One cannot argue against the need for quality assurance when it comes to software development. An organization’s reputation can be negatively affected due to the poor quality, or defects dispensed in the software they produce, and can ultimately lead to losing a large number of clients. In extreme cases, these security loopholes can become the fundamental cause of major security breaches.
Let’s consider the example of the unpatched vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s software which has led the way for countless Zero-day Exploits, data breaches, and a huge crowd of concerned customers. The report released by BeyondTrust highlights various circumstances which resulted from such system vulnerabilities.
Table of Contents
What is Software/Application testing?
Software testing is a process to detect hidden errors, or functional inconsistencies in a software’s code by running the software through various tests. After the successful completion of testing rounds, a detailed report is prepared by the tester, which assists developers in making sure that the software runs error free, and fix all the identified issues, such as –
- Architectural Errors
- Poor Designs
- Invalid Functionality
- Security Loopholes
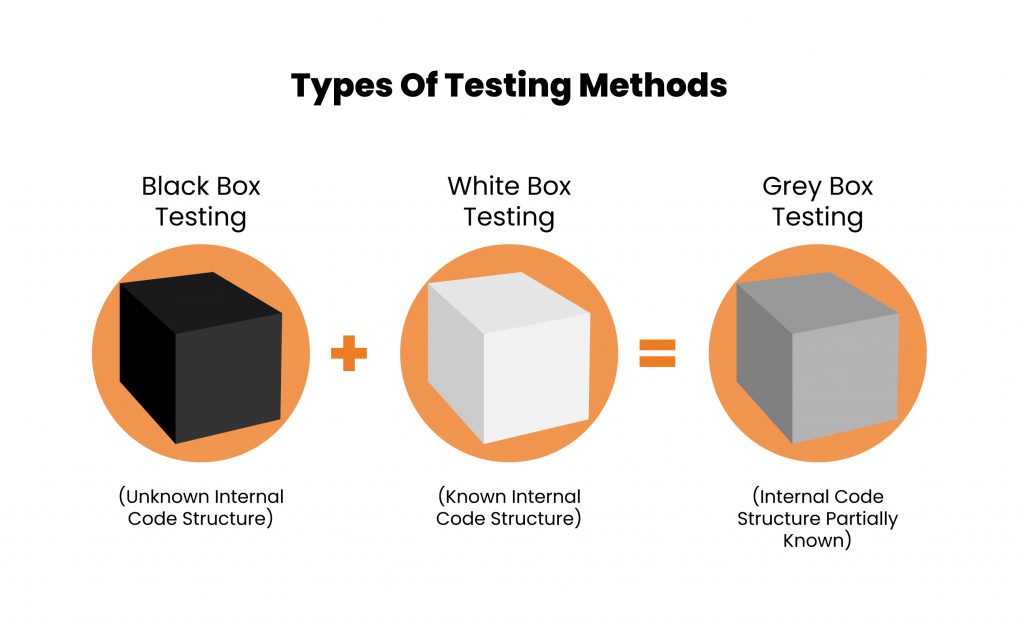
Though there are various types of software testing, the widely used testing measures are considered to be Black Box Testing, White Box Testing, and Grey Box Testing. These testing measures differ majorly in their approach, yet are collectively effective in helping developers keep their code clean and functional.
Let us get a thorough understanding of these testing methods.
BLACK BOX TESTING
Also known as Behavioral Testing, Black box testing is a software testing technique where the application is tested without the knowledge of its internal code structure. The name only depicts that the software program is not perceived through the tester’s eyes. This type of testing commonly focuses on only the input and output of the software system.
Some of the errors tested by this method are –
- Function errors
- Interfacing errors
- Database errors
- Performance errors
- Initialization errors
Black Box Testing Techniques
- Information Gathering – As the first step of every security assessment procedure, information gathering involves extracting knowledge about the application from outside sources by using Search Engine Discovery/ Reconnaissance and Web App Fingerprint.
- Configuration and Deploy Management Testing – Application Configuration management weakness are assessed in this technique, along with hunting sensitive information from the backups and old, unrefined files.
- Data Validation Testing – This technique employs Reflected Cross-Site Scripting, Stored Cross-site Scripting and SQL Injections to examine whether the provided data is valid or complete.
- Cryptography – Black Box Testing inspects the unencrypted channels through which sensitive information is sent, as well as examination of weak SSL/TLS ciphers and the protection of the application’s transport layer.
How is Black Box Testing performed?
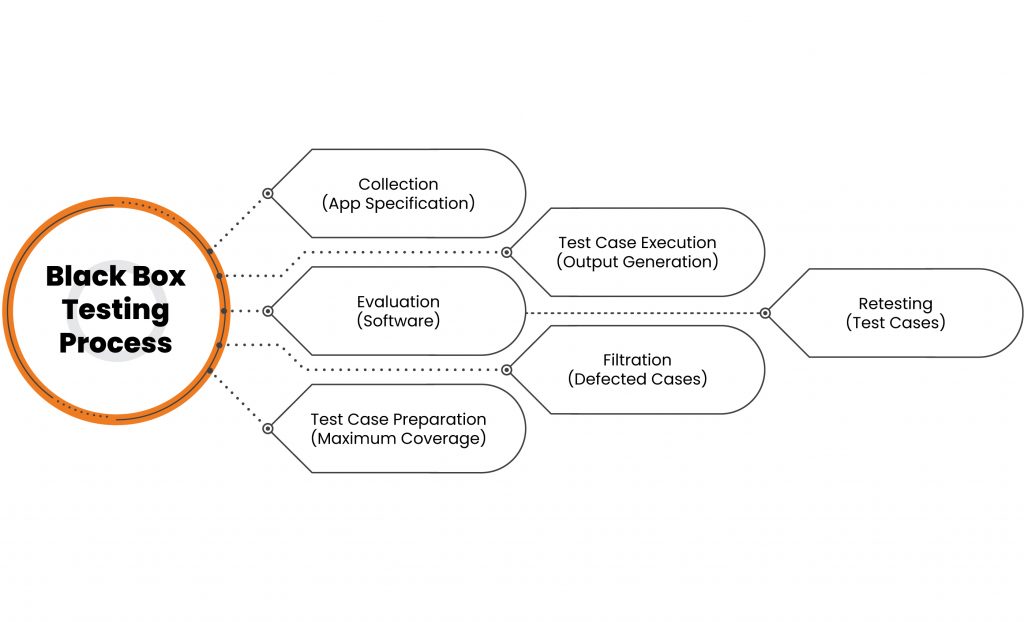
The basic methodology of any Black Box Testing is as follows:
- Understanding specifications of the application which is to be tested with a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document.
- Evaluation of the software with a set of valid inputs to save time and get good test coverage.
- Test cases preparation for the maximum coverage of inputs.
- Running of test cases in the system to generate outputs.
- Marking of the ‘Failed’ steps and sending them for fixing to the development team.
- Retesting of the test cases.
WHITE BOX TESTING
This type of software testing evaluates and verifies the ‘source code’, or the internal workings of a software system, such as its code and infrastructure. White Box is an essential part in a modern Continuous Integration(CI)/Continuous Delivery (CD) of automated build processes. Some of the software code of the following are tested by this method –
- Internal security holes
- Poorly structures paths
- Specific input flow
- Expected output
- Conditional loop functionality
White Box Testing Techniques
White Box Testing typically involves surveying the application for vulnerabilities with reference to notable security standards, such as SANS Top 25 and OWASP Top 10 Application Security Risks.
- SANS Top 25 – This well-known, and most frequently utilized, compilation of security vulnerabilities depicts the common errors found in all types of systems.
- OWASP Top 10 – The Open Web Application Security Project’s Top 10 illustrates the 10 common vulnerabilities found in an application, such as Injection, Broken Authentication and Session Management, Cross-site Scripting, and many more.
How is White Box Testing performed?
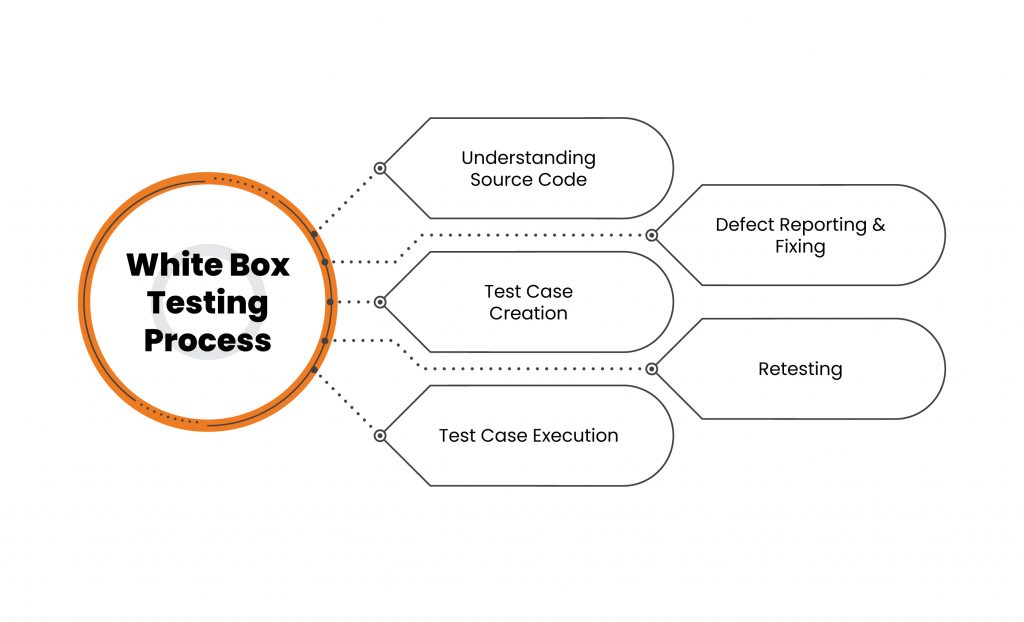
To simplify the process of a white box test, it can be divided into two basic steps –
- Understanding of the Source Code
The fundamental of every testing process is to learn and understand the source code of an application. White box testing involves internal testing, which requires testers to have a thorough knowledge of languages used in programming of the applications they are testing. Since security is the main motive of performing a test, the tester’s awareness of secure coding practice is essential.
The tester should be able to detect and identify security issues within an application’s code to keep the attackers from taking advantage of the vulnerabilities by injecting malicious code into the application.
- Test Case Creation and Execution
The following basic step involves testing the application’s code to review its proper flow and structure. One way to do this is by writing additional code so the application’s code can be tested. This method requires a deep technical understanding of the code, and is performed by the developer. The other method involves Manual Testing, trial and error method, and the use of various tools for the execution of the testing procedure, such as MobSF, BurpSuite, Dex2Jar, and many more.
GREY BOX TESTING
Grey Box Testing is a combination of Black Box Testing and White Box Testing techniques. In Black Box, the tester is not aware of the internal workings of the application being tested, while White Box Testing allows the tester to have that knowledge freely. Grey Box Testing grants a partial information of the internal structure to the tester, including the access to internal data and design for the purpose of creating test cases.
Grey Box Testing Techniques
- Identity Management Testing – This Grey Box Testing technique evaluates Role Definitions, User Registration Process, and Account Provisioning Process to detect vulnerabilities.
- Authentication Testing – Components of the authentication process are tested, such as Default Credentials, Weak Lock Out Mechanism, the Bypass Authentication Schema and the credentials transported over an encrypted channel.
- Authorization Testing – Through Directory Transversal File Include, Bypass Authorization Schema and Privilege Escalation, the Authorization Mechanism is tested to discover vulnerabilities.
- Session Management Testing – This technique Tests things like Cookie Attributes, Session Fixation and Session Hijacking to analyze the application.
- Input Validation Testing – Through certain Injection attacks, like SQL Injection, XML Injection, SSI Injection, and Cross-site Scripting attacks, the application’s vulnerabilities are highlighted.
How is Grey Box Testing Performed?
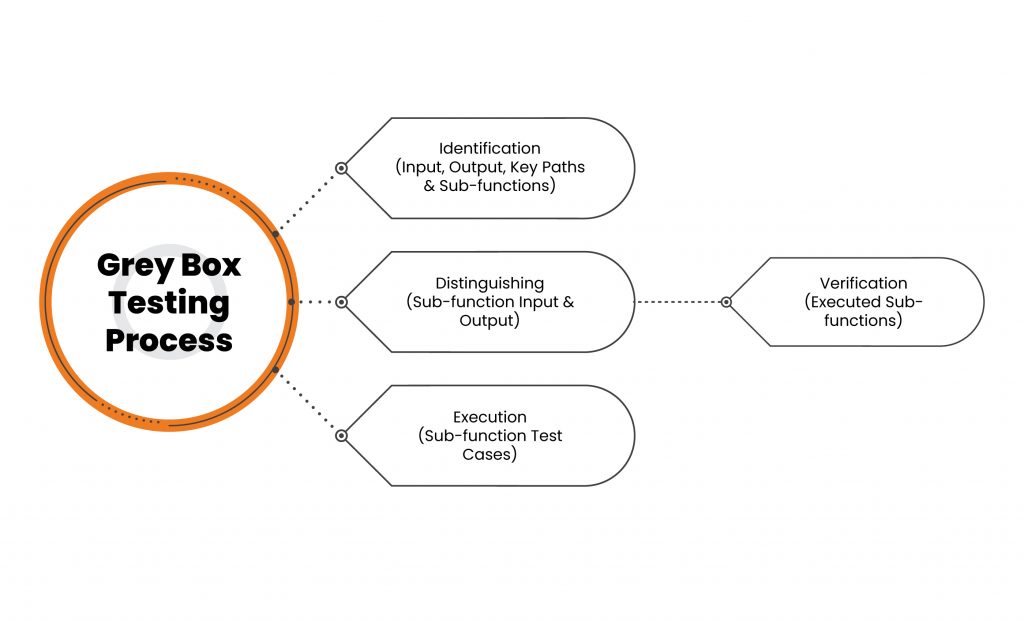
Since Grey box testing does not require a tester to design the test cases, these cases are created based on the algorithm evaluating the program’s internal conditions, behavior and structural knowledge. The tester only carries the test out and interprets the result by ensuing the following steps:
- Identification and selection of the inputs from Black and White box testing methods, and the verification of likely outputs from these inputs.
- Identifying the key paths for testing phase, and understanding sub-functions for deep-level testing.
- Identifying likely inputs and outputs for the, and from the, sub-functions.
- Executing sub-function test cases, and verifying the outcomes.
Test Your Software Successfully With Kratikal
Kratikal is a CERT-In empanelled organization providing a complete suite of well executed VAPT services, such as Web/Mobile Application Testing, Network Penetration Testing, Cloud Penetration Testing, and many more, along with a Secure Code Review. Our team of security testers have testing experience of over 250 weeks, which has given them a chance of gaining expertise in the field.
We carry out VAPT using Black Box, White Box, and Grey Box Testing techniques, with tools like BurpSuite, Nmap, Dex2Jar, etc., to make the testing procedure easy and smooth with our homegrown scripts. Kratikal also offers security audits for both standard and regulatory Compliance, such as ISO/IEC 27001, SOC2, GDPR, HIPAA, and others.
The testing techniques can vary in their methodologies, but they all possess the same goal; to keep our IT infrastructure secure. Do you practice regular security testing for the well-being of your organization’s framework? Comment down below to share your thoughts!









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *