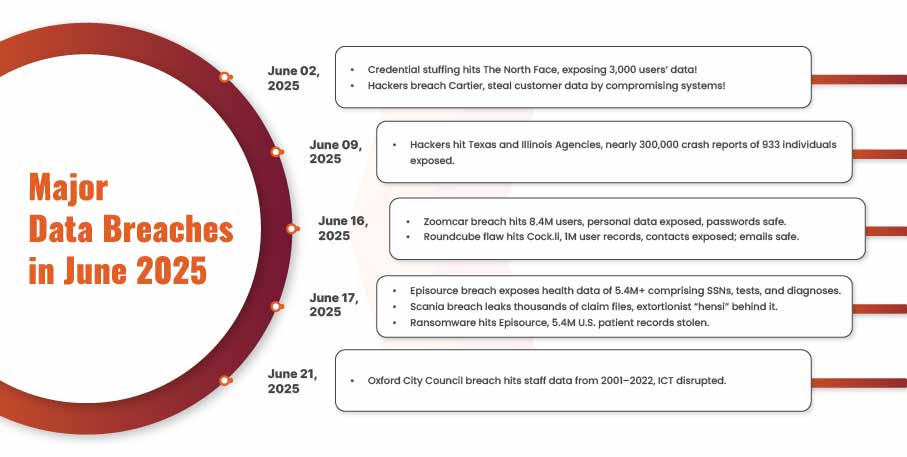
In June 2025, the world witnessed the largest credential leak in history, 16 billion stolen logins exposed by infostealer malware, marking a new peak in the global data breach epidemic. Records say that in 2023, around 3200 data breach incidents with ~419 million exposed records came into light. A slight dip from 2023 was recorded in 2024 with ~3158 data breach incidents. In the first quarter of 2025, 824 breaches with over 91 million exposed records have shaken organizations so far!
Despite a minor drop in breach count from 2023 to 2024, the scale of data exposed soared in 2024. Approximately 1.73 billion individual records were compromised in 2024, a 312% increase over 2023. This spike was driven by a handful of mega-breaches: six incidents in 2024 each exceeded 100 million records compromised. Ticketmaster’s breach alone exposed ~560 million records. You can never tell when and how the bad actors will infiltrate your organization, costing you years of hard work. Proactive defense is a must. However, if unfortunate events hover, your teams must be aware of the crucial subsequent steps after a data breach. This is what this blog is all about!
Table of Contents
Data Breach Scenario in 2025 – The Present and What’s Anticipated
A single education technology breach in early 2025 accounted for ~71.9 million of those records, demonstrating how one incident can dominate the year’s impact. If breaches proceed at this pace, 2025 may see a comparable or higher incident count than 2024. Furthermore, June 2025 brought news of the largest credential leak in history.
Data Breaches by Industry Sector – The Top 2
- Financial Services: In Q1 2025, the financial sector suffered the most breaches of any sector. 193 incidents, nearly a quarter of all reported. In 2024, finance also overtook healthcare as the top sector by number of compromises, with hundreds of incidents reported. The average cost of a financial sector breach was about $6.08 million in 2024 and is expected to fall between $10 and $11 million in 2025.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations have long been a breach hotbed. In 2024, healthcare breaches declined to 536, falling to second place behind finance. For the 14th year in a row, healthcare breaches had the highest average cost of any industry, about $9.77 million per incident in 2024, and are expected to reach around $10.1 million by 2025.
Other sectors that are a high target in case of data breaches are manufacturing and industry, government, and education. Retail, tech, and professional services also faced data breaches in the last few years. These incidences underline the fact that no industry is untouched, attackers will target any organization with valuable personal or proprietary data.
Financial Impact of Data Breaches in 2024
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2024 was $4.88M.
- This marked a 10% increase over 2023, the largest in a decade.
- The average cost per compromised record was $165.
- Mega-breaches (50 – 60M records) cost around $375M.
- Healthcare had the highest breach cost at $9.8M on average.
- Finance, tech, and energy sectors saw costs exceeding $5 – 6M.
- Top cost drivers include downtime, fines, lost trust, and response efforts.
- The average breach lifecycle was 258 days in 2024.
- Breaches contained within 200 days cost 23% less.
- Using AI cut response time by 98 days, reducing overall costs.
The above data points show that data breaches are serious, and here are the most important steps that you need to follow if your organization becomes a victim.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
What To Do After a Data Breach?
Here’s what your organization should do:
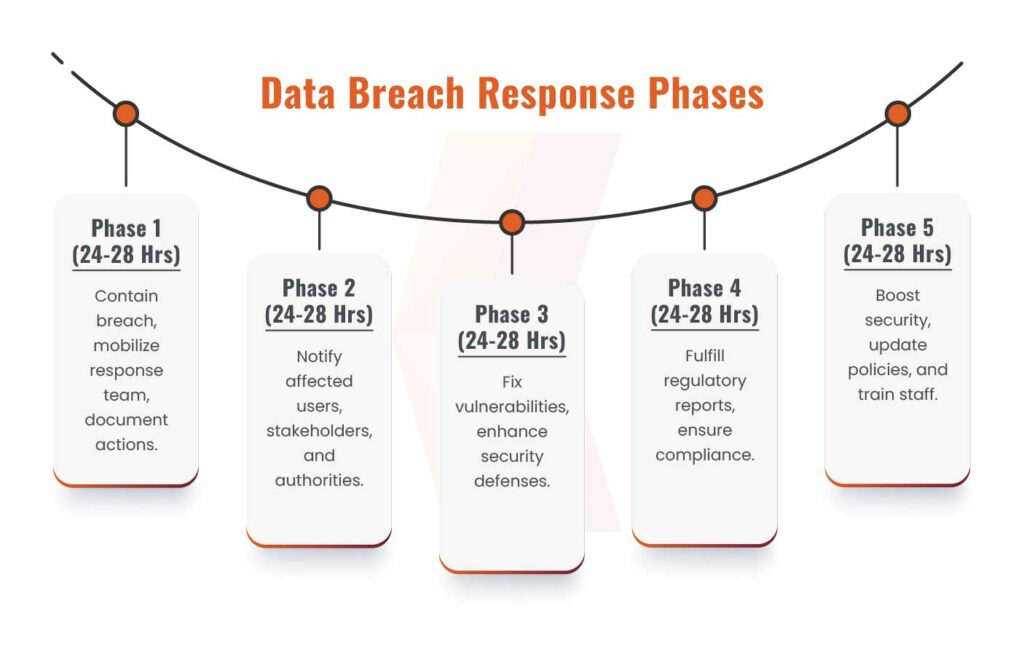
Phase 1: The First 24 – 48 Hours
Contain the Breach (First 2 – 4 Hours):
The moment you realize something is wrong, like a hacker got in, or sensitive data is exposed, you need to act fast. The goal is to stop the damage from spreading. This means:
- Disconnecting affected systems from the network
- Locking down any exposed cloud or data access
- Making sure evidence is not erased, as it’ll help with the investigation
Activate the Response Team (Within 4 – 6 Hours):
Once the breach is under control, your incident response team jumps in. In case you do not have an incident response team, get in touch with CERT-In Emapanelled Security Auditors like Krtaikal. An incident response team includes:
- Security experts (to investigate and fix issues)
- Legal (to handle compliance and regulations)
- Communication professionals (to manage what to tell customers or the media)
- CISO to guide decisions
Document Everything (Throughout the 48 Hours):
Every step taken from how the breach was found to who did what needs to be written down. Keep a clear timeline and log of actions:
- When the breach was discovered
- What steps were taken and when
- Who was involved in the response
This is important for:
- Reporting to regulators
- Insurance claims
- Learning from mistakes to prevent it from happening again
Phase 2: Decide Who and How to Notify
Once the breach is under control and the response team is working, the next big step is to notify the right people fast.
Assess & Plan (Within 24 – 48 hours)
Next, ask these questions:
- What data was leaked? Whose data is it?
- What laws apply? Because different rules apply in different countries/states.
- Do we need to inform the police or a regulator before telling the public?
Write & Approve Messages (Within 48 – 72 hours)
Your messages must:
- Explain what happened and when.
- Describe the type of personal data involved (like names, emails, or bank info)
- Tell people what you’ve done to stop the breach.
- Suggest steps they should take (like changing passwords)
- Offer help like credit monitoring, if needed
- Share contact details for questions
Start Sending Notifications (Within 72 hours by law)
- Send letters or emails to affected people (emails only if legally allowed).
- Public statements or press releases, if contact info is missing or if required by law.
- Updates on your website for wider communication
Set up a dedicated helpline or support team to assist affected individuals and ensure prompt responses. Prepare a clear FAQ to provide consistent answers. Document all communications for legal and internal records. Also, be prepared for a surge in queries and respond with empathy and accuracy to maintain trust.
Phase 3: Find and Fix Vulnerabilities
Once the breach is contained, the next step is to find out how it happened and make sure it doesn’t happen again. This needs a careful yet quick approach to protect your IT infrastructure while keeping your business running. Contact cybersecurity professionals like Kratikal, who are experts in conducting VAPT. Kratikal can conduct in-depth vulnerability assessment and penetration testing for you and suggest patching recommendations, followed by re-testing.
You can also automate your security posture with AutoSecT. It is an AI-powered pentest and VMDR platform that runs real-time scanning and delivers AI-verified results ensuring complete security of your inventory (network, cloud, web app, mobile app and API). To know more about, click here.
How Kratikal Performs VAPT ?
At Kratikal, the VAPT process is structured, thorough, and designed to ensure real-world security. Here’s how we do it, step-by-step:
Step 1: Information Gathering
We begin by collecting key details about your assets like devices used, network layout, and communication protocols. This helps us understand your environment inside out.
Step 2: Planning & Analysis
Next, we create a testing plan that mimics real-world cyberattacks, using a comprehensive set of test cases. Our goal is to test effectively while ensuring your live systems stay safe and stable.
Step 3: Vulnerability Detection
We use industry-standard tools to scan each part of your IT infrastructure. This helps us identify possible weak points or vulnerabilities in your organization infra.
Step 4: Penetration Testing
We focus on the most likely attack paths and manually exploit vulnerabilities to see how far an attacker could get. This is where most of the testing happens. We even create custom scripts based on your business logic for accurate results.
Step 5: Reporting
Once testing is done, we share a detailed report outlining each vulnerability, its severity, potential impact, and step-by-step recommendations. We also provide proof-of-concept examples to show exactly how the flaws can be exploited.
Step 6: Report Discussion
Our experts sit with your development team to explain every issue in detail, including threat levels and how to fix them. We ensure your organization understands the risks and the solutions clearly.
Step 7: Patch Recommendation
Your development team works on fixing the vulnerabilities, guided by our recommendations and in coordination with our security experts.
Step 8: Re-Testing
Once the fixes are done, we conduct a second round of testing to confirm all vulnerabilities have been successfully patched and your system is secure.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Phase 4: Complete Your Legal and Compliance Responsibilities
Once the breach is under control and vulnerabilities are fixed, the next important step is to fulfill all legal and compliance requirements. In India, a data breach is to be reported to CERT-In within 6 hours of detection. Notify affected individuals within the given time frame based on the country and law. Maintain documentation throughout the entire response process.
- Follow Legal Standards
Compliance services help businesses follow privacy and data protection laws. This reduces the risk of penalties and ensures sensitive data is handled properly.
- Setting Strong Security Practices
They also help build solid security practices like using encryption, managing user access, performing regular risk checks, and ensuring safe data handling. This lowers the chance of breaches in future.
- Continuous Monitoring and Audits
Compliance involves regular audits and system checks to identify weak spots. With constant monitoring, issues can be found and fixed before a breach happens.
- Creating Response Plans
Compliance frameworks include ready-to-use incident response plans. These plans outline how to detect, report, contain, and recover from a breach. Having this in place helps reduce the damage and ensures a quick, organized response.
Phase 5: Focus on Long-Term Recovery and Business Continuity After a Data Breach
After managing the immediate impact of a data breach, the next step is to focus on long-term recovery and preventing future incidents. This is because investing in security now reduces future risks and costs. Preventive action is far cheaper and more effective than reacting to another breach.
Focus on Security Improvements (1 – 3 months)
Build a stronger defense with:
- AI-powered pentest and VMDR platform for faster threat detection and response
- Real-time monitoring
- Better data classification to control shadow data
- Stronger access controls and authentication
- Regular security checks and vulnerability scans
Business Continuity (1 – 2 weeks and ongoing)
To keep operations running:
- Update policies based on lessons learned
- Train employees to boost security awareness
- Strengthen cloud security for better data protection
If there’s one lesson from the rising number of breaches in 2025, it’s this: no organization is too small or too secure to be a target. The cost of inaction is simply too high. Whether you’ve already experienced a breach or are preparing for the future, your next step must be clear: act fast, communicate transparently, fix the gaps, and toughen your defenses.
FAQs
- What should an organization do immediately after a data breach?
Immediately isolate affected systems, activate the incident response team, preserve evidence, and begin breach containment. Document all actions and assess notification requirements under applicable laws.
- Why is post-breach VAPT important for organizations?
Post-breach VAPT helps identify how the breach occurred, uncovers hidden vulnerabilities, and ensures they are patched to prevent repeat attacks.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *