Generative AI (GenAI) has emerged as a powerful tool for enterprises. However, a recent report by LayerX revealed a startling statistic: 89% of enterprise GenAI usage is invisible to organizations, exposing them to critical security risks. This blog delves into the report’s findings, its implications for data security, and the steps organizations can take to mitigate these risks.
Table of Contents
The Rise of GenAI in Enterprises
Generative AI, which includes tools like ChatGPT, has become increasingly popular in the corporate world. These tools are used for a variety of purposes, from automating customer service to generating content and analyzing data. The allure of GenAI lies in its ability to perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention, thereby increasing efficiency and productivity. However, the rapid adoption of GenAI has also brought about significant challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the lack of visibility into how these tools are being used within organizations. According to the LayerX report, nearly 90% of GenAI usage occurs outside the visibility of IT departments. This phenomenon, known as “shadow AI,” poses a significant threat to data security.
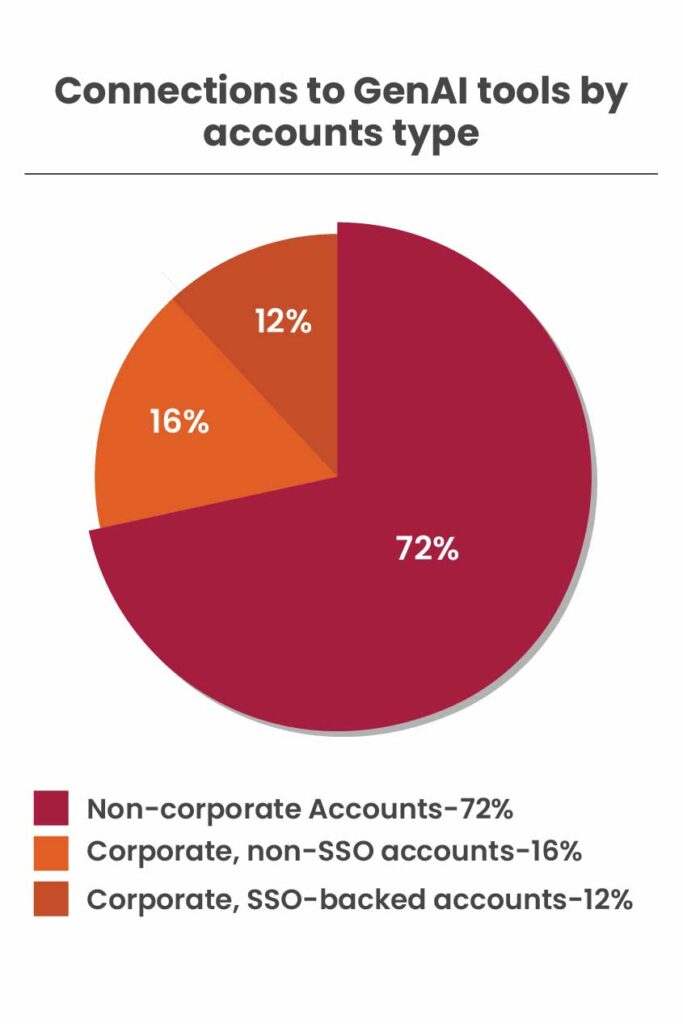
The significant majority of connections to GenAI tools are made using non-corporate logins. Specifically, 71.6% of requests for these tools were made through personal accounts. Among the 28.4% of logins using corporate accounts, 58.7% (equivalent to 16.6% of total logins) did not utilize Single Sign-On (SSO). Consequently, only 11.7% of all GenAI application logins met the highest standard of using a corporate account backed by SSO.
The Invisible Threat of Shadow AI
Shadow AI refers to the use of AI tools and applications that are not sanctioned or monitored by an organization’s IT department. This can happen when employees use personal accounts to access GenAI tools or when they use tools that have not been approved by the organization.
The implications of shadow AI are profound. When GenAI tools are used without proper oversight, organizations are left blind to the potential risks. Sensitive corporate data, including business information, customer data, financial plans, and source code, can be exposed to unauthorized access. The report found that pasting corporate data into GenAI applications occurs almost four times a day on average among users who submit data to these tools.
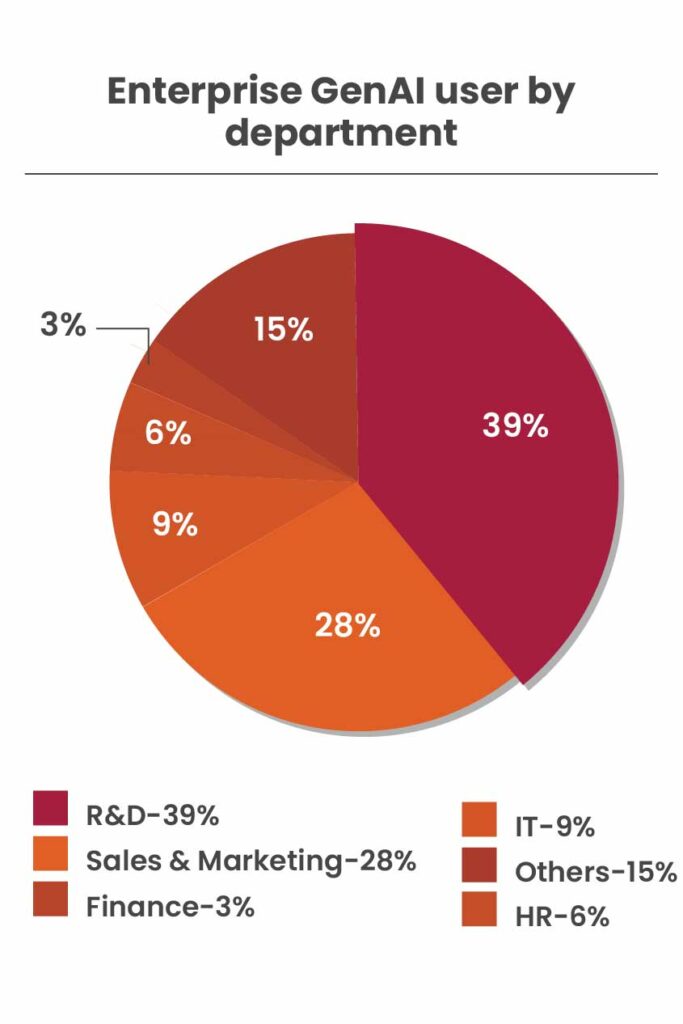
The lack of visibility into GenAI usage creates a fertile ground for data leakage and unauthorized access. The LayerX report reveals that 39% of regular GenAI tool users are software developers, meaning that the highest potential for data leakage is of source and proprietary code. This not only exposes sensitive information but also increases the risk of using risky code in the organization’s codebase.
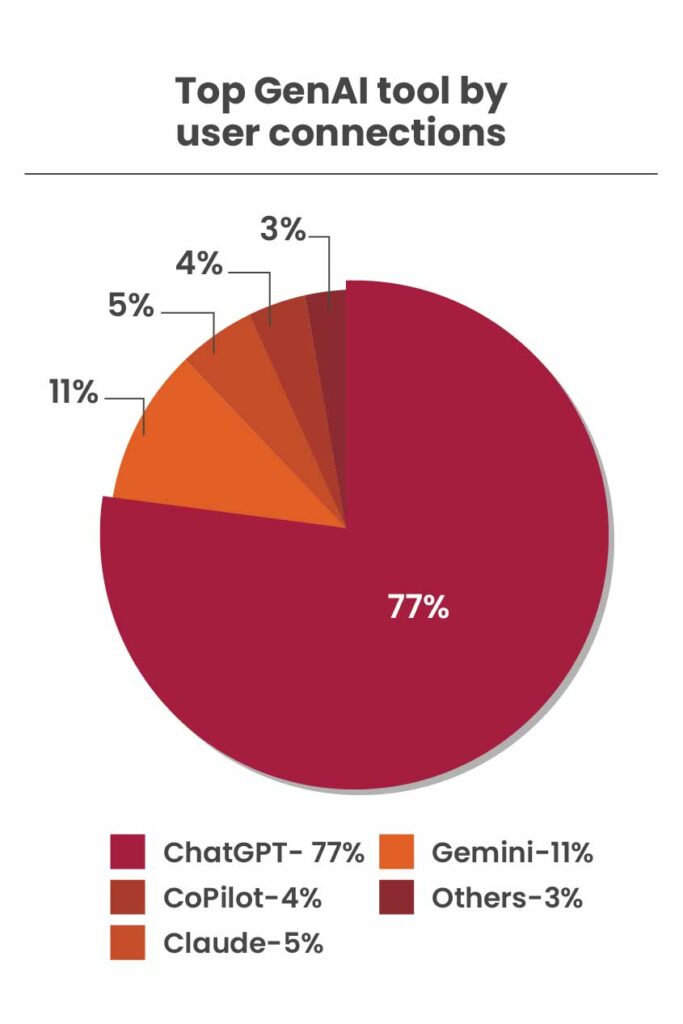
When examining the most-used GenAI tools, OpenAI’s ChatGPT leads the pack, commanding 77% of activity. Following at a distant second is Google’s Gemini with 11%. Interestingly, Anthropic’s Claude AI engine ranks higher than Microsoft Copilot, with 5% and 4% of activity, respectively. Other large language models (LLMs) account for the remaining 3%.
In terms of usage patterns, there is a notable difference between heavy and casual users. The top 5% of the most frequent GenAI users engage with these tools more than four times a day on average. In contrast, the bottom 50% of users access GenAI tools only once or twice a month. This suggests that, although GenAI tools have quickly gained traction, most users still interact with them sporadically, indicating that AI usage has not yet become a regular part of their daily routines.
Moreover, the report highlights that 20% of enterprise users have installed GenAI-enabled browser extensions, which can bypass Secure Web Gateways (SWGs) and other security controls. These extensions create an overlooked “side door” for data exposure, allowing sensitive corporate data to be accessed by remote large language models (LLMs) without the organization’s knowledge or ability to track the data.
The Need for Security Strategies
To effectively manage the risks associated with GenAI, organizations should consider the following best practices:
Implement Advanced Encryption Methods:
Protect sensitive data by using advanced encryption techniques. This ensures that even if data is exposed, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Conduct Regular Security Audits:
Audit the use of GenAI tools within the organization regularly. This helps identify unauthorized usage and potential vulnerabilities.
Develop an Incident Response Plan:
Prepare for potential data breaches by developing a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, including communication with affected parties and mitigation measures.
Monitor and Control Data Flow:
Implement tools that monitor and control the flow of data to and from GenAI applications. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
How to Plan for GenAI Usage: What Enterprises Must Do Now?
The recent findings underscore the immediate necessity for enterprises to devise new security strategies to effectively manage the risks associated with Generative AI (GenAI). Traditional security tools are no longer sufficient in the modern, AI-driven workplace, where many applications are browser-based. These outdated tools often lack the capabilities needed to detect, control, and secure AI interactions right at the source—the browser.
Incorporating browser-based security measures is essential, as they provide critical visibility into various aspects of AI usage within an enterprise. This includes access to AI SaaS applications, unidentified AI tools beyond well-known ones like ChatGPT, and AI-enabled browser extensions. Such comprehensive visibility allows for the implementation of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions specifically tailored for GenAI. By doing so, enterprises can safely integrate GenAI into their operations, thereby future-proofing their business against potential security threats.
Conclusion
The rapid adoption of GenAI in enterprises presents both opportunities and challenges. While these tools can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency, they also pose significant risks to data security. The findings of the LayerX report underscore the urgent need for organizations to adopt new security strategies to manage the risks associated with shadow AI.
By implementing advanced security measures, conducting regular audits, educating employees, and investing in technologies, organizations can mitigate the risks and harness the full potential of GenAI. As the use of GenAI continues to grow, it is imperative for organizations to stay vigilant and proactive in their approach to data security.
As a CERT-In empanelled organization, Kratikal is equipped to enhance your understanding of potential risks. Our manual and automated Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) services proficiently discover, detect, and assess vulnerabilities within your IT infrastructure. Additionally, Kratikal provides comprehensive security auditing services to ensure compliance with various regulations, including ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, PCI DSS, and more, assisting your business in adhering to legal requirements set forth by diverse governments.
FAQs
- How are organizations using GenAI?
Generative AI can personalize experiences, content, and product recommendations to individual preferences. In the financial sector, it can create customized investment recommendations, analyze market data, and simulate various scenarios to suggest new trading strategies.
- What are the primary risks associated with shadow AI?
The primary risks include data leakage and unauthorized access to sensitive corporate data such as business information, customer data, financial plans, and source code.
- Why is there a need for browser-based security measures in managing GenAI usage?
Browser-based security measures provide visibility into AI usage, including access to AI SaaS applications and AI-enabled browser extensions, and help implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions.
Ref link: https://thehackernews.com/2025/02/89-of-enterprise-genai-usage-is.html







![Top Cloud Security Challenges Businesses Face in 2026 [Updated]](https://kratikal.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Top-Cloud-Security-Challenges-Businesses-Face-300x155.jpg)

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *