Ransomware as a service has become quite a popular and profitable business for cybercriminals. These cybercriminals often collaborate with malware developers and carry out coordinated cyberattacks. This approach to a ransomware attack is highly impactful and multiplicative in nature. Most of the RaaS tools and services are available on the dark web.
The biggest implication of the RaaS attacks is that it has become an illegal enterprise with a well-structured business model. The threat actors (also known as affiliates) often sell their malware or lease it to other cybercriminals in return for a share of the ill-earned ransom money.
Table of Contents
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
What is RaaS?
Ransomware as a service (RaaS) is a kind of business model that imitates the concept of ‘Software as a Service (SaaS)’. It allows the affiliates to provide hackers and other cybercriminals with readymade tools that execute ransomware scripts.
The affiliates who develop the ransomware script and embed it into software earn some percentage of the ransom payment. According to an article by Bank Info Security, the ransomware cases rose to 33% in late 2019, among which affiliates earned an average of 80% of the ransom payments.
Earlier, ransomware attacks were only carried out by individuals who had high expertise in coding and application development. But in recent years, many threat actors have adopted the SaaS model. This adoption has diluted the necessity of technical expertise and resulted in an increase in the frequency of these attacks.
Examples of Ransomware as a Service
According to the FBI’s IC3, there were 2,084 ransomware complaints filed in the first seven months of 2021. An article by Cybercrime Magazine, a ransomware attack is expected to incur a financial loss of $265 billion to organizations by 2031. It is likely that most of the attacks will come through the RaaS approach.
There are several cases of ransomware attacks from the past few years that have alarmed the world. Among them, the massive attacks on CNA Financial and Colonial Pipeline are quite popular. In May 2021, Colonial Pipeline reported that it was under a cyberattack that halted their 5500-mile operations. Similarly, in March, the data of over 75,000 employees were exposed due to ransomware attacks. They had to pay $40 million for a ransom.
There are several infamous ransomware gangs that have gained widespread recognition for their cybercrime services. Since 2016, hundreds of ransomware attacks have been carried out by RaaS provided by notorious groups like REvil, DarkSide, and Dharma ransomware.

(Source: Health IT Security)
Ransomware Service Providers
The primary mechanism of availing RaaS is through a subscription-based model. RaaS is popularly known as pay-for-use malware. There are some infamous managed service providers (MSPs) that are responsible for providing ransomware services. These include Apex Human Capital Management, CloudJumper (for Ryuk), IT By Design, MetroList, CorVel (for Ryuk), PM Consultants, iNSYNQ, TSM Consulting (for REvil), PerCSoft (for Ryuk), SCHOOLinSITES, TrialWorks, Unnamed MSP, BillTrust (for BitPaymer).
Ransomware as a Service Business Model
The first and foremost element of this model is an ‘Exploit Code’ which is developed by an expert malware operator. The developers collaborate with reputable affiliates, where they take a particular plan of subscription for distributing the ransomware scripts.
At this point, the role of affiliates is to create software in which they can embed the ransomware script. The reputation of any service provider depends on whether or not the software created by them facilitates a low chance of discovery and a high chance of successful penetration.
The complete ransomware is developed as a multi-end user infrastructure licensed for distribution. The operational mechanism of this model is the same as that of SaaS (Software as a Service) products. So, the affiliates have to choose between one-time or monthly subscriptions.
Then, these affiliates carry out attacks on victims and become a medium between ransomware gangs and victims. Apart from that, there is another element that is a money launderer, who is responsible for receiving ransom payments and distributing them to primary ransomware gangs and affiliates.
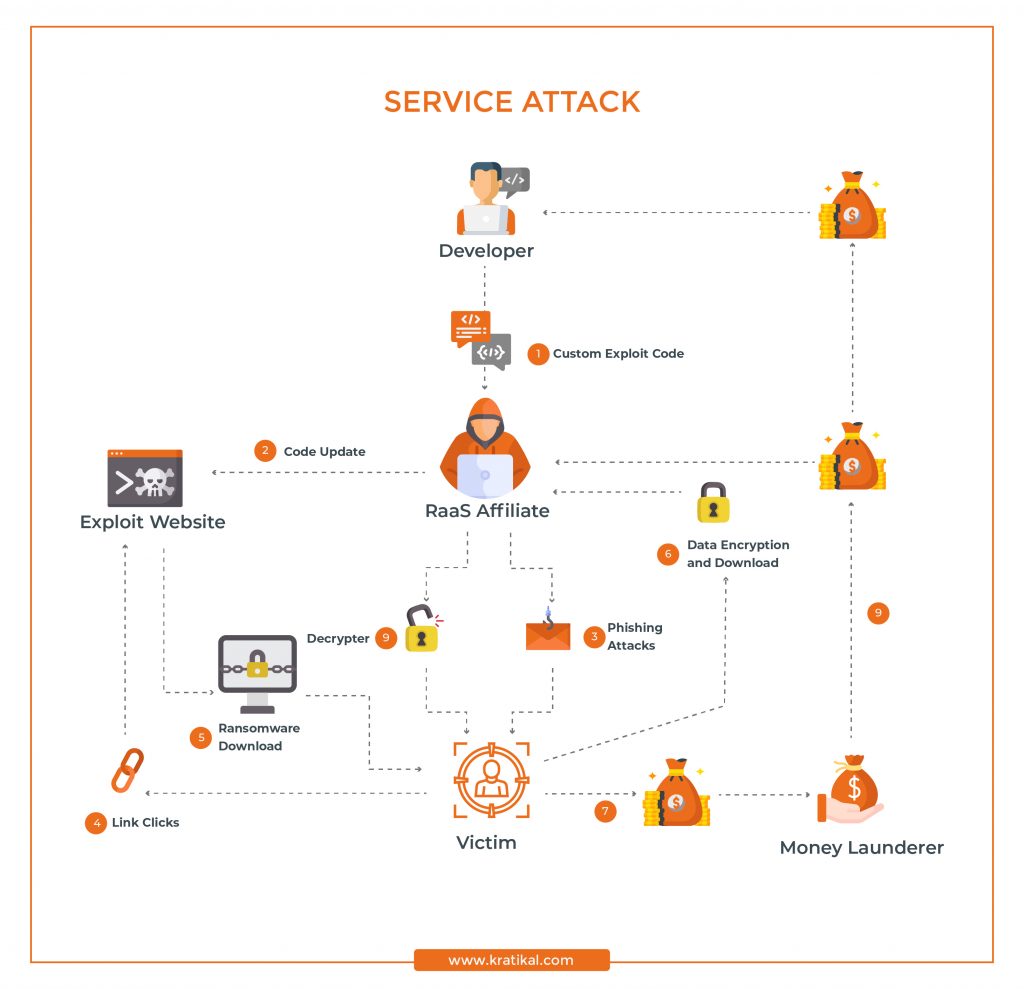
How Does Ransomware as a Service Attacks Work?
RaaS affiliates make multiple attempts at a data breach, primarily through phishing. This method involves tricking users and stealing sensitive information. RaaS affiliates send an effective and convincing phishing email that seems legitimate to victims, tricking them into activating a cyber threat unknowingly.
Once ransomware gets into the system, it disables the firewall and other antivirus software. When the defense is compromised, it triggers a download of additional components for remote access. This vulnerable node becomes a gateway to retrieve data from the entire business.
Then affiliates encrypt all the data present in the system and make it inaccessible to everyone in the organization. When it is done, the process of extortion and ransom begins. Usually, a text (.txt) file is sent to the victim’s computer, as shown in the example below. This file provides instructions to the victim organizations with information on the ransom price.
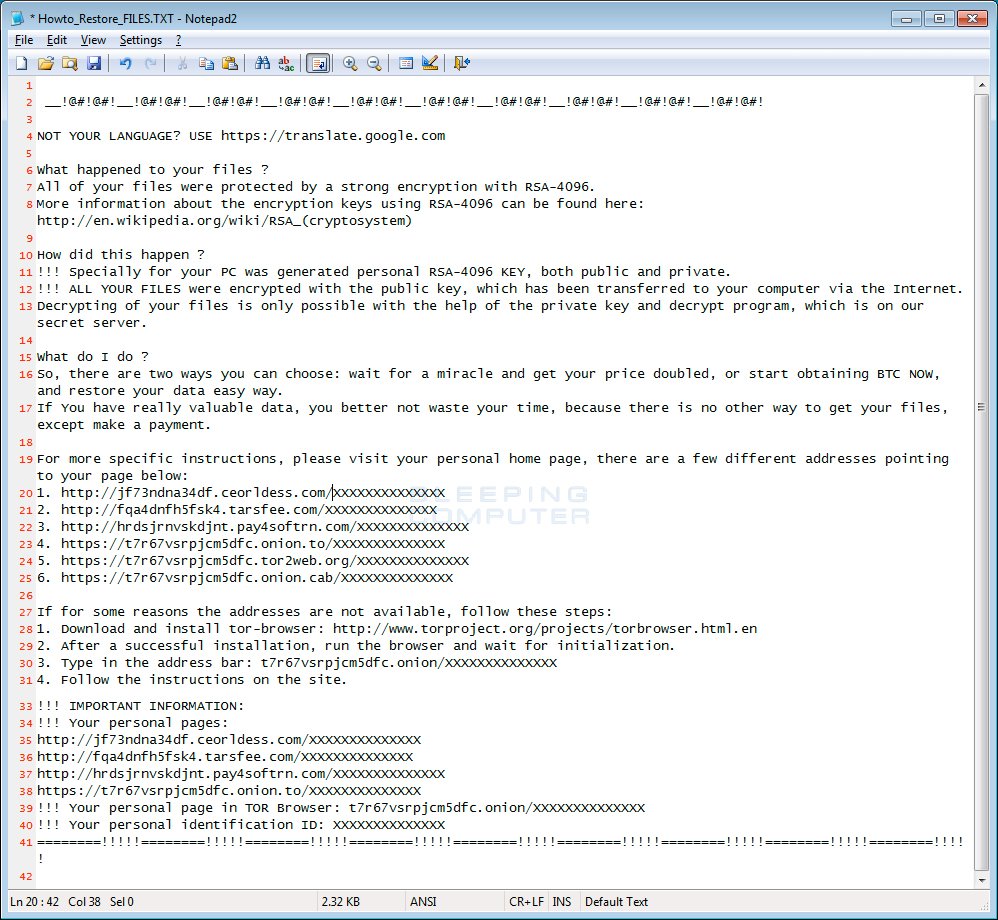
Example of a text file on victim’s PC (Source: Bleeping Computer)
How to Detect RaaS Threat Actors?
There is usually no foolproof defense against ransomware attacks. However, in most cases, ransomware attacks are carried out through phishing emails. So, an organization must carry out phishing awareness training to make sure that employees have optimum knowledge about identifying phishing emails.
On the technical level, organizations can have a dedicated cybersecurity team whose responsibility is to carry out threat hunting. Ransomware detection through threat hunting is quite an effective approach to detect and prevent ransomware attacks. In this process, a hypothesis is developed based on data on attack vectors. The hypothesis and data help in developing a tool that could detect the trigger of the attack and prevent it immediately.
Threat hunting tools are employed to monitor the network for suspicious activity, unusual file executions, etc. These utilize the lookout for Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) to detect ransomware attack attempts. Furthermore, different situational models of threat hunting are employed, which are specific to the industry and the target organization.

(Source: Gfycat)
How to Stop RaaS Attacks?
The technical procedures can be specifically carried out by cybersecurity experts. But there are numerous precautionary measures that can be taken by individuals and organizations to prevent ransomware attacks. Some of them are listed below.
- An organization must have a strong anti-phishing tool employed in its organization.
- All the endpoint connections should be monitored consistently.
- Every employee must be educated and trained in cybersecurity awareness and should know how to identify phishing attacks.
- Set up DMARC, DKIM, and SPF on your email domain server to prevent phishing and BEC attacks.
- Get consistent and regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing.
- Back up your data regularly in multiple places. Make sure all the backed-up data is encrypted.
- Empower your employees with a phishing incident response tool like Threat Alert Button, so that they can report malicious emails.
- Make sure that all the software and devices are updated regularly.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *