2019 has been a good year; not for many; but definitely for cyber-criminals. While we might still be coping-up with the news of a data breach incident that would have occurred two days ago; we hear another case of an organization’s infrastructure being breached. Let’s hit the ground zero.
Table of Contents
- 0.1 1. Google Chrome cast Hack
- 0.2 2. Germany’s Biggest Cyber attack
- 0.3 3. Ethereum Classic lost $ 1.1 million to hackers
- 0.4 4. Australian Parliament Cyber-attack
- 0.5 5. Leaked Database of Chinese citizen found online
- 0.6 6. Wiping out VFEmail.net
- 0.7 7. Attackers were selling the information on dark web
- 0.8 8. Indane gas breach
- 0.9 9. Aadhar details leaked
- 0.10 10. 1 million ASUS systems affected by massive supply chain attack
- 0.11 11. Bithumb suffers the loss of $19 million
- 0.12 12. Georgia Institute of Technology suffers data breach
- 1 What is the reason behind the success of these attacks?
- 2
- 3 What should organizations do in order to safeguard themselves?
1. Google Chrome cast Hack
It was almost a normal day of the winters of January, when thousands of people who had been using Google’s Chromecast streaming dongles, Google Home smart speakers as well smart TVs with built-in Chromecast technology; got their systems hacked. Hackers left a display pop-up to inform users that their systems are exposed to public internet. However, the odd thing about this hack was that attackers forced people to subscribe to the YouTube sensation ‘Pewdiepie’.
2. Germany’s Biggest Cyber attack
Around the same time, Germany was hit by the biggest cyber-attack in its history. Hackers hacked into the twitter accounts of more than hundred German politicians and accessed their highly sensitive personal information including email addresses, phone numbers, private chats, photographs of victims’ ID, bills as well as the credit card information. Attackers leaked the data on a twitter account called ‘@_0rbit’. German federal police dived into an investigation and soon, a 20-year old local student was arrested.
3. Ethereum Classic lost $ 1.1 million to hackers
While German police was celebrating its victory, popular cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase Ethereum Classic, experienced one of the worst days in its history. People who were using its services were forced to pay twice the coins for any of its services. This resulted in the loss of around $ 1.1 million Ethereum Classic digital currency. This resulted in the immediate fall in the prices of the digital currency. Hours later, Ethereum Classic accepted that there were almost ‘51% successful attacks’ with multiple block reorganization. Attackers are still under the cover and Ethereum Classic is still investigating.
4. Australian Parliament Cyber-attack
In the beginning of February, Australian parliament faced one of the biggest cyber attacks with its server being hacked by what the Australian parliament referred to as ‘the work of a sophisticated state actor’.
5. Leaked Database of Chinese citizen found online
In January 2019, cybersecurity experts discovered a huge unsecured database worth 854.8 GB; lying openly on the internet. The database was stored on an instance of MongoDB and consisted records of approximately 202 million Chinese citizens who were apparently job candidates. Soon the database was taken off, however, MongoDB has displayed the list of dozen of IP addresses that have accessed this database.
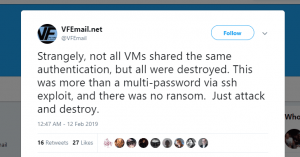
6. Wiping out VFEmail.net
U.S. based email service ‘VFEmail.net’ informed its users that all their data as well as backup worth two decades of data was lost. It was discovered that the attacker’s IP address was 94[.]155[.]49[.]9 and the username was “aktv,”, apparently registered in Bulgaria.
7. Attackers were selling the information on dark web
In one of the shocking instances, it was revealed that attackers were selling information of approximately 747 million accounts on the dark web. These accounts were stolen from 24 very popular websites. Most of these websites had no idea that they were compromised with, however, a few have confirmed that they suffered from data breach.
8. Indane gas breach
LPG gas company, Indane, became the victim of yet another case of data breach, where Aadhar number of approximately 6.7 million customers were leaked.

9. Aadhar details leaked
MongoDB is once again the talk of the town. A database known as GNCTD worth 4.1 GB in size, has been found on MongoDB instance. The database consisted of approximately 458,388 individuals’ Aadhar and Voter ID numbers along with references as well as email addresses with “transerve.com” domain for users who were registered with “super admin” and “senior supervisor” designations.
10. 1 million ASUS systems affected by massive supply chain attack
Taiwan based world’s fifth largest PC maker, ASUS, revealed that approximately 1 million systems were affected by massive supply chain attack known as ShadowHammer.
11. Bithumb suffers the loss of $19 million
On March 30th, the news of a humungous $19 million theft from the South Korean, Bithumb cryptocurrency exchange, fell into the ears of people. Hackers had compromised Bithumb’s hot EOS as well as XRP wallets and transferred approximately 3 million EOS (~ $13 million) and 20 million XRP (~ $6 million) to the newly-created accounts.
12. Georgia Institute of Technology suffers data breach
Georgia Institute of Technology was hit badly by cyber-criminals when a data breach led to the theft of the personal information of around 1.3 million current as well as formal faculty members, student as well as the applicants. According to the university, outside entities gained access to the web application of the university’s database.

Data breach statistics
What is the reason behind the success of these attacks?
The first quarter of the year has seen a number of data breaches that have targeted big organizations. Attackers are learning, adapting as well molding their modus operandi with the changing time. On the other hand, organization are still being old school.
Procrastination:
2019 took a start with Google Chromecast devices being hacked. This happened because a group of attackers exploited a bug that was lying down for five years like a ticking time bomb. Evidently, Google was aware of this vulnerability but kept on ignoring the bug.

Being Ignorant to the details:
In most of the cases, organizations are unaware of the fact that they are undergoing a cyber-attack. ASUS is one such victim since the attack was ongoing during the second half of 2018 and the company had no clue.
Lack of proper cyber-security measures:
Many a times, the data travelling in the forms of packets is not well encrypted and thus data can be easily stolen away by attackers. Indane Gas was victimized because of a vulnerability that was present in its mobile application.
What should organizations do in order to safeguard themselves?
Organizations can employ preventive cyber-security measures in order to safeguard data security and ensure that the network as well as the infrastructure of the organization is free from vulnerabilities and loopholes. Cyber-security companies ensure the same with a number of managed security services such as vulnerability assessment and penetration testing, web application testing, network penetration testing, server security testing etc. Kratikal is one of the fastest growing cyber security start-ups in the country. With its team of expert pen testers, the company has provided managed services to a number of businesses to industries like Healthcare, banking, insurance etc. These services have enabled organizations to conduct businesses without worrying about various issues related to the cyber security of the organization.








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *