With more individuals having access to the internet, the world has undergone a profound change. The situation has altered as a result of how we now communicate and complete daily duties. By entering our personal information online, we can share documents, make payments online, and buy items. But are we aware that disclosing our personal information in such transactions exposes us to risks?
What happens to our information or where our personal information goes are different ways to phrase the question. The IP address is also included in this list of personal data, along with banking and contact information and social media profiles.
The businesses have informed us that they are gathering our personal information to better serve us. Do you honestly believe this information is used to serve us better, though? It’s a resounding NO.
This blog will detail GDPR Compliance, a new European regulation implemented to alter how businesses gather, retain, and use customer data.
Table of Contents
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
What is GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation which was implemented on 25th May 2018. The regulation came into force for all local privacy laws across the EU and EEA region. The new European privacy regulation is applicable to those companies selling and storing personal information about citizens in Europe including companies in other continents.
The main purpose of GDPR is to protect individuals and the data that describes them to ensure the organization that collects that data. Personal data must be protected against unauthorized processing or accidental damage.
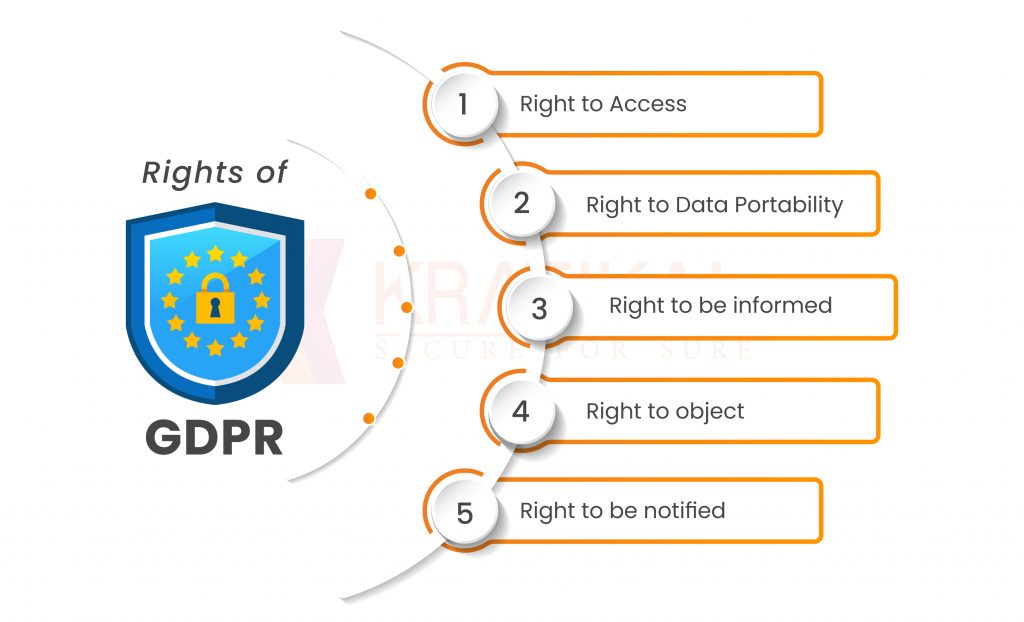
Rights of GDPR
There are few rights of the individuals under GDPR –
- Right to Access – Individuals have the right to request access to their personal information and to know how it will be used by an organization after it has been collected.
- Right to Data Portability -Data portability is the act of moving personal information from one service provider to another. The individuals have the right to transfer their data.
- Right to be informed – This right extends to any information that the organization collects, however, before any such information is gathered, the individuals concerned must be informed and their consent obtained.
- Right to object – The processing of personal data for direct marketing purposes can be stopped at any time by an individual. Before the process begins, the individuals should be given a clear explanation of their rights.
- Right to be notified – Within 72 hours of learning about a data breach, individuals have the right to get notified.
Checklist of step-by-step Privacy Policy
A complete checklist of the step-by-step privacy policy is listed below for the organization to follow-
- Raise Awareness among key decision-makers.
- Documentation of all policies and procedures.
- Review and update the current privacy policy.
- Review current individual rights.
- Analyze procedures for Subject access requests(SAR).
- Determine, record, and justify the legal justification for all data processing operations.
- Review and refresh existing consent.
- Institute special protection for children’s data.
- Detect, report to the ICO, and investigate personal data breaches.
- Adopt Data Protection by Design.
- Assign a Data Protection Officer.
- Select a Data Supervisory Authority.
- Governance and Accountability.
- Data Subject rights.
- Data Protection Impact Assessment.
Who is Subject to GDPR Compliance?
Every organization that gathers personal information from any citizen of an EU member state is required to abide by GDPR. The organizations mentioned here must adhere to GDPR even though they are located outside the EU.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
How to achieve GDPR Compliance?
Organizations must take a number of measures to guarantee that they are processing personal data in accordance with the GDPR principles in order to achieve GDPR compliance. Here are some crucial actions businesses can take to comply with the GDPR:
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): Companies are required to designate a DPO to manage GDPR compliance and make sure that all employees have received GDPR training.
- Review Data Processing Activities: Any personal data that an organization collects, stores, or processes must be identified by reviewing all of its data processing operations.
- Obtain Consent: People’s express consent is required before organizations can process their personal data.
- Provide Access to Data: People have the right to seek access to any personal information an organization may have about them, and organizations are required to grant access to that information within one month of receiving the request.
- Implement Technical and Organizational Measures: Technical and organizational safeguards must be put in place by organizations to guard against unauthorized access, loss, or harm to personal data.
- Conduct Regular Audits: To make sure they are in compliance with GDPR requirements and to find any areas for improvement, organizations must perform regular audits.
- Report Data Breaches: Within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach, organizations are required to notify the supervisory authority of any data breaches.
Violation of GDPR
The European Commission established strict GDPR regulations to safeguard the security and privacy of EU citizens’ personal data. GDPR violations are subject to penalties. Penalties are calculated based on a number of factors, including the seriousness of data breaches and the extent of the harm done.
- The maximum sanction for failing to keep proper records of the gathering and use of personal data is 10 million euros, which is equal to 2% of annual revenues.
- These fines can go up to 20 million euros or as much as 4% of yearly earnings if any of the regulatory agencies’ directives are disregarded.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Conclusion
Organizations processing the personal data of EU citizens must adhere to the GDPR. Businesses may make sure they are GDPR compliant and safeguard the privacy of the personal data of their consumers by taking the above actions. Businesses must take GDPR compliance seriously because failure to do so could result in severe financial penalties and reputational harm.
Kratikal, a cert-in empanelled organization, is regarded as the best organization for compliance needs due to its knowledge, experience, and proactive attitude. One can achieve GDPR compliance and make sure their personal data is secure by working with Kratikal. They assist with locating weaknesses and resolving them. We offer security audits for compliance, with GDPR being one of the most important compliances, to help your business comply with the laws and regulations set forth by various governments.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *