Almost every organization today recognizes the value of data in enhancing customer and employee experiences, as well as driving smarter business decisions. However, as data grows in importance, protecting it has become increasingly challenging. A strong data protection strategy is now essential, as hybrid environments spread critical information across cloud platforms, third-party services, and on-premises infrastructure, while threat actors continuously develop innovative methods to exploit vulnerabilities.
In response, many organizations are prioritizing data protection, only to encounter a lack of clear guidelines or structured advice. Although each organization’s data protection strategy will be unique, there are several key components and best practices to consider when designing an effective framework.
While the terms data protection and data privacy are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct concepts. Data privacy determines who is allowed to access specific data, whereas data protection involves the tools, policies, and measures that enforce and restrict that access. Compliance regulations ensure that organizations honor users’ privacy requests, while companies are responsible for implementing safeguards to protect sensitive information.
Data protection and privacy typically focus on personally identifiable information (PII) and personal health information (PHI). These practices are critical for business operations, strategic development, and financial stability. By safeguarding data, organizations can prevent breaches, protect their reputation, and more effectively meet regulatory requirements.
Table of Contents
Gist on Data Protection Strategy & Compliance Implementation
A well-defined data protection strategy ensures that an organization’s sensitive information, including customer, employee, and business-critical data, is effectively safeguarded against unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. When coupled with proper compliance implementation, it enables organizations to meet legal and regulatory obligations while fostering trust and transparency with customers, partners, and stakeholders. A comprehensive approach combines strategic planning, advanced security controls, regular audits, employee training, and monitoring systems to proactively manage risks.
One key distinction between data protection and data security is data protection’s emphasis on accessibility and availability. While data security primarily aims to safeguard digital information from unauthorized access and malicious actors, data protection goes beyond this. It encompasses the same security measures as data security while also addressing authentication, data backup, secure storage, and compliance with regulations such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Importance of Data Protection Strategy and Compliance
Data privacy refers to the protection of personal and sensitive information, ensuring that any data collected, stored, processed, or shared respects the rights of the individual to whom it belongs.
Organizations must follow a strict data protection strategy and compliance requirements, taking responsibility for safeguarding users’ information. This involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring data is not misused, and providing individuals with control over their own data. Adhering to compliance standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, not only protects users but also helps organizations avoid regulatory penalties and build trust with their customers.
Data privacy has become increasingly critical in the digital age for the following reasons:
Data Proliferation:
The rapid growth of the internet and modern technologies has led to an exponential increase in the volume of data generated, stored, and shared. This surge has made protecting sensitive information increasingly challenging.
Digital Transactions:
The shift to digital transactions has transformed how individuals and businesses handle financial activities. Sharing personal information—such as credit card details, email addresses, and social security numbers—has become routine, making data privacy a top priority.
Cyber Threats:
As technology evolves, so do cyber threats. Ransomware, identity theft, and data breaches are becoming more frequent, highlighting the need for strong data protection measures to secure sensitive information.
IoT and Big Data
Internet of Things (IoT) devices—from smart home gadgets to industrial sensors—collect and transmit real-time data. This data, often analyzed as Big Data for trends and decision-making, raises privacy concerns. Organizations can address these concerns by:
- Effectively understanding and managing their data.
- Securing networks against unauthorized access through VPNs or SSH.
- Enforce strict controls over data storage and backups.
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
- Educating users on data privacy and security best practices.
Machine Learning Models
The increasing use of AI and machine learning introduces additional complexities for data privacy. These models rely on large datasets, which often include sensitive information, necessitating careful handling and protection.
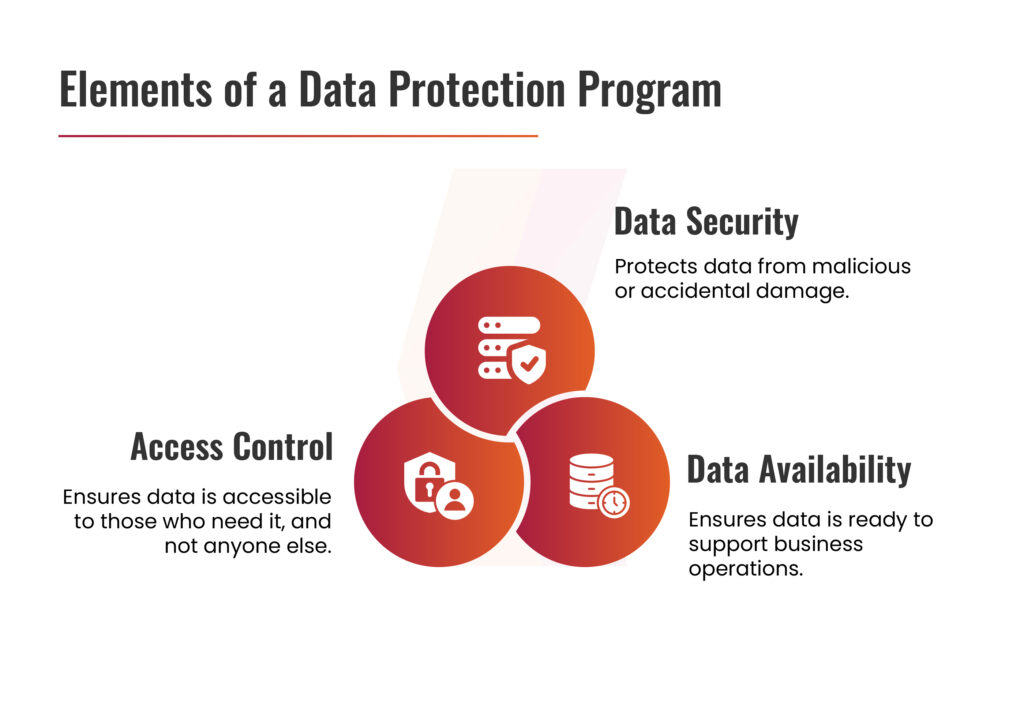
Components of Data Protection Strategies
Data Access Management Controls
Access controls are essential for preventing unauthorized access, use, or transfer of sensitive data. They ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific information while allowing employees to perform their tasks with precisely the permissions they need—no more, no less.
Organizations can implement role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conduct regular reviews of user permissions to maintain security. Identity and Access Management (IAM) initiatives further enhance access control by assigning each user a unique digital identity. Permissions are tailored based on roles, compliance requirements, and other relevant factors, enabling organizations to protect critical assets without disrupting legitimate business operations.
Incident Response
Incident Response (IR) encompasses an organization’s processes and tools for identifying and addressing cyber threats, security breaches, and attacks. Its primary goal is to prevent incidents where possible and to minimize the financial and operational impact of any that occur.
Integrating incident response into a comprehensive data protection strategy enables organizations to take a proactive stance on cybersecurity, strengthening their defenses against hackers and reducing potential business disruptions.
Adhering to Compliance Standards
Governments and regulatory authorities are increasingly emphasizing the importance of data protection, establishing laws and standards that organizations must follow to conduct business responsibly.
Non-compliance with these regulations can result in substantial fines and legal penalties. Implementing a strong data protection strategy helps organizations maintain ongoing compliance by establishing clear internal policies and procedures.
How Can Kratikal Help You in Data Protection and Compliance Implementation?
Kratikal helps organizations strengthen their data protection and compliance posture through a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity solutions. From implementing data protection frameworks and conducting regular security assessments to ensuring alignment with global standards like GDPR, ISO 27001, and HIPAA, Kratikal provides end-to-end support. Our team of experts assists in identifying vulnerabilities, mitigating risks, and establishing strong governance policies that safeguard sensitive data. With advanced tools such as our AI-powered AutoSecT platform for continuous vulnerability management and compliance monitoring, Kratikal empowers businesses to stay secure, compliant, and resilient in today’s evolving threat landscape.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Conclusion
An effective data protection strategy combined with strong compliance implementation is essential for safeguarding sensitive information, maintaining trust, and ensuring adherence to global regulations. As cyber threats continue to evolve and digital ecosystems expand, organizations must adopt proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and clear governance frameworks. By embedding data protection and compliance into their core operations, businesses can strengthen resilience, minimize risks, and ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly data-driven world.
FAQs
- What is data protection compliance?
It requires putting measures in place and adhering to established guidelines to ensure data is managed securely and responsibly. Major data compliance frameworks include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Who is responsible for data protection compliance?
Everyone within an organization has a role in maintaining data protection compliance. This responsibility should be clearly defined in the organization’s Data Protection Policy, emphasizing that anyone who handles personal data carries a duty to ensure it is managed securely.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *