A data backup policy defines the rules and procedures that guide an organization’s approach to creating and managing backup copies of its data. It forms a crucial component of the broader data protection, disaster recovery, and business continuity strategy.
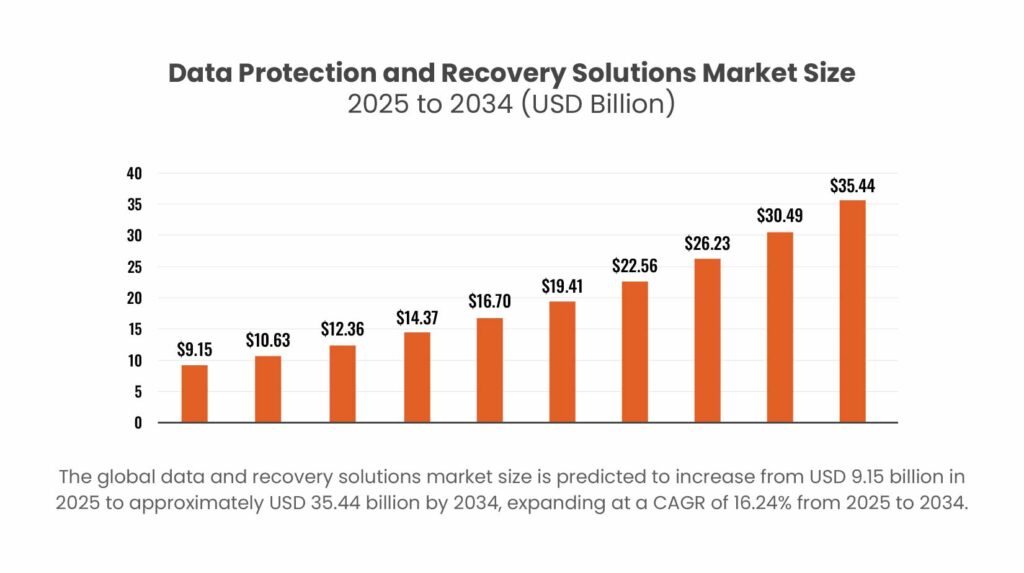
The growing importance of data security is reflected in market trends — the global data backup market is projected to reach USD 35.44 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 16.24% from 2025 to 2034. This growth highlights the increasing need for robust backup policies that safeguard critical business information and ensure operational resilience.
An effective backup policy clearly defines what data needs to be backed up, how often backups should occur, and where the data will be stored. It should also include provisions for incremental backups—performed after an initial full backup—and specify the roles and responsibilities of IT personnel involved in the backup process, including the backup administrator, if applicable. This blog includes clear guidelines, policies, and procedures for data backup and security to help organizations protect data, ensure continuity.
This blog outlines comprehensive guidelines, policies, and procedures for effectively backing up and securing data, including encryption, access control, offsite storage, immutable backups, and regular security testing. By implementing a structured data backup strategy, organizations can ensure the information remains secure, recoverable, and resilient against cyber threats, accidental loss, and operational disruptions.
Table of Contents
Guidelines for Data Backup
Companies can effectively secure data by adhering to established guidelines that have proven to be effective. The following methods ensure your data remains well-protected against potential threats:
Data Encryption
It is the process of converting information into a secure, coded format that can only be accessed or decrypted by someone possessing the correct encryption key. This ensures that data remains unreadable and protected, even if intercepted or stolen by unauthorized individuals.
How to Implement Encryption Effectively?
To secure data, organizations should:
- Use the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 256-bit key, recognized as the industry gold standard.
- Apply encryption both at rest (for stored data) and in transit (for data transmitted over networks).
Implement encryption key management practices, including secure storage, regular rotation, and strict access controls.
Access Control Management
Access control mechanisms are a combination of policies and technologies designed to restrict access to sensitive information. They ensure that only authorized users can view or modify specific data, based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
A Microsoft study revealed that 99.9% of compromised accounts lacked multi-factor authentication (MFA), highlighting the critical role of access control in protecting confidential data.
How to Implement Effective Access Control?
To strengthen access control:
- Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA), requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as passwords and mobile authentication apps.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict access according to users’ organizational roles.
Perform regular audits to ensure access permissions remain accurate and appropriate.
Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
A security audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s information systems to uncover vulnerabilities, outdated configurations, or weak controls. In contrast, continuous monitoring provides real-time oversight of network and system activity, enabling the detection of unauthorized access attempts as they occur.
How to Implement Effectively?
- Conduct annual or bi-annual security audits to identify system weaknesses, outdated software, and improper access configurations.
- Deploy Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools for real-time monitoring and alerts on suspicious activity.
- Set up automated notifications for unauthorized access or unusual system behavior to enable rapid response to potential threats.
Data Backup, Security and Disaster Recovery
Backup security involves protecting copies of critical data to ensure they remain available in case of accidental loss, cyberattacks, or other disruptions. A disaster recovery plan (DRP) outlines the processes and procedures to restore data and maintain business operations following a security incident or system failure.
How to Implement Effectively?
- Encrypt all backups to safeguard sensitive information against potential breaches.
- Store backups securely in off-site locations or utilize cloud-based solutions with integrated encryption and security features.
- Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, including regular testing, detailed recovery procedures, and clearly defined responsibilities for all team members.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Policies to Backup and Secure Data
With downtime costing organizations an average of $9,000 per minute, data loss is far more than an inconvenience—it poses a serious threat to business continuity.
Looking to eliminate that risk? Here are seven key methods to create a robust and fail-safe backup policy.
Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
A strong backup strategy begins with the 3-2-1 backup rule, a proven approach that ensures data redundancy and disaster recovery readiness.
It involves:
- Maintaining three copies of data: one primary version and two backups.
- Using two different storage types to reduce failure risk, such as combining on-premises storage with cloud backups.
- Keeping one backup off-site to ensure recoverability even if local systems are compromised.
However, with the growing sophistication of cyber threats, the traditional 3-2-1 model is no longer enough.
The 3-2-1-1-0 framework enhances cyber resilience by adding:
- One immutable copy that cannot be altered, deleted, or encrypted by attackers.
- Zero backup errors through regular integrity checks, ensuring data is complete, uncorrupted, and ready for instant recovery.
Implement Immutable Backups
Hackers often target backups, encrypting or deleting them to prevent recovery and demand ransom. Immutable backups ensure that stored data remains secure and unalterable—even by administrators.
How to achieve immutability:
- Use WORM (Write-Once, Read-Many) storage to prevent any modifications after data is written.
- Enable S3 Object Lock or similar immutability features to ensure backups remain unchanged for the defined retention period.
- Keep at least one backup offline to protect against malware that can propagate through connected networks or devices.
Use Offsite Backups
Relying only on local backups creates a single point of failure. Offsite secure backups add an extra layer of protection, ensuring data can be recovered even if primary environments are compromised.
Best practices for offsite backups include:
- Storing backups in geographically separate locations to protect against regional outages or natural disasters.
- Encrypting backups both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access during storage and transfer.
- Automating offsite replication with strict access controls to minimize human error and reduce the risk of insider threats.
Encrypt Your Backups
Unencrypted backups pose a significant security risk, as attackers can access sensitive information if the data is stolen. Encrypting backups ensures that even in the event of a breach, the data remains unreadable and useless to unauthorized parties.
Key strategies for encryption include:
- Using AES-256 encryption for both data at rest and in transit, adhering to industry security standards.
- Storing encryption keys separately from backup environments to prevent unauthorized decryption.
- Implementing end-to-end encryption for cloud backups to maintain protection throughout the data’s lifecycle.
Automate Backup Testing
A backup that cannot be restored when needed is no better than having no backup at all. Regular testing is critical to ensure that data remains complete, intact, and fully recoverable.
Effective approaches include:
- Performing automated integrity checks after each backup to detect corruption or incomplete transfers.
- Conducting routine disaster recovery drills to verify recovery speed and effectiveness under real-world conditions.
- Monitoring backup success rates with real-time alerts to quickly identify and resolve any failures.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Procedure of Data Backup in an Organization
A well-defined data backup procedure ensures that an organization’s critical information is securely copied and can be quickly restored when needed.
Identify and Classify Critical Data
The foundation of any backup strategy is understanding what data truly matters. Start by identifying and classifying information based on:
- Business impact: Which data is essential for day-to-day operations?
- Regulatory or compliance importance: For example, financial records, customer personally identifiable information (PII), or sensitive intellectual property.
- Operational value: Configuration files, software binaries, or databases critical for operational recovery.
Classifying data such as high-priority, medium-priority, and low-priority helps determine backup frequency, storage type, and access levels. This prioritization ensures that mission-critical data is never left vulnerable and that resources are allocated efficiently.
Secure and Encrypt Backup Data
Backing up data is only half the battle; protecting it is equally important. Cyber threats, insider risks, and accidental deletion make data encryption and secure storage essential:
- Encryption: Use AES-256 encryption for both data at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if backups are intercepted, they remain unreadable.
- Key Management: Store encryption keys in a secure, isolated environment and limit access strictly to authorized personnel. Regularly rotate keys to enhance security.
- Immutable Storage: Implement Write Once, Read Many (WORM) or other immutable storage solutions. Immutable backups prevent accidental or malicious modification, deletion, or ransomware encryption.
- Layered Storage: Consider a mix of on-premises, cloud, and offsite backups to reduce risk of localized failures or cyberattacks.
By combining encryption, strict access controls, and immutability, organizations can ensure backup data remains tamper-proof and secure at all times.
Test and Monitor Backup Integrity
A backup that cannot be restored is essentially useless. Regular testing and monitoring are critical to guarantee that your backup workflow is reliable and actionable:
- Automated Integrity Checks: Verify that backup files are complete, uncorrupted, and fully accessible. This ensures recoverability without surprises during emergencies.
- Recovery Drills: Conduct periodic disaster recovery simulations to validate the full restoration process, from file retrieval to system recovery. This helps teams identify gaps and improve response times.
- Real-Time Monitoring & Alerts: Implement monitoring tools that track backup success and failures in real-time. Automated alerts allow IT teams to address issues immediately, minimizing downtime and preventing data loss.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs of backup activities, including access history and restoration attempts. This strengthens compliance with regulatory requirements and provides accountability.
Continuous Improvement
A strong backup workflow is dynamic, not static. Organizations should continuously:
- Update backup strategies to include new systems, applications, and data types.
- Review retention policies to ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
- Evaluate emerging backup technologies, such as immutable cloud snapshots or AI-driven anomaly detection, to enhance security and efficiency.
Conclusion
A comprehensive data backup strategy is no longer optional—it is a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity and business continuity framework. By implementing well-defined guidelines, policies, and procedures, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure, recoverable, and resilient against both accidental loss and cyber threats.
Following best practices such as encryption, access control, off-site storage, immutable backups, and regular testing, combined with a clearly defined backup policy and real-time monitoring, enables businesses to minimize downtime, maintain operational continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements.
In an era of evolving cyber threats and increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, a strong data backup and disaster recovery program not only safeguards critical information but also reinforces trust, operational stability, and long-term resilience.
FAQs
- What are the 4 types of data backup?
Backup programs may vary in execution, but the four most commonly used types are full, differential, incremental, and mirror backups.
- What is an example of a data backup?
Data backup can be performed using various methods, including physical media, dedicated hardware appliances, software-based solutions, and cloud services. The selection of an appropriate backup method depends on factors like data volume, frequency of updates, required recovery speed, and budget constraints.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *