For financial technology (FinTech) organizations, cloud security is both a top priority and a significant concern, as highlighted by a study conducted by McKinsey and the Institute of International Finance (IIF). FinTech companies increasingly rely on cloud computing to power services such as mobile banking, digital payments, and investment platforms. However, as cyber threats grow more sophisticated and regulatory demands tighten, these firms face rising challenges—especially from cloud vulnerabilities. These weaknesses can expose sensitive financial data and critical infrastructure to cyberattacks. This is where FinTech cloud security plays a vital role, offering end-to-end protection across cloud-native infrastructures and workloads. In this blog, we’ll explore the essentials of FinTech cloud security—what it is, why it’s critical, how it functions, and how your organization can leverage it to safeguard digital innovation.
Table of Contents
Fintech Industry on a Global Scale
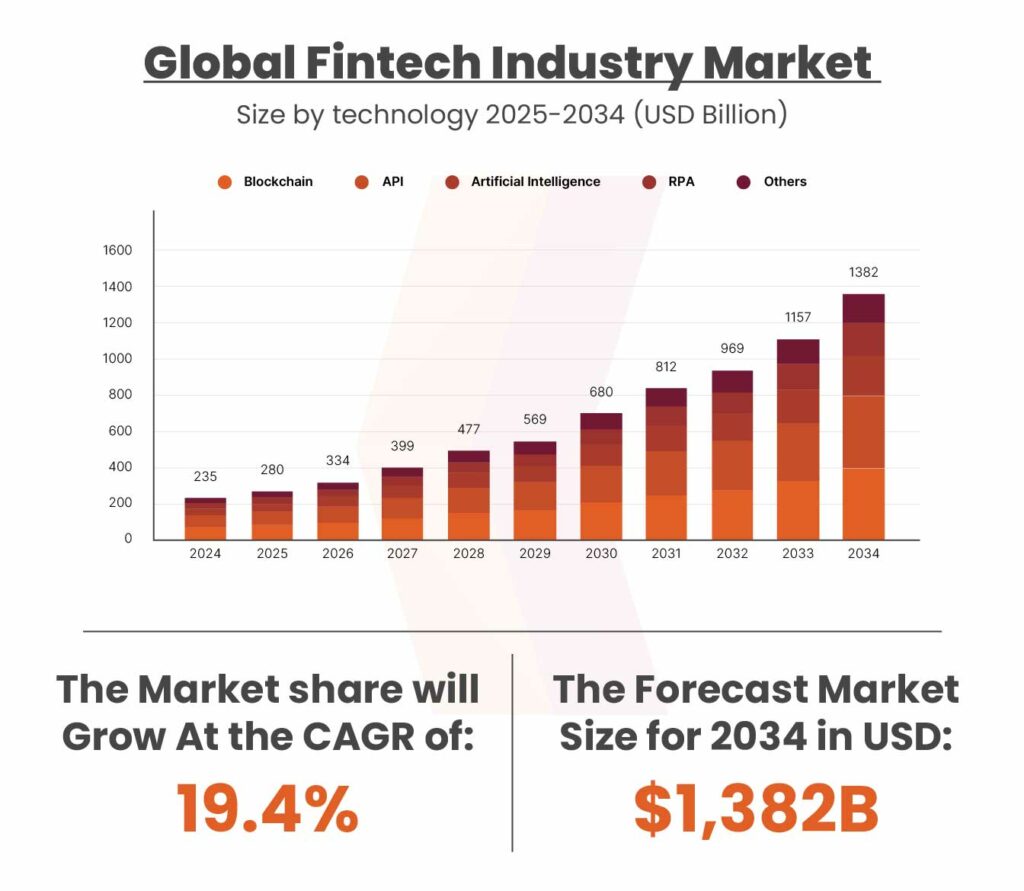
The increasing integration of advanced technologies into financial operations is making a significant impact. Valued at $280 billion in 2025, the global FinTech market is projected to soar to $1,382 billion by 2034. In this article, we aim to highlight the key trends driving this remarkable growth.
Cloud Security Vulnerabilities in Fintech and Their Prevention Measures
As fintech transforms the financial landscape, it also encounters distinct security challenges. Let’s explore some of the most pressing cloud security threats currently affecting fintech companies.
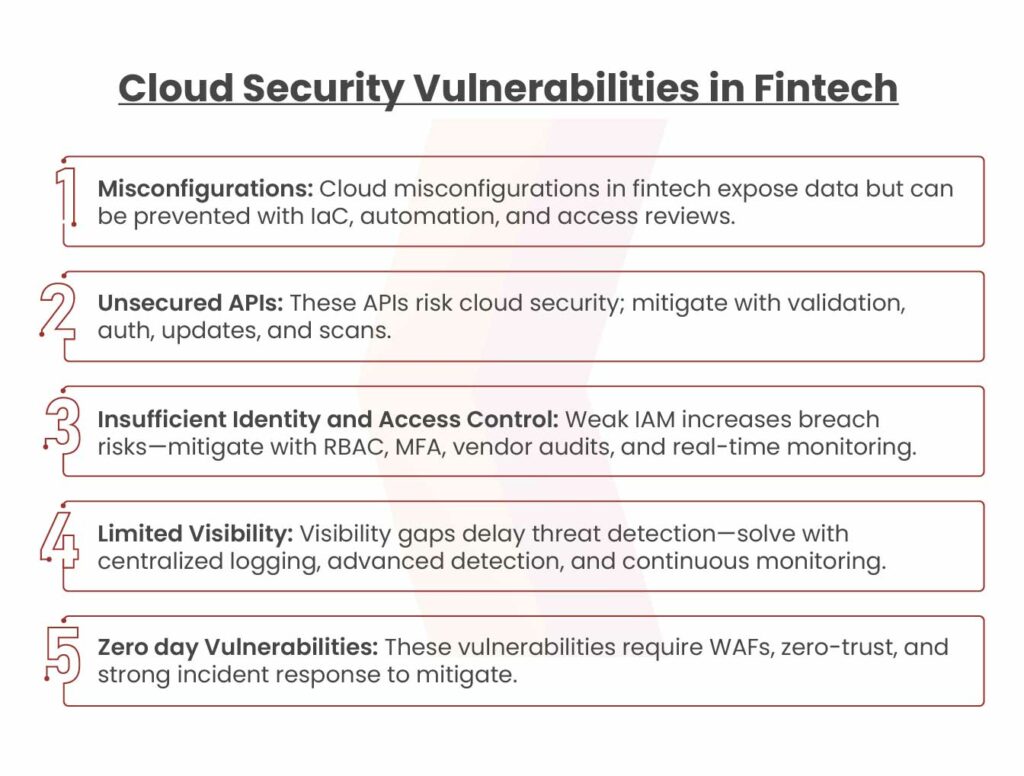
Misconfigurations
Cloud misconfigurations—such as open ports, unsecured storage, excessive permissions, and poor secrets management—pose serious risks to fintechs by exposing sensitive data and increasing vulnerability to cyber threats. These errors can occur across various components of cloud infrastructure, often due to a lack of monitoring or inconsistent settings. A notable example is the May 2023 Toyota breach that exposed 260,000 customer records due to misconfigured cloud settings.
Ways to Prevent Misconfigurations
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Utilize IaC to automate infrastructure deployment, eliminating the need for manual configurations and ensuring consistency, thereby reducing the risk of human error.
- Automated Configuration Checks: Leverage configuration management or cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to perform routine checks and maintain secure settings across your cloud environment.
- Access Reviews: Conduct regular audits of access controls, removing inactive accounts and revoking permissions for employees who have left the organization.
Unsecured APIs
API-related attacks are among the most prevalent cloud security threats today. According to a research report, 92% of surveyed organizations experienced at least one API-related security incident last year. Application Programming Interface (API) vulnerabilities typically stem from inadequate security practices during the design, configuration, or implementation stages. These flaws can open the door to various threats, including Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, injection attacks, data leaks, and privilege escalation.
Since cloud APIs enable interaction between cloud-based applications, even a single poorly secured API can lead to widespread damage. Common causes of unsecured APIs include weak authentication and authorization protocols, outdated API versions, and a lack of endpoint protection.
Ways to Prevent Unsecured APIs
- Input Validation and Data Sanitization: Establish clear rules for acceptable input formats and data types to prevent the entry of malicious content. Sanitize inputs by removing harmful elements like HTML tags or special characters that could trigger injection attacks.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: Implement limits on the number of requests a user or system can make. Use throttling to slow down request processing after a certain threshold to prevent abuse.
- Authentication and Authorization: Secure APIs using strong authentication methods such as passwords or tokens, and enforce role-based access control to manage user permissions effectively.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep APIs up to date with the latest software versions to patch known vulnerabilities and improve security.
- API Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular API scans to detect and address vulnerabilities proactively, ensuring a more secure API environment.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Insufficient Identity and Access Control
Weak identity and access management (IAM) occurs when there’s inadequate control over who can access systems and data, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. This often results from poor password practices, missing authentication layers like multi-factor authentication (MFA), a lack of regular access reviews, and unchecked privilege escalation.
Key Strategies to Reduce Access Related Threats
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on job responsibilities to avoid overly broad access, ensuring users only have the minimum rights needed.
- Strong Authentication: Use robust methods like one-time passwords (OTP), multi-factor authentication (MFA), or biometrics to secure user identity.
- Vendor Access Management: Regularly audit and control third-party access to prevent unnecessary exposure.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring to quickly detect and respond to any unusual or unauthorized user activity.
Limited Visibility
This lack of transparency often stems from inadequate monitoring systems, insufficient insight into user activities, and the absence of real-time reporting. Such visibility gaps delay the detection of suspicious behavior and other threats, causing organizations to miss critical opportunities to identify and respond to known attack patterns.
Effective Strategies to Enhance Visibility
- Centralized Logging: Establish comprehensive activity and audit logs to monitor user actions and provide valuable data during incident investigations.
- Advanced Threat Detection: Deploy sophisticated threat detection solutions to observe user behavior and generate alerts when anomalies occur.
- Continuous Monitoring: Utilize automated tools for ongoing surveillance, enabling proactive detection and faster response to potential threats.
Zero Day Cloud Vulnerabilities
Zero-day cloud vulnerabilities are security flaws that remain unknown to the cloud service provider but are discovered and exploited by attackers. These vulnerabilities can be present in cloud provider services, virtual machines, or other infrastructure components. When exploited, they can trigger a cascade of damaging events with lasting effects.
Effective Methods to Reduce Zero-Day Vulnerabilities:
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Deploy a WAF to defend against common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Zero-Trust Security Model: Adopt a zero-trust approach that requires strict authentication and authorization for all users and devices.
- Strong Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan, and ensure your teams are well-trained to act swiftly when an incident occurs.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
How Kratikal Can Help You With Cloud Security?
Kratikal empowers organizations to enhance their cloud security posture with AutoSecT, a cutting-edge Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solution that provides continuous, comprehensive monitoring of cloud environments. AutoSecT automatically scans your cloud infrastructure to detect misconfigurations, security vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps that could expose your organization to cyber risks. By delivering real-time alerts and actionable insights, it enables your security teams to proactively address potential threats before they escalate.
Additionally, AutoSecT supports adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements, helping you maintain compliance effortlessly. With Kratikal’s AutoSecT, you gain a powerful ally in securing your cloud-native workloads, ensuring your cloud assets remain protected, resilient, and aligned with best security practices.
FAQs
- How frequently should cloud vulnerability assessments be performed?
Although continuous vulnerability scanning should be in place, comprehensive vulnerability assessments can be conducted on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on the organization’s security requirements and compliance obligations.
- What are the top three security threats in cloud environments?
Cloud security risks like misconfigurations, data breaches, and unauthorized access need to be tackled with advanced cybersecurity solutions to protect business operations.






![Top Cloud Security Challenges Businesses Face in 2026 [Updated]](https://kratikal.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Top-Cloud-Security-Challenges-Businesses-Face-300x155.jpg)


Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *