Organizations’ reliance on IT infrastructure for their financial and operational activities is growing exponentially. IT General Controls or ITGC ensures the IT systems work securely and efficiently. These controls keep in check how well information is managed, whether the IT infrastructure is compliant with the business, regulatory, and legal requirements; reliability and security of data and other IT assets; and the implications of these controls over automated and manual processes. If these controls are weak, it can cause problems for other applications or asset checks. So, it’s important to implement ITGC rightfully and plan regular audits for the IT systems.
Table of Contents
What are IT General Controls?
ITGC are rules and policies. They are a type of internal controls that guide an organization on how to manage its information technology. The controls make sure that the IT infrastructure is secure, efficient, and in line with the regulations. Furthermore, it ensures that IT systems are properly developed and maintained. It also keeps in check the security of recovery and backup rules as well as daily operations.
IT General Controls serve different purposes for different industries. For healthcare or finance, these general controls are necessary to stay aligned with standard guidelines like HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc. For some industries, these controls help maintain their cybersecurity posture and improve the operational efficiency of their IT infrastructure.
Key Areas
These controls help organizations meet security and compliance benchmarks related to their IT environment. Some key areas of ITGC that ensure IT systems are secure, well-managed, and reliable include:
- Access Control: Controlling access to physical locations where technology is stored.
- Computing Infrastructure: Ensuring applications, software, hardware, networks, and servers are properly installed and work properly and securely.
- Data: Handling, protecting, and managing information effectively.
- Development and changes: Making sure new updates are done securely and follow rules.
- User Accounts: Creating and managing user accounts to control who can access systems.
- Backup and recovery: Securing data from theft or loss, ensuring there are copies of data and systems to recover from failures.
- Daily operations: Managing and monitoring IT assets to keep them reliable and efficient.
ITGC Compliance Frameworks
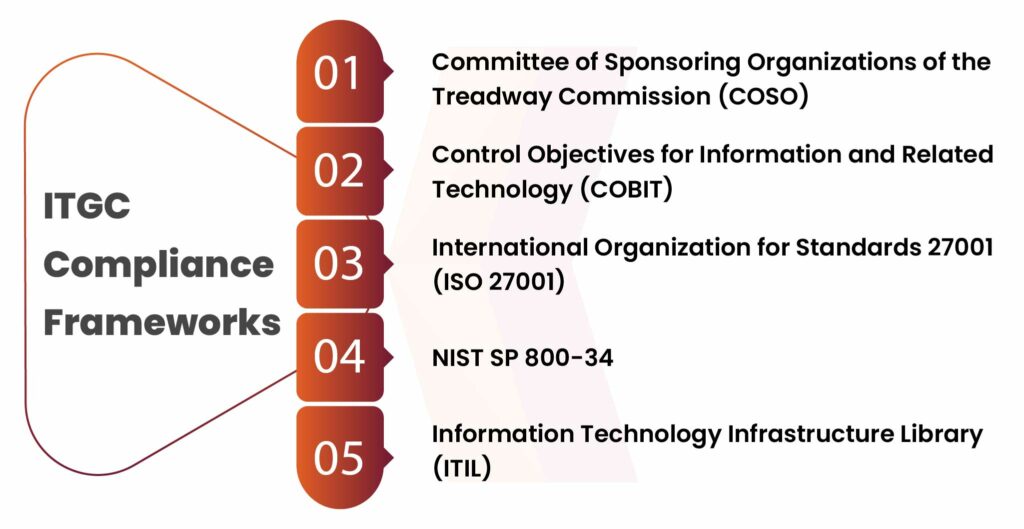
Organizations must make sure they have the right ITGC in place. Some compliance frameworks help organizations categorize and organize the general controls as not all controls apply to all organizations. These frameworks ensure that their IT assets meet the compliance and security requirements and prepare them for audit.
COSO Internal Control Framework
COSO stands for Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). This framework provides guidelines for the design and implementation of internal control related to risk management. It has five key elements:
- Control Environments
- Current Control Practices
- Information and Communication processes
- Monitoring and Oversight activities
- Risk Evaluation and Management
COBIT IT Control Framework
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is an IT framework designed by ISACA (Information System Audit and Control Association). This is similar to a guide that brings together ideas from other popular IT frameworks focusing on IT security and how it connects to business risks. It also provides clear objectives and methods for IT General Controls. COBIT has five key principles, they are:
- Using one unified framework.
- Addressing stakeholder needs.
- Distinguishing between governance and management.
- Adopting a holistic governance approach.
- Covering the entire organization.
ISO 27001 Framework
ISO 27001 is a standard that provides guidelines to design, implement, improve, maintain, monitor, and review information security management systems. These standard guidelines help organizations reduce legal, physical, and technical risks.
- Policy Drafting
- GAP Assessment
- Implementation
- Auditing and Training
- Certification
Who Needs to Implement IT General Controls?
Organizations that deal with and store private and sensitive information of their clients and stakeholders must implement ITGC. Apart from that, organizations that are responsible for managing, using, and safeguarding their IT assets and data need to implement these controls. Following these ensures the organization’s IT applications and software follow the compliance rules as well as reduce cyber risks.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
Role of ITGCs in Preventing Cyber Security Breaches
IT General Controls help protect sensitive data. It helps limit access to sensitive information, thus, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This restriction prevents hackers from gaining access to or stealing sensitive data.
Implementing these controls ensures that the IT systems are authorized and tracked. Henceforth, maintaining the integrity of systems and recording the modifications correctly.
ITGC requires organizations to regularly back up data and have a strong recovery plan. In case of a cyberattack, this enables quick recovery, reducing operational disruptions and protecting the organization from financial and reputational damage.
The controls also mandate continuous monitoring of IT assets. Ongoing monitoring helps identify and fix vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. Regular vulnerability assessments (VAPT) are key to spotting and addressing security gaps.
IT General Controls Implementation – Kratikal’s Approach
Kratikal adopts the following approach to implement the Information Technology General Controls:
Planning Stage
Kratikal starts by identifying the necessary IT General Controls to implement in a particular organization. Multiple factors are considered when deciding on the controls. A few of these including industry type, data collection methods, data storage, usage, and location are considered in making this decision.
Defining the Scope
After the planning stage is complete and the appropriate ITGCs are selected, the experts select a timeline for the implementation of these controls. This is done by evaluating the capacity of managed service providers (MSPs), if involved, along with available resources. The timeline is usually planned by working backward from a target end date.
Assessment of Risk in Current IT Infrastructure
The present status of the organization’s IT infrastructure is evaluated to identify any associated risks or areas that need improvements. The security gaps are eliminated based on relevance and the need to meet the compliance requirements. Also, for each ITGC selected, a baseline is created.
Designing and Implementing
Next, the Kratikal team creates a plan to design and implement the chosen controls. This plan is based on the findings from the risk assessment done in the previous stage. The selected general controls are then combined with necessary security enhancements to create a strong framework.
Testing the ITGCs Implemented
The final step is testing the implemented IT general controls to ensure they are effective. Therefore, extensive testing is done on each control to identify any issues and confirm that the controls work properly in all scenarios.
IT General Controls Audit Process
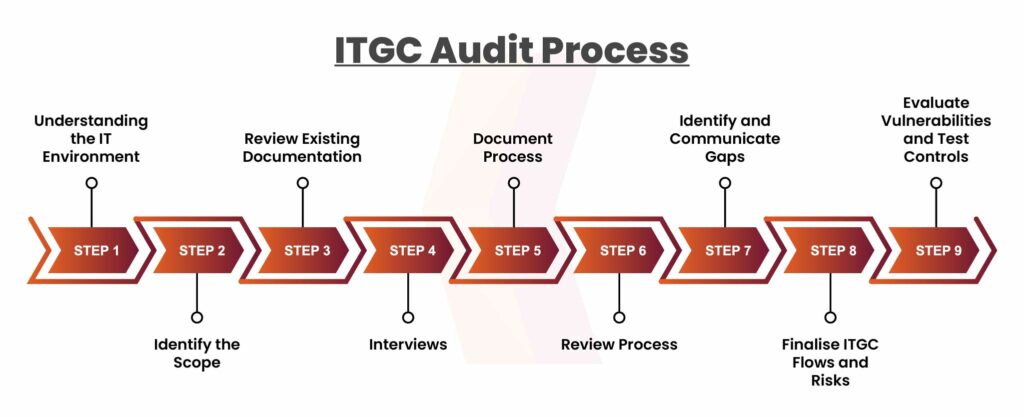
Firstly the audit team understands how the organization’s IT infrastructure functions and what technology they use. Next, the auditors determine what areas will be included in the audit. They evaluate the documents already available, such as policies or previous audit reports, to understand the current controls. Next, they talk to key people in the organization, like IT staff, to learn about the ITGCs they have in place. At this stage, the auditors write down the processes and controls currently being used in the organization. They examine the review processes to ensure they are being followed correctly. If they find any areas where controls are missing or weak, they share this with the team. Lastly, they confirm if these controls are in place followed by looking at the test controls to see if they effectively prevent issues.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
As an end-note here are some best practices for organizations. Use compliance security frameworks like COSO, COBIT, or ISO 27001 to guide your IT security team as well as prepare for audits. Regular monitoring and updating the IT assets helps eliminate hidden vulnerabilities. Ensure that third-party vendors also align with IT General Controls at the time of purchasing new IT assets. These practices strengthen defenses and reduce security breaches.
FAQs
- What is ITGC in cyber security?
IT General Controls are guidelines for an organization to manage, secure, and increase the efficiency of its information technology infrastructure. It also helps the organization develop and maintain its IT systems and achieve compliance.
- What are the main IT General Controls?
Physical Security and Environment Security, Logical Security, Change Management, Backup, and Recovery, Incident Management, and Information Security are the main IT General Control types.
- How are IT General Controls implemented?
ITGC is implemented in the following manner – Planning, Defining the Scope, Risk Assessment in Current IT Infrastructure, Designing and Implementing and Testing the ITGCs Implemented.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *