According to Transforma Insights, the wide form of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in use globally is expected to nearly double from 15.1 billion to 29 billion in 2030. These gadgets are available in a wide variety of bureaucracies, along with smart cars, smartphones, health video monitors, alarm clocks, and favorite family home appliances like coffee makers and refrigerators. Ensuring each instrument is properly capable and able to handle increasing workloads is a major concern for manufacturers and solution providers in the IoT space. This is where IoT testing comes into play, ensuring that IoT devices and systems not only satisfy their specific requirements but also provide the expected level of performance.
Table of Contents
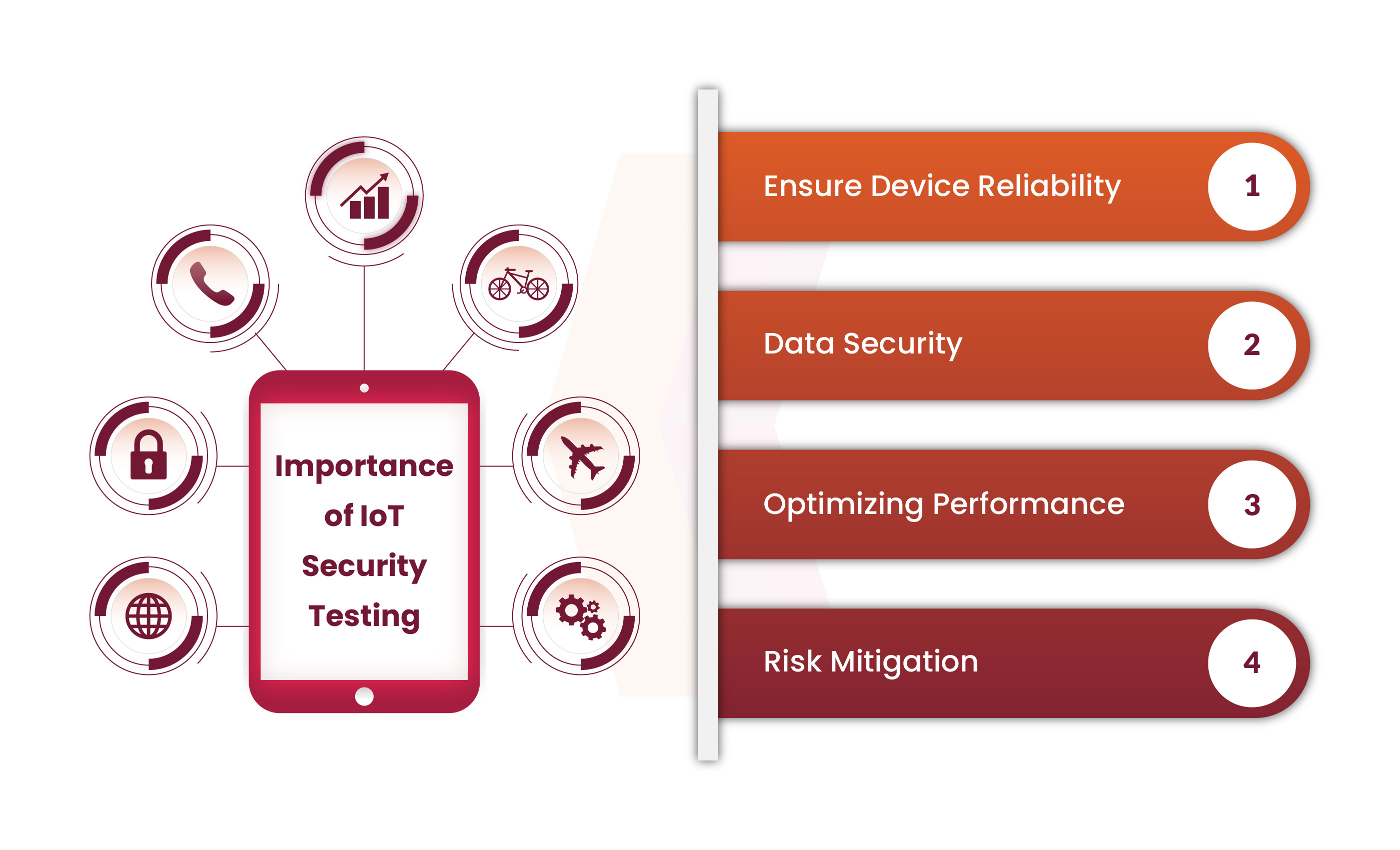
Why is IoT Testing Important?
There’s a saying in hacking, if it’s in the cloud it can rain anywhere. That means if you can access the device from the internet then anyone can. It is discoverable by other threat actors and also can give unauthorized access.
In our internal research, we have found that many smart buildings are easily accessible from the web.
(Building management solution exposed on internet)
During our pentest our team found most of them were running on the vulnerable application, using default settings and credentials which can be found on the website of the IoT product.
( Smart Building software vulnerable to misconfiguration)
Here are key reasons why IoT testing is important:
Ensure Device Reliability
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are essential to both daily living and business operations. Testing is necessary to ensure that those devices operate consistently under a range of circumstances and to reduce the risk of faults or breakdowns that would likely interrupt important operations.
Data Security
IoT devices frequently send sensitive data, so it is critical to give strong security measures a top priority. Testing is a vital tool for identifying gaps and vulnerabilities in a tool’s security measures, providing a buffer against system failures that could jeopardize user privacy or data.
Optimizing Performance
Testing makes it possible to evaluate an Internet of Things (IoT) device’s performance in a variety of scenarios, including reaction times, the effectiveness of data transmission, and standard functioning. Performance optimization is essential to ensure reducing the risk of slow response times.
Risk Mitigation
IoT testing is essential for lowering the risks connected to IoT devices, such as data loss or security vulnerabilities. Proactively detect and eliminate risks to assist organizations in enhancing the reliability and validity of IoT solutions.
Challenges in IoT Testing and Solution to Overcome Them
Below are effective strategies to tackle these challenges:
Security Concerns
Security issues persist as a prominent challenge in the IoT landscape. The increasing diversity of IoT devices makes them increasingly attractive targets for attackers. Setting information and device security as a top priority can help prevent capability breaches. IoT testing security challenges and difficulties include consumer passwords, unpatched vulnerabilities, hacks, data theft, and many more.
Solution
- Conduct comprehensive security testing, which should involve IoT penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Incorporate secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL and robust authentication mechanisms.
- Consistently update the firmware and software of devices to address and patch security vulnerabilities.
Privacy Issues
Within the spectrum of IoT testing challenges, a diverse range of concerns emerges, with particular emphasis on privacy issues in today’s digital landscape. The significant challenge lies in navigating the delicate balance between gathering data from IoT devices and respecting the privacy of users. Here are some key points such as data collection sensitivity, user consent, compliance, and much more.
Solution
- Ensure adherence to compliance and standards
- Incorporate effective data and encryption protocols.
- Enforce data anonymization, encryption, and transparent privacy policies
Scalability
Scalability is a major IoT challenge due to the surging number of devices. Managing IoT infrastructures becomes complex, spanning data storage, processing, and device integration. Handling the colossal volume of generated data requires scalable storage solutions, while processing power must scale for real-time insights. Integrating diverse IoT devices into existing systems poses additional complexity as the landscape evolves.
Solution
- Conduct scalability testing to pinpoint hindrances and optimize the system architecture.
- Incorporate load-balancing mechanisms for the even distribution of traffic.
- Implement IoT security testing for dynamic scaling in response to demand.
Following Compliance
Ensuring compliance, especially with strict frameworks like GDPR, is crucial for expanding IoT security testing operations. Adherence demands meticulous data handling, user consent, and privacy protection. Incorporating compliance into IoT development is vital, involving robust encryption, transparent data practices, and proactive measures to mitigate risks and maintain user trust. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, emphasizing the importance of making regulatory adherence a core principle for sustainable IoT growth.
Solution
- Stay updated on applicable regulations and standards in the regions where the IoT solution is set to be implemented.
- Incorporate testing for compliance
- Coordinate with legal and compliance teams to ensure alignment with regional requirements.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Best Practices for IoT Testing
Adhering to IoT device security best practices is crucial for continuous user, device, and data protection. The strategy should outline security measures, their implementation, and ongoing monitoring. Here are a few IoT security testing best practices:
IoT Endpoint Protection
Securing IoT devices involves a crucial step: hardening through IoT endpoint protection. This process includes addressing vulnerabilities in high-risk ports like Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP), securing wireless connections, and ensuring encrypted communications. Protection against malicious code injection is also essential.
Organizations may safeguard their networks from advanced threats, such as ransomware and malware, by putting endpoint protection into place. Devices at the community edge are strengthened, giving safety personnel total visibility, instantaneous insights into connected devices, and a smaller attack surface.
IoT Gateway Security
Enterprises can enhance IoT device protection through IoT gateway security, enforcing internet access policies, and blocking unauthorized software, like malware. A Secure Web Gateway (SWG) with features such as application control, thorough HTTPS and SSL inspection, remote browser isolation, and URL filtering is crucial, especially as organizations migrate to the cloud and enable remote connections. This helps prevent security risks for web-based traffic, safeguarding IoT devices from external and internal cyber threats. Additionally, employing threat monitoring solutions prevents data leaks, while virtual private networks (VPNs) encrypt browsing data, securing users’ internet activity from potential hacker snooping.
Securing Cloud API
Cloud application programming interfaces (APIs) facilitate communication and integration for IoT applications and systems, playing a crucial role in connecting services and transferring data. The potential consequences of a compromised or hacked API are severe, leading to a significant data breach. Hence, ensuring the security of cloud APIs is paramount, achieved through measures such as authentication, encryption, tokens, and the implementation of API gateways. For instance, web API security safeguards data during transmission across the internet, while REST APIs employ encryption for data and internet connections, ensuring the security of shared information between servers and devices.
Protection of Data Storage
As IoT devices and sensors generate escalating amounts of sensitive data, encompassing financial, personal, and biometric information stored in cloud-based or hardware storage solutions, the implementation of robust security measures becomes paramount. Ensuring the security of this information during storage or transfer is crucial. Securing data storage involves the utilization of efficient and up-to-date antivirus solutions, along with monitoring and scanning tools that comprehensively address real-time IoT threats across the network. Essential features include flexible reporting and scanning capabilities, notification systems, antimalware protocols, and a centralized management console that offers in-depth visibility into network activity.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Conclusion
The rapid expansion of IoT devices demands robust IoT testing methodologies to address security, privacy, scalability, and regulatory compliance challenges. Implementing measures such as endpoint protection, gateway security, securing cloud APIs, and safeguarding data storage is crucial. Proactively adhering to regional regulations and embracing best practices in IoT security testing is essential for sustainable growth. Organizations can develop resilient IoT systems that fulfill user expectations through addressing obstacles and incorporating optimal methodologies.
Kratikal, being a CERT-In empanelled auditor plays a crucial role in delivering top-notch security services. We presently work with 400+ SMEs and 150+ large companies. Leveraging our extensive expertise, we offer comprehensive analysis and robust defense mechanisms to counter the persistent threat of cyber attacks. Engaging with Kratikal enables prompt identification and resolution of security vulnerabilities, effectively thwarting malicious hackers from exploiting weaknesses.







Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *