Established in the year 1947, ISO or International Organization for Standardization is a non-profit organization that sets up international standards for any industry or sector. ISO has members from 165 countries and 785 technical committees as well as subcommittees that are working day and night for developing standards.
This is done with the help of a technical team consisting of subject matter experts that have immense knowledge and experience. The organization has published 22595 international standards and other documents.
Take a Moment to Stay Tuned Forever
Subscribe to get weekly cyber security updates!
Why do we need ISO standards?
Since ISO standards are meant to help organizations in a secured, smooth, and legally sound functioning; these standards are widely accepted around the world. Some of the other reasons are government tenders, credibility on international platforms, enhancing the efficiency of your business, customer satisfaction, marketability, etc.
IT sector adopts the 27000 family standards that are related to information technology security techniques. These are:
- ISO/IEC 27000 — Information security management systems (ISMS) — Overview and vocabulary
- ISO/IEC 27001 —These standards specify an information security management system in the same formalized, structured, and brief manner.
- ISO/IEC 27005 — Information security risk management
- ISO/IEC 27006 — Requirements for bodies offering audit as well as certification of ISMS
- ISO/IEC 27007 — Guidelines for ISMS auditing (focused on auditing the management system)
- ISO/IEC 27010 — Information security management for inter-sector as well as inter-organizational communications
- ISO/IEC 27032 — Guideline for cyber security
- ISO/IEC 27033-6 —Securing wireless IP network access
- ISO/IEC 27034-1 —Guideline for application security
- ISO/IEC 27034-2 —Organization normative framework
- ISO/IEC 27034-6 — Application security: Case studies
- ISO/IEC 27035-1 — Information security incident management: Principles of incident management
- ISO/IEC 27039 — Intrusion prevention
- ISO/IEC 27043 — Incident investigation
ISO 27001

ISO 27001 (Source: ISO)
ISO 27001 or formally known as ISO/IEC 27001:2005 is a set of specifications for managing risks to the security information that an organization holds. An ISMS constitutes procedures and policies that include all the legal, physical, and technical aspects involved in an organization’s information risk management process.
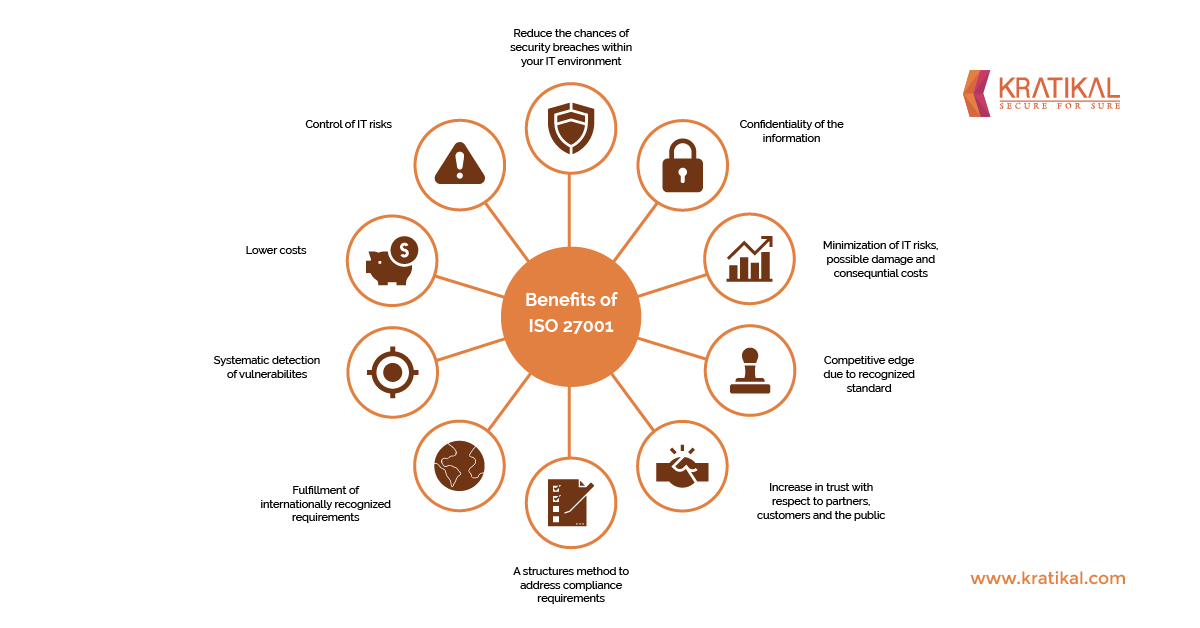
The latest version of ISO is ISO 27001:2022 provides a set of standard requirements for the Information Security Management System (ISMS). These standards help in establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, maintaining as well as improving ISMS. Overall, ISO 27001 helps the organization in:
- Protecting client and employee information,
- Effective management of risks to information security
- Compliance management with other regulations like GDPR, SOX, etc.
- Safeguarding sensitive as well as confidential data and information
- Identifying safety issues and minimizing risk exposure
- Make products compatible with each other
- ISO 27001 can be implemented in any of the sectors where confidentiality of data is crucial. For example, Banking, IT sector, Finance, Healthcare, etc.
- Exploring new markets for business expansion
- Complying with legal requirements since laws, regulations and contractual requirements can be fulfilled by implementing ISO 27001.
How to initiate compliance management in your organization?
Compliance Management in Organizations
Compliance management is one of the services that a leading cyber security company provides. It ensures that your business security standards are in line with ISO 27001 standards. It generally has a 5-phase approach including:
- SCOPE DETERMINATION: The compliance team works on understanding the business and ISMS context, indulging in discussions at various levels with decision-makers to understand your business processes in detail.
- GAP ANALYSIS: Gap analysis involves asset identification, existing control identification, and risk assessment. Security professionals map out the existing as well as the required security infrastructure of all business processes. Security experts determine the areas where there is a deviation from the necessary requirements and make action plans to fill those gaps.
- IMPLEMENTATION: Here, security experts start by implementing compliance for the organization. Each department and team that has been covered in the scope is provided with a list of security controls, access controls, communication channels, SOPs, etc. Once this is done, they conduct an efficiency check to determine the efficiency of the controls that have been introduced.
- INTERNAL AUDIT: Also known as ISO:27001 Pre-Audit; here, security experts ensure whether the implemented controls and processes are being followed within the organization. These tests check the level at which ISO 27001 has been implemented and its adaptation in the organization.
- CERTIFICATION: This process is carried out by independent auditors and not by the implementer. The security professionals bring in the auditor for the process of certification. Thus, taking care of the end-to-end process from scope determination to certification, hence, easing the process for the client.
These standards help in setting parameters for organizations within an industry and thus ensures that ISO accredited organization functions in a smooth and secure manner without worrying about abiding by the law.







Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *