Enterprise cybersecurity involves a wide-ranging method aimed at protecting company networks, data, apps, and cloud platforms from a rising number of cyber threats. It focuses on lowering weaknesses, strengthening security measures, and keeping operations steady even when attacks happen. This approach relies on modern technology, security platforms, and clear policies supported by employee training to boost the company’s defense systems. By adopting these measures, businesses reduce the chance of data leaks, maintain customer trust, follow regulations, and stay prepared to operate in an ever-changing digital world.
Table of Contents
Importance of Enterprise Cybersecurity Strategy
The significance of enterprise cybersecurity lies in its role in shielding organizations from the financial, operational, and reputational damage caused by cyberattacks. With threats becoming more frequent and attackers worldwide leveraging advanced tactics and techniques, IT infrastructures are increasingly at risk.
Beyond financial impacts, cyberattacks can disrupt operations, cause downtime, reduce productivity, and erode customer trust—ultimately leading to loss of business. By adopting comprehensive cybersecurity measures, organizations can secure their assets, maintain continuity, and protect their brand reputation.
Best Practices for Enterprise Cybersecurity
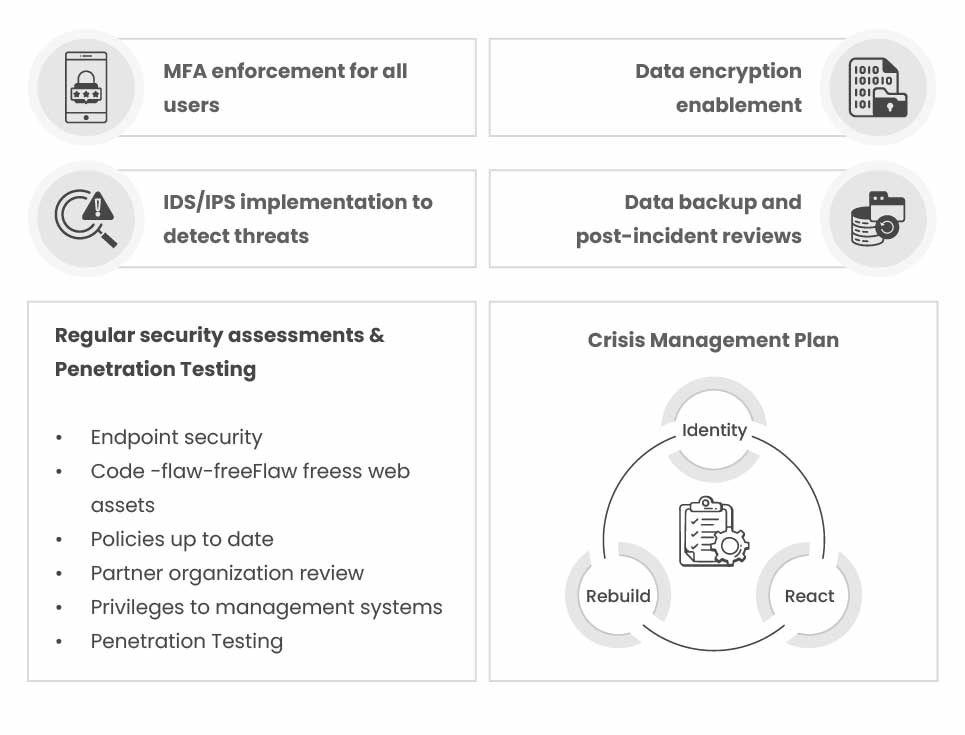
MFA Enforcement for All users
The first essential step in enterprise security is implementing strong authentication. Require users to provide more than one factor when logging in—such as biometrics, one-time password tokens, or smartphone verification—choosing methods that best suit your workforce.
Give priority to protecting administrative accounts with elevated privileges, as unauthorized access to these can cause severe damage. Ensure these accounts have the highest level of protection. Apply multi-factor authentication (MFA) to mobile applications and remote access APIs, enforce strong password requirements for all users, and distribute password policies across devices as they connect. Finally, streamline offboarding by automating account removal when employees exit the organization.
Implement IDS/IPS to Monitor Threats
Strengthen enterprise cybersecurity by deploying Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) or Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). While both serve a similar purpose, they run continuously, monitoring network traffic and comparing it against global threat databases to quickly identify risks.
These tools alert security teams about unauthorized file transfers, suspicious changes in administrative privileges, and unusual network slowdowns that may signal an attack.
With machine learning–driven prevention, IDS/IPS can automate threat detection. While not replacements for firewalls or antivirus solutions, they are a critical addition to the enterprise security toolkit.
Conduct Regular Penetration Testing
Enterprise security depends on continuous monitoring and testing to identify vulnerabilities across networks, endpoints, and web assets. This includes ensuring remote devices are secured, applications are updated promptly, and partner organizations follow strong security practices. Regular audits of access controls, privilege management, and penetration testing further help detect weaknesses, prevent privilege creep, and strengthen overall defenses against evolving threats.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Implement Data Encryption
Protect sensitive data by encrypting it both at rest and in transit across network endpoints. Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to secure remote access and apply encryption features offered by cloud service providers.
For stronger protection, adopt end-to-end encryption solutions that secure files wherever they move, monitor data access and location, and block unauthorized transfers. This approach not only enhances data security but also simplifies compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Prioritize Crisis Management
Crisis management is a vital aspect of enterprise cybersecurity. Organizations should operate with the mindset that data breaches are inevitable and establish clear procedures to respond swiftly and restore operations.
An effective crisis response follows three steps:
- Identify threats quickly using advanced detection tools.
- React immediately—notify clients if their data is exposed, contain malicious activity, and evaluate the breach’s impact.
- Rebuild securely by restoring systems from backups, auditing vulnerabilities, checking for APTs, and maintaining transparent communication with customers.
Data Backup and Post Incident Reviews
Data backups play a crucial role in restoring operations and protecting customer information. Use a secure cloud or off-site backup provider for critical data, maintain multiple copies of high-priority files, and perform daily backups for the most valuable assets.
Full backups of all company data are often impractical at scale, but backing up critical application workloads incrementally ensures recovery after incidents. Post-attack, review disaster recovery processes to evaluate backup effectiveness, restoration speed, and any signs of data corruption.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Effective Solutions for Enterprise Cybersecurity
Enterprise cybersecurity might seem like solving a tricky puzzle, but you can make it clearer by narrowing in on three main parts. Each part handles a specific security need, and they come together to create a solid defense to protect your company.
Here’s how it breaks down:
Network Security
Companies need to ensure secure access to network resources. Network security solutions include:
- End-to-end encryption of all critical data
- Endpoint protection via remote access VPNs
- Single Sign-on and MFA systems to exclude unauthorized users
- Antivirus and antimalware tools
- Password management to strengthen credentials
- Security policies are distributed to every endpoint
Cloud Security and Data Protection
Enterprise cybersecurity must secure cloud assets and data within cloud environments. Key solutions include:
- Privilege management to restrict access only to necessary resources
- Cloud VPNs to anonymize users and encrypt data in transit
- Cloud-native firewalls to control access and block malicious activity
- Encryption tools offered by cloud service providers (CSPs)
- SD-WAN architecture to secure all network assets
Cybersecurity Checklist for Enterprises

How Kratikal Can Help You in Enterprise Security Testing?
Securing large-scale enterprises requires a strategic, multi-layered cybersecurity approach. At Kratikal, we specialize in providing end-to-end enterprise security testing that covers every digital asset — from networks and cloud environments to web and mobile applications.
Our methodology combines automated scanning with in-depth manual VAPT to uncover vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit. Beyond detection, we focus on prioritizing risks based on business impact, ensuring that remediation efforts deliver maximum security value.
Kratikal also supports organizations with compliance audits for globally recognized standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA, helping enterprises meet regulatory demands while strengthening trust with clients.
With our advanced VMDR platform, AutoSecT, businesses gain real-time visibility into their security posture, automated compliance mapping, and actionable insights to reduce risks quickly.
FAQs
- What is the role of enterprise cybersecurity?
Enterprise cybersecurity plays a crucial role in assessing and managing third-party risks, enabling organizations to choose trusted partners and collaborate securely to achieve business goals. It also promotes company-wide awareness, where a strong cybersecurity strategy educates employees and reinforces the organization’s overall security posture.
- What is enterprise cybersecurity management?
Enterprise cybersecurity encompasses the wide range of measures and practices organizations adopt to safeguard their digital assets against cyber threats. These assets span websites, databases, email systems, and cloud storage, all essential to the smooth functioning and resilience of modern businesses.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *