their presence undetected, and acting to achieve their goals. The job is to test an organization’s defenses, challenge security assumptions, and explore various attack methods to identify any gaps or vulnerabilities. Overall, the red teaming exercise helps understand the organization’s strengths and weaknesses in a real-world attack scenario.
Table of Contents
How are Red Teaming Assessments Performed?
Red teaming is an ethical hacking practice where security experts simulate real-world attackers’ tactics to assess an organization’s defenses. These exercises involve attack simulations to identify vulnerabilities in people, processes, and technologies without causing harm. Red team members conduct thorough reconnaissance and launch time-bound simulated attacks on targets like endpoints, cryptographic tools, and firewalls. They often face off against blue teams, documenting vulnerabilities and techniques. Exercises conclude with a detailed report and remediation. Let’s discuss the process in detail:
Reconnaissance
Red team gathers information about the target like email addresses and other important facts. The more information is gathered, the better the plan of the attack becomes.
Weaponization
Experts create a deliverable payload, which means, building an attack weapon. Once delivered, it can exploit the vulnerabilities. This helps understand the organization’s loopholes and weak lines of code.
Delivery
The next step is delivering it to the right address where the attack is to be launched. The security team’s main goal behind this is to cause damage to the target system using the attack weapon.
Exploitation
A vulnerability in the target system is exploited to run the harmful code. It is similar to finding a secret door that attackers use to sneak into the system.
Installation
The red team installs the deliverable payload after successfully exploiting the target to steal information. This is done to check the various ways an organization can be hacked.
C2 Execution
The experts take possession of the target system remotely using commands. This helps understand to what extent an organization’s data can be compromised.
Techniques of Red Teaming
Red team activities replicate the tools and methods used by real-world attackers to test and evaluate an organization’s security defenses.
Here are some commonly used red-teaming techniques:
Social Engineering
Utilizes tactics such as phishing, smishing, vishing, spear phishing, and whale phishing to extract sensitive information or gain access to corporate systems from unsuspecting employees.
Physical Security Testing
Evaluates an organization’s physical security measures, such as surveillance systems and alarm mechanisms.
Application Penetration Testing
Analyzes web applications to identify security flaws caused by coding errors, such as SQL injection vulnerabilities.
Network Sniffing
Monitors network traffic to gather information about an IT system, including configuration details and user credentials.
Brute Forcing Credentials
Attempts to guess passwords systematically by leveraging credentials from previous breaches, testing commonly used passwords, or utilizing automated scripts.
What are the 3 Questions to Consider Before a Red Teaming Assessment?
Each red team assessment is tailored to different aspects of an organization, but the methodology consistently involves reconnaissance, enumeration, and attack. Before starting a red team assessment, engage with key stakeholders in your organization to understand their concerns. Consider the following questions when defining the objectives of your upcoming assessment:
- What could happen in my organization to cause serious reputational or revenue-based damage (e.g. ex-filtration of sensitive client data or prolonged service downtime)?
- What is the common infrastructure used throughout the organization (consider both hardware and software)? In other words, is there a common component on which everything relies?
- What are the most valuable assets throughout the organization (data and systems) and what are the repercussions if those are compromised?
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Benefits of Red Teaming
Red Team Methodology encompasses a range of techniques, including penetration testing, to improve the security of a target system. It offers a comprehensive perspective on the security posture of an organization.
The process involves penetration testing, social engineering, physical intrusion, application layer exploitation, and network service exploitation.
Key benefits of implementing Red Team Methodology within an organization include:
- Evaluation: By exposing the organization to simulated cyberattacks, red team testing provides a realistic assessment of the effectiveness of its security policies and procedures.
- Risk Assessment: Red team methodology enables organizations to categorize their assets based on their level of risk, allowing for focused security efforts.
- Vulnerability Discovery: Red team testing helps uncover and expose hidden security weaknesses and vulnerabilities within the system.
- Increased ROI: By simulating real-world attacks, red team testing helps organizations maximize the return on their security investments by identifying and addressing critical vulnerabilities.
- Compliance: Red team analysis helps organizations identify areas of non-compliance with industry standards and regulations, allowing for timely remediation.
- Prioritization: Red team tactics can help organizations prioritize vulnerability remediation efforts, cybersecurity investments, and the implementation of security measures.
Red Teaming Approach By Kratikal
Intelligence Gathering
We, at Kratikal, initiate our red teaming exercise by gathering comprehensive information about the target through public tools like Maltego and similar resources. This process helps our testers understand various aspects of the target organization, including its human community, technology, and environment. Furthermore, we also develop and procure specialized tools needed for the engagement.
OSINT Framework
For more advanced information gathering, our red teaming experts use the OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence) Framework. It is a cybersecurity framework that makes data collection easier. With OSINT, our team can access a diverse range of data, such as:
- external/internal network IP range
- software technologies
- cloud assets
- web and mobile applications
- previously breached credentials and other information sources
- IoT devices, and more
Planning and Mapping the Attacks
At this stage, our experts outline the types of ethical hacking methods to be used for execution, focusing on several key areas –
- uncovering hidden and inaccessible subdomains
- identifying misconfigurations in the client’s cloud infrastructure
- spotting weak authentication practices, etc.
We also review known vulnerabilities in network and web applications to determine how to exploit these weaknesses further. Additionally, scripts are prepared for social engineering attacks that involve phone calls.
Launching the Attacks
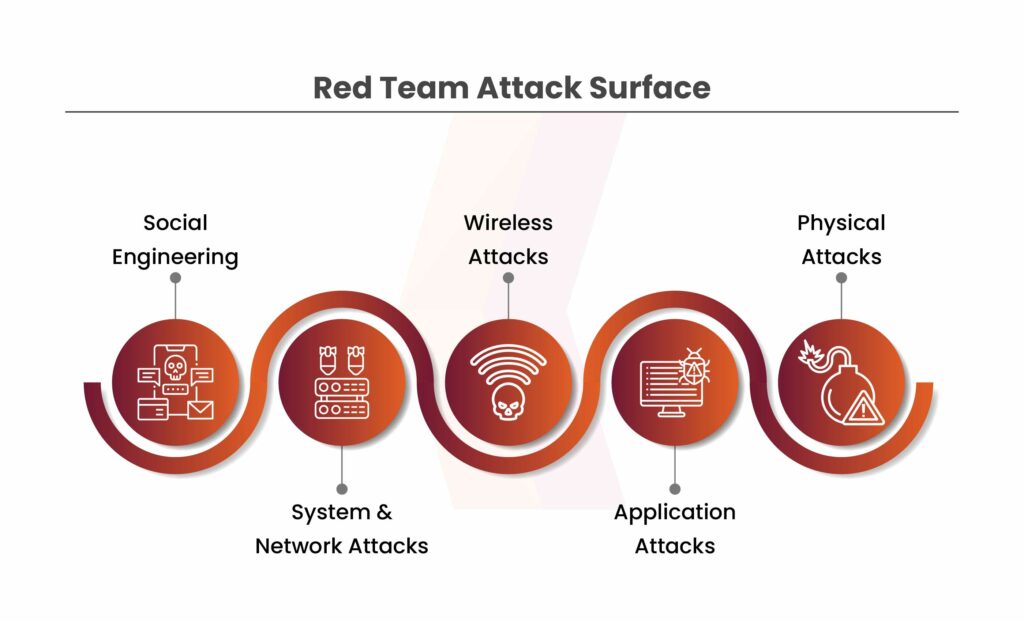
Our Red Team now puts their ethical hacking plans into action. This is done by targeting servers, apps, and networks. The motive behind it is to break into these systems, bypass physical security, and use social engineering to trick staff through face-to-face interactions, email, phone, fax, or SMS. This stage sets the platform for escalating our attacks and installing further tools. Our Red Team experts’ attack surface includes:
- Social engineering
- System and network attacks
- Wireless attacks
- Application attacks
- Physical attacks.
Documentation and Reporting
At this stage, we document our findings and prepare the report. It is tailored to the specific goals of the exercise and highlights any vulnerabilities found in the exercise. Our report includes a strategy for fixing each issue to reduce risk. The main content of our report is as follows:
- An executive summary
- An overview of strategic strengths and weaknesses
- Identified vulnerabilities with risk ratings
- Affected lines of code for each security risk
- Proof of concepts for each vulnerability
- Detailed steps for remediation.
Physical Security Pentesting
Next, we perform the physical penetration testing following guidelines from the NIST 800 Series and OSSTMM. We carefully examine the target’s physical locations and internal systems to find possible security weaknesses and gaps in the current security measures.
This process involves two phases:
- Active Reconnaissance -This is the phase where we gather information that’s available offline.
- Covert Observation -In this phase, our experts visit the target organization’s locations, take photos, and document potential vulnerabilities like unsecured entry points or bypassed barriers.
Attack Plan and Pretexting
We then prepare a Red Team Operations Plan (RTOP). It brings together all the intelligence gathered in earlier stages. It includes creating a believable story for social engineering, setting targets and goals, estimating how long tasks will take, and listing essential equipment and insights about the target locations. Once the plan is approved, we prepare the necessary gear and get everything ready, including printing a “get out of jail” letter, to ensure a smooth execution.
Exploitation and Post-Exploitation
In this phase, we put the Red Team Operations Plan (RTOP) into action. We use fake access cards, tailgating to enter buildings, bypassing locks and alarms, using social engineering tricks, and other approved techniques to meet our goals. Different tactics are used at the same place depending on the time of day. Once our red team successfully enters a location, the planned activities are carried out to gather evidence, prove the attack’s success, and identify vulnerabilities.
Post Engagement Report
Our final step is generating a comprehensive Post-Engagement Report for Risk Mitigation. We prepare the report after combining the results from information gathering, OSINT, attack planning, and execution. This report gives a clear summary of what was done, includes evidence and observations, and offers thoughtful recommendations.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Conclusion
Red teaming is a security practice that simulates cyberattacks to identify and address vulnerabilities within an organization. By mimicking the tactics of malicious actors, red teams help organizations strengthen their security posture, prioritize remediation efforts, and ultimately protect sensitive data and systems. Through a combination of technical expertise, social engineering, and physical security assessments, red teaming provides valuable insights into an organization’s security weaknesses and helps organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of red teaming?
Red teaming is a cybersecurity testing process where ethical hackers simulate non-destructive cyberattacks. This simulation helps organizations uncover system vulnerabilities and implement targeted enhancements to their security measures.
- What is the scope of red teaming?
Red team engagements involve identifying specific targets and gathering intelligence about their infrastructure, security measures, and vulnerabilities. Based on this information, a detailed attack plan is created, outlining techniques and tools tailored to the target’s security posture and objectives.
- What are the capabilities of red teaming?
Red teams simulate real cyber-attacks to help organizations identify vulnerabilities and test their incident response capabilities. This proactive approach strengthens the organization’s overall security posture, reducing the risk of exploitation by actual threats.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *