2025 has emerged as one of the most disruptive years for cybersecurity, marked by unprecedented breach volumes, record-breaking credential leaks, and cascading supply-chain failures. Across just 12 months, cyber incidents have impacted governments, healthcare systems, financial institutions, SaaS providers, airlines, retailers, and critical infrastructure, proving that no industry or geography remains insulated.
Table of Contents
- 0.1 2025 Global Cybersecurity Overview
- 0.2 A Gist of Cyber Incidents in 2025
- 1 Get in!
- 2 Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
2025 Global Cybersecurity Overview
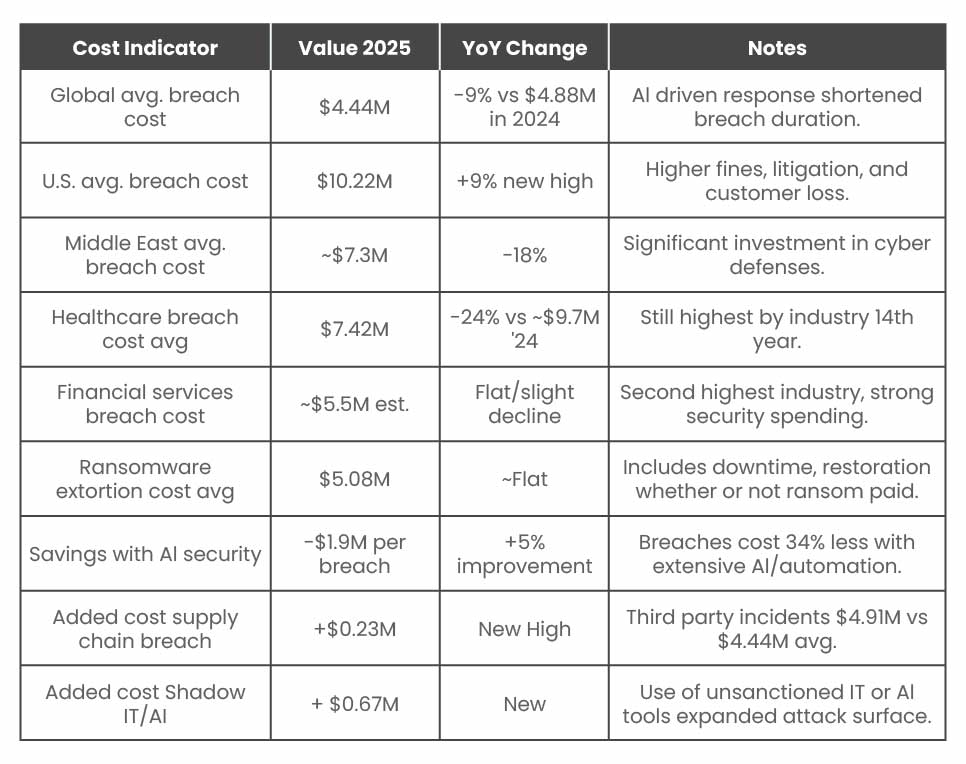
The year 2025 signals a turning point for global cybersecurity, where the scale and cost of cyber threats have reached unprecedented levels. No longer confined to IT teams, cyber risk has become an economic and geopolitical issue. Below is a comparison of key global cybersecurity indicators between 2024 and 2025.
| Metrics | Year 2024 | Year 2025 | Outlook |
| Yearly cost of cyber threat. | $8 Trillion | $10.5 Trillion | +31% projected year-on-year growth. |
| Average global cost per data breach | A record-setting $4.88 million | $4.44 million | -9% slight reduction |
| Ransomware-linked breaches | 32% of breaches | 44% of breaches | Reflecting a significantly higher prevalence. |
| Third-party-related breaches | 15% of breaches | 30% of breaches | Doubling supply-chain-driven risk. |
| Global cyber insurance market | $20.8 Billion | $24–25 Billion | 18% market growth. |
A Gist of Cyber Incidents in 2025
Cyber incidents in 2025 show a clear escalation in attack scale, sophistication, and impact. From ransomware and supply-chain breaches to zero-day exploits, threats continued to disrupt businesses and critical services. The key highlights below summarize the major patterns observed.
January Incidents 2025
The analyzed incidents reveal a sharp rise in large-scale data breaches, ransomware attacks, and infrastructure-level disruptions across multiple industries. Education, banking, hospitality, legal services, fintech, and core internet infrastructure were all impacted, highlighting that no sector is immune.
Most breaches stemmed from credential compromise, ransomware, and insecure infrastructure, leading to exposure of highly sensitive personal, financial, and operational data. Collectively, these incidents affected tens of millions of individuals, caused regulatory penalties, and emphasized the urgent need for continuous monitoring, stronger identity controls, and proactive cyber resilience strategies.
Scale of Impact
Individuals affected:
- 62+ million students
- 9.5 million teachers
- Millions of consumers, guests, and legal clients
Data exposed:
- Personal identifiers (SSNs, medical data, financial records)
- 7.8 TB of hotel guest and corporate data
Infrastructure impact:
5.6 Tbps DDoS attack using 13,000+ IoT devices
Financial impact:
$2 million regulatory settlement (Fintech breach)
Link of the Post:
February Incidents 2025
February cyber threats highlight a sharp rise in large-scale data breaches, financial fraud, and crypto theft across multiple industries. Sectors impacted include fintech, food delivery, accounting, IoT, payment processing, and financial services. Attackers exploited unauthorized access, third-party compromises, exposed databases, and insecure file transfer mechanisms. These weaknesses led to widespread exposure of sensitive personal, financial, and operational data. The incidents reveal ongoing gaps in supply-chain security, data protection, and continuous monitoring. The impact ranged from multi-million-dollar settlements to record-breaking billion-dollar crypto thefts, increasing business, reputational, and compliance risks.
Scale of Impact (Aggregated)
Data Exposed:
- 2.7 billion records (IoT smart device breach)
- 400 GB of stolen enterprise data (Fintech SFTP breach)
- 1 million+ stolen credit cards shared on the dark web
Financial losses:
- $7.25 million breach settlement
- $1.5 billion cryptocurrency theft
Attack vectors observed:
- Third-party compromise
- Exposed databases
- Credential and access abuse
- Web skimming
- Insecure wallet transfer processes
Link of the Post:
March Incidents 2025
The analyzed cyber incidents from March highlight a continuing rise in large-scale data breaches across diverse industries, including education, technology, surveillance, petroleum, and healthcare. Attackers exploited weaknesses such as website vulnerabilities, compromised credentials, inadequate security protocols, and stealthy malware, leading to the exposure of sensitive personal, financial, and operational data. Collectively, these incidents underscore the persistent risk to personal and organizational data and emphasize the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity controls, continuous monitoring, and proactive risk mitigation.
Scale of Impact (Aggregated)
Individuals Affected:
- 3 million+ applicants (Education)
- 2 million+ stalkerware users (Surveillance)
- 560,000+ patients (Healthcare)
- Undisclosed number of employees/customers (Petroleum & Technology breaches)
Data exposed:
- Names
- Test Scores
- Financial Aid Information
- Social Security Numbers
- Medical Records
- Email Addresses
- IP Details
- Plaintext Credentials
- Confidential Organizational Data
Key Attack Vectors Observed:
- Website vulnerabilities
- Compromised credentials
- Stalkerware / malware
- Unauthorized access to unprotected databases
Link of the Post:
April Incidents 2025
Cyber incidents across HRM, healthcare, IT, software applications, and retail sectors demonstrate a continued surge in data breaches, ransomware attacks, and targeted cyber fraud. Attackers exploited misconfigured cloud environments, unsecured servers, social engineering tactics, and ransomware campaigns, resulting in the exposure of sensitive personal, financial, and organizational data. While some attacks led to massive data exposure, others caused direct financial losses without data leaks, highlighting the diverse nature of cyber threats. Collectively, these incidents underscore the importance of strong security controls, proactive monitoring, and employee awareness programs in mitigating risks across various industries.
Scale of Impact (Aggregated)
Individuals / Data Records Affected:
- 21 million screenshots (HRM employee monitoring)
- 4.7 million customers (Healthcare)
- An undisclosed number of IT clients (Cloud breach)
- Cryptocurrency users targeted (Software-Application)
Financial Losses:
€20 million (Retail ransomware attack)
Key Attack Vectors Observed:
- Unsecured servers and misconfigurations
- Cloud environment vulnerabilities
- Social engineering and phishing tactics
- Ransomware deployment and operational disruption
Link of the Post:
May Incidents 2025
An analysis of recent threat activity across the retail, data analytics, healthcare, monitoring software, and technology sectors indicates a significant escalation in large-scale data breaches and supply-chain–driven compromise events. Most incidents originated from insecure third-party platforms, misconfigured databases, and application-level security gaps, resulting in the exposure of sensitive personal identifiers and authentication credentials. The attacks range from targeted retail intrusions to large-scale credential dumps affecting global user bases, collectively placing hundreds of millions of accounts at risk. Increasing regulatory enforcement and financial penalties reflect growing accountability, while the scale of exposure underscores the need for stronger vendor risk governance, continuous security monitoring, and data protection controls.
Scale of Impact (Aggregated)
Total Individuals / Records Exposed:
- 184 million users (global credential leak)
- 3.2+ million email addresses (spyware apps)
- 360,000+ identities (data analytics firm)
- Retail customers via a third-party breach
Regulatory / Financial Impact:
$700,000 fine imposed for healthcare data leak involvement
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
June Incidents 2025
The reported incidents indicate a sharp escalation in high-impact cyber threats spanning InfoSec, AI, telecommunications, healthcare, and aviation sectors. The attacks range from record-breaking credential leaks and malware distribution via search ads to nation-state espionage, ransomware-driven healthcare disruption, and targeted airline intrusions. Collectively, these events demonstrate how attackers are exploiting stolen credentials, malware, social engineering, and supply-chain weaknesses to achieve large-scale compromise, persistence, and operational disruption. The scale, sophistication, and cross-industry spread highlight a critical need for stronger identity security, Zero Trust adoption, and continuous threat monitoring.
Incident Breakdown (By Numbers)
By Attack Type
Data breaches / credential exposure: 2 incidents (40%)
- 16 billion leaked credentials
- Healthcare ransomware data exposure
Malware & Spyware distribution
Fake DeepSeek website via Google Ads
Cyber-espionage (nation-state)
China-linked Salt Typhoon telecom campaign
Ransomware/Extortion operations
Hospitals and airlines impacted
Link of the Post:
July Incidents 2025
The observed cyber incidents highlight a sharp rise in data breaches, third-party compromises, misconfigurations, and active cyber-operations across online platforms, luxury retail, financial services, enterprise IT, and aviation. Most breaches stemmed from cloud misconfigurations, third-party platform abuse, social engineering, and zero-day exploitation, exposing highly sensitive personal, financial, and operational data. In parallel, state-aligned and hacktivist cyberattacks demonstrated how cyber operations are increasingly being used for disruption, espionage, and geopolitical impact, extending beyond data theft to consequences such as grounded flights and infrastructure outages.
Incident Breakdown (By Numbers)
By Attack Type
Data Breaches/Data Exposure
- Dating app message leak (1.1M records)
- Luxury fashion customer data breach
- Life insurance customer data exposure (majority of 1.4M users)
Zero-Day Exploitation & Malware Attacks:
ToolShell SharePoint zero-day campaign
Cyber warfare/hacktivism & DDoS:
Ukraine-linked cyber offensive disrupting Russian aviation and infrastructure
Consolidated Impact Metrics
Users Affected
- 1.1M+ private messages
- 1.4M+ insurance customers
- 143,000+ luxury brand customers (Turkey alone)
Operational Disruption
- Enterprise SharePoint takeovers
- Dozens of airline flights are grounded
Data volume theft:
~100 TB exfiltrated in a cyber warfare operation
Link of the Post:
August Incidents 2025
Across multiple industries, the analyzed incidents illustrate a sustained wave of ransomware attacks, credential theft, and third-party CRM compromises affecting government, SaaS, aviation, healthcare, and technology sectors. A common theme is social–engineering–driven access (vishing and SMS phishing) targeting Salesforce environments, alongside ransomware operations causing service disruption and data exfiltration. While some breaches exposed limited business contact data, others led to large-scale operational outages and confirmed data theft, highlighting persistent weaknesses in identity security, third-party risk management, and incident containment.
Consolidated Impact Metrics
Records exposed:
- ~2.55 million CRM records (tech giant)
- CRM contact data across SaaS and airline platforms
Data Exfiltrated:
176 GB claimed by ransomware group (pharma sector)
Operational disruption:
State government services and pharma operations impacted
Third-party involvement:
3 out of 5 incidents (60%) linked to Salesforce or external platforms
Link of the Post:
September Incidents 2025
Across multiple critical sectors, the analyzed incidents demonstrate a clear escalation in supply-chain compromises, ransomware operations, credential and token exposure, and cloud backup misuse spanning automotive manufacturing, internet infrastructure, cybersecurity vendors, aviation, and government finance. Attackers increasingly leveraged third-party platforms, CRM tools, cloud APIs, and managed service providers to gain indirect access to high-value targets. Several incidents caused real-world operational disruption, including airport outages, while others exposed highly sensitive data such as employee SSNs, API tokens, firewall configurations, and government financial records, underscoring systemic weaknesses in vendor risk management, identity security, and incident containment.
Consolidated Impact Metrics
Individuals Affected:
~870,000 unique emails and extensive PII (automotive supply-chain breach)
Organizations Impacted:
- 25 companies
- ~200 municipalities
- Multiple universities
Sensitive Assets Exposed:
- Employee names & SSNs
- 104 API tokens
- Firewall configuration backups
- Up to 1.5 TB of government financial data (claimed)
Operational Disruption:
Multiple European airports with delays and cancellations
Link of the Post:
October Incidents 2025
The incidents underscore how vendor dependency, credential theft, open-source exposure, and delayed patching are amplifying cyber risk at scale. Weaknesses in SaaS and outsourcing providers cascaded across industries, exposing millions of customer and citizen records within hours. In parallel, infostealer malware and compromised development platforms fueled mass credential leakage and source-code exposure, while the scale of Microsoft’s final Windows 10 Patch Tuesday highlights how unpatched vulnerabilities continue to drive active exploitation. Together, these cases illustrate how a single weak link can trigger ecosystem-wide compromise.
Consolidated Impact Metrics
Records Exposed
- 5+ million SaaS customer records
- 6.6 million individuals across 325 pension schemes
- 183 million stolen login credentials
Data volume leaked:
- 1 TB (outsourcing provider)
- 570 GB across 28,000 repositories
Organizations affected:
- 40 organizations in a CRM campaign
- Hundreds of enterprises via GitLab exposure
Regulatory Impact:
£14 million fine imposed on outsourcing provider
Vulnerability landscape:
172 Windows 10 flaws patched, including 6 zero-days (3 actively exploited)
Link of the Post:
November Incidents 2025
Approximately 67% of the incidents involved confirmed breaches, with zero-day vulnerabilities playing a role in two-thirds of cases. Half of the incidents were tied to third-party vendors or integrations, reinforcing that indirect access paths now pose risks equal to direct platform flaws. The convergence of ERP exploitation, ransomware pressure, and supply-chain exposure highlights the urgent need for stronger vendor governance, rapid patching, and continuous monitoring of external application access.
Consolidated Impact Metrics
Individuals Affected:
44,000 banking customers exposed (16.7% of incidents with quantified impact)
Data Types Compromised:
- Intellectual property and product designs
- Operational and financial ERP data
- Employee, customer, and supplier records
- Highly sensitive PII (SSNs, tax IDs, account details)
Industries Impacted:
Enterprise software, optical & electronics manufacturing, financial services, IT services, software development
Attack Techniques Observed:
- Unauthenticated remote code execution
- Zero-day ERP exploitation
- Token abuse via third-party integrations
- Image-based RCE delivery (JPEG)
Link of the Post:
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Conclusion
The cyber incidents of 2025 reveal a threat landscape defined by scale, speed, and systemic impact, where ransomware, credential theft, zero-day exploitation, and third-party compromise have driven record-breaking breaches across nearly every industry. Over the year, cybercrime costs surged to an estimated $10.5 trillion, with 44% of breaches involving ransomware and 30% linked to supply-chain or third-party failures, double the previous year. Attacks exposed billions of records, including 16 billion leaked credentials, disrupted critical services with 5.6 Tbps DDoS attacks, and resulted in the theft of 100+ TB of data, while major regulatory penalties underscored rising accountability. Together, these trends confirm that cyber risk in 2025 has evolved into an enterprise-wide, economic, and geopolitical challenge demanding stronger identity security, vendor governance, continuous monitoring, and rapid vulnerability management.
Preventing similar large-scale incidents requires organizations to move beyond reactive security toward continuous risk reduction. This includes enforcing strong identity and access management with MFA and least-privilege controls, rigorously governing third-party and SaaS integrations, continuously monitoring for credential abuse and anomalous behavior, and accelerating patch management for internet-facing and high-value systems. Equally critical are Zero Trust adoption, regular incident simulations, secure DevOps practices, and real-time visibility across cloud and hybrid environments. Together, these measures are essential for containing the blast radius, preventing cascading failures, and mitigating the economic and operational fallout of cyberattacks in an increasingly interconnected digital ecosystem.
FAQs
- What is the biggest threat in 2025?
As 2025 unfolds, the threat from U.S.-based violent extremists is expected to remain elevated. This includes ideologically driven domestic violent extremists (DVEs) as well as foreign terrorist organizations (FTOs)–inspired homegrown violent extremists (HVEs).
- Which industries were most targeted?
No sector was immune. Heavily impacted industries included:
– Education and healthcare
– Financial services and insurance
– SaaS and enterprise IT
– Aviation and transportation
– Retail and luxury brands
– Government and critical infrastructure









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *