Has anyone noticed that IT is no longer the same as it was a few years ago? Apart from IT equipment, we are now concentrating on network infrastructure security. The expectation of today’s work-from-anywhere workforce is that IT will enable seamless, secure connectivity to all devices and that our business tools will be highly tailored and instantaneously available. They require frequent maintenance and vulnerability patching to ensure that no vulnerabilities exist. Improper configuration, wrong configuration processing, and weak encryption keys might expose the entire network to risks. In today’s world, ensuring overall network security and safeguarding network equipment is the best option for any company. To protect the firm from cyber dangers, it is essential to begin deploying network security testing solutions.
Table of Contents
Network Infrastructure Security With Cyber Security
The Zero Trust Paradigm is defined as a security model, a set of system design principles, coordinated cybersecurity and system management strategy. The security guidelines presented here will introduce new network designs aimed at achieving more mature zero-trust principles in order to mitigate common vulnerabilities and shortcomings in existing networks.
In simple terms, network security is a set of configurations and regulations that use software and hardware technologies to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of computer networks.
Given the current circumstances and the growing magnitude of cyberattacks due to the pandemic, everybody working towards strengthening network security should be aware of network-related cyberattacks. Let’s go over the primary network infrastructure and network security testing in greater detail.
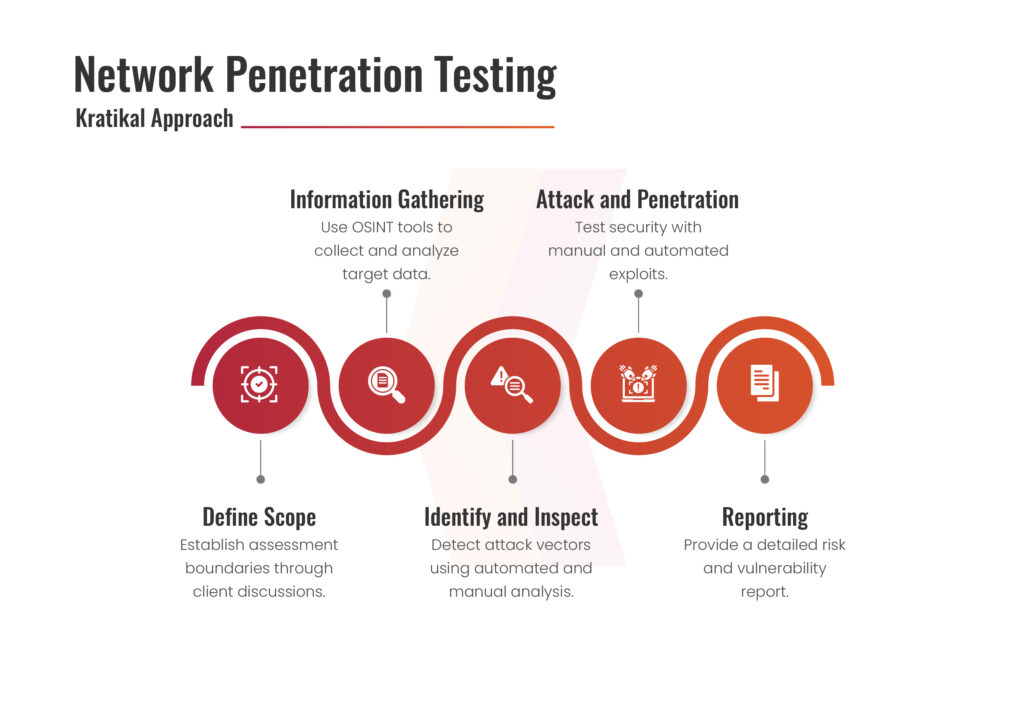
Six Guidelines on Network Infrastructure Security
We’ll look at the six primary elements of network security now that we’ve covered the basics, architecture, and design.
- Perimeter and Internal Defense Devices to be Installed
Multiple layers of defense should be created against external threats since the strategy is defensive to protect individual components, like:
- Inbound and outbound traffic should be logged into a network monitoring service.
- To control traffic, firewalls should be in place across the network.
- An ISP (Internet Service Provider) is to be installed to help with the external network connection.
- Multiple dedicated remote log servers are deployed.
- Similar Network Systems to be Grouped Together
To prevent adversary lateral movement, similar systems within network devices should be grouped together. It is advised that similar systems be separated into separate subnets, VPNs, or routers. Workstations, servers, and printers, for instance, should all be kept separate.
- Back Door Connections to be Removed
Back-door connections are defined as connections between two or more devices in distinct network zones. It is highly suggested that all back-door connections be removed, and that caution be exercised when connecting devices to multiple networks.
- Access Control Perimeter to be Utilized
To apply a perimeter rule that specifies which connections to allow, and to create rulesets that focus on only allowing those connections and rejecting anything else. The major goal of this rule is to allow several sorts of connections to be rejected by a single rule. To prevent unnecessary internal network access, these access control parameters should be configured with appropriate laws.
- NAC ( Network Access Control) is a Solution
Consider a solution that detects and authenticates each unique device connected to the network. Unauthorized physical connections are prevented, and approved physical connections are monitored, using a NAC system. One such example is port security, which appears to be tough to control.
- VPN Gateways to be Limited
The most crucial gateway is a VPN, which can be accessed over the internet and is vulnerable to brute force attacks, network scanning, and zero-day vulnerabilities. These flaws should be mitigated by eliminating all unnecessary functionalities and implementing stringent traffic filtering rules.
Conduct Periodic Network Security Testing
Many vulnerabilities and security difficulties can be avoided by following the aforementioned network security and infrastructure principles. In light of this delicate scenario, it is imperative that we all be cyber-aware and secure while working. Organizations are expected to take the lead in providing proper cyber awareness training to employees and assisting them in combating current cyberattacks.
With so many network infrastructure security issues and vulnerabilities attacking the network these days, being proactive and addressing these faults as soon as possible is the only prudent course of action.
Network VAPT can help you find any vulnerabilities in your network architecture that could be exploited. As a result, make it a habit to perform network penetration testing regularly from an authentic and trusted cybersecurity service provider like Kratikal to keep your business safe from both internal and external threats.
FAQs
- Why is Network Infrastructure Security important?
Network Infrastructure Security refers to the strategies and technologies used to protect an organization’s network from cyber threats. It includes measures like firewalls, access controls, encryption, and network segmentation to safeguard data, devices, and users.
- What is Network Security Testing, and how does it help?
Network Security Testing involves evaluating your network’s security by identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses that hackers could exploit. It includes techniques like network VAPT and compliance checks.
- How often should Network VAPT be conducted?
Network VAPT is a process that combines scanning for security flaws and simulating real-world attacks to assess the strength of a network’s defenses. It is recommended to conduct VAPT at least quarterly or after major infrastructure changes.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *