Your small business is one of the estimated 350 to 450 million Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) worldwide. There are 6.3+ crore enterprises in India alone. With SMBs being one of the easiest and the most preferred epicentre for the hackers ulterior motive, cybersecurity for small business should not be put forward as a question. Here is an attempt to guide young businesses thrive without leaving any gates open to pull back down or worse, shut down! What is the risk? No solution can help unless you understand how serious the risk factor is.
Table of Contents
- 1 Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
- 1.1 Cybersecurity for Small Business – How To Approach Effective Security?
- 1.1.1 Establish a Strong Security Foundation
- 1.1.2 Cybersecurity for Small Businesses – Essential Measures
- 1.1.2.1 Firewalls and Network Security
- 1.1.2.2 Endpoint Protection (Antivirus/Anti-Malware)
- 1.1.2.3 Secure Configuration and Patch Management:
- 1.1.2.4 Access Control and Identity Management
- 1.1.2.5 Enforce a Robust Password Policy
- 1.1.2.6 Data Backup and Recovery
- 1.1.2.7 Employee Security Awareness Training
- 1.1.2.8 Threat Monitoring and Incident Response
- 1.2 Cybersecurity for Small Business – VAPT
- 2 Get in!
Cybersecurity for Small Business – Why Do You Need It?
We are talking facts here. The numbers are concerning and every small business must be aware of the same:
Impact of Cyberattacks in Small Business
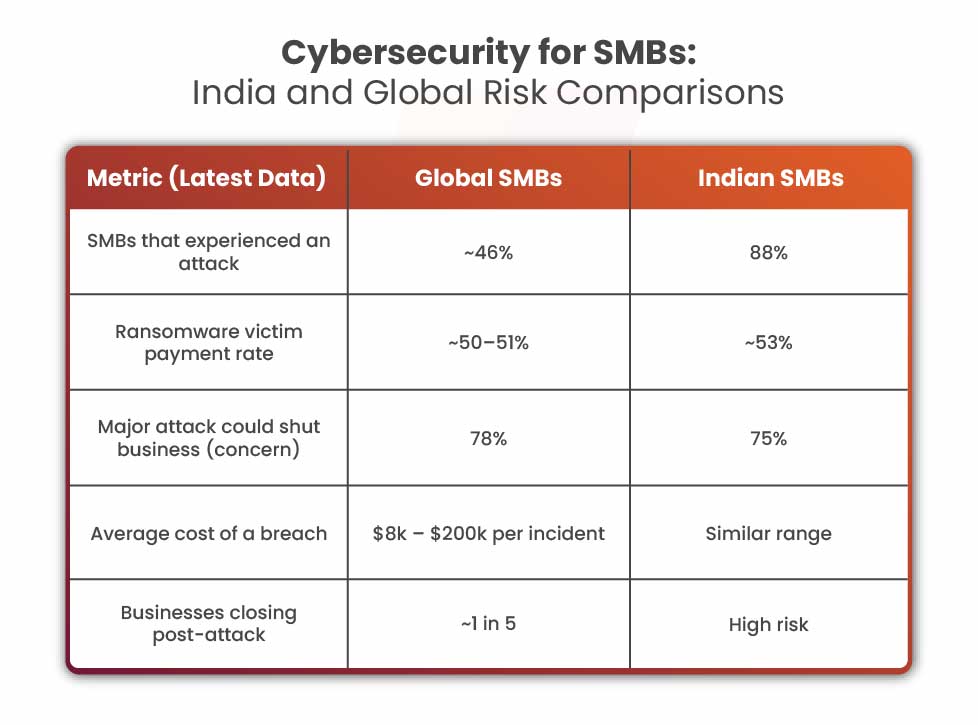
- A recent global survey of 5,000 SMB owners found 46% have experienced a cyberattack on their current business.
- 94% of SMBs had faced at least one cyberattack by 2024, a jump from 64% in 2019.
- Surveys show 78% of SMB leaders are now concerned that a severe cyberattack could shut down their business.Nearly 1 in 5 attacked SMBs end up filing for bankruptcy or closing.
- Over 559 million cyberattacks targeted SMBs globally in just one quarter (Q2 2024).
- A late-2024 survey of 1,400+ IT professionals at small and mid-sized firms found 88% of these businesses experienced a cybersecurity incident in the past 12 months. This suggests that virtually 9 in 10 small businesses in India fell victim to some form of cyberattack within a year.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
- In 2025, 90% of Indian CISOs expect a cyberattack in the next 12 months, the highest level of concern globally. 74% admitted their organizations are not fully prepared to respond to sophisticated attacks.
- Malware infections (viruses, trojans, spyware) account for a large share of SMB incidents – roughly 18% of all cyberattacks on small businesses involve malware payloads. 75% of SMBs say they could not continue operating if hit by a major ransomware attack.
- Roughly 51% of small businesses victimized by ransomware end up paying the attackers, about half paying out-of-pocket, and half via cyber insurance.
- Human error contributes to an estimated 95% of cybersecurity incidents in small businesses
Industry-Specific Impact on Small Business Cyberattacks
According to Verizon’s data, 46% of all breaches globally involve businesses with <1,000 employees, and breaches in industries like healthcare, finance, and retail often affect smaller organizations that hackers perceive as softer targets.
- Targeted Industries: Tech Industry, IT, Financial Services, Insurance Firms and Manufacturing.
- Global SMB Sectors: Financial and professional Services (small accounting firms, clinics, or legal offices), Retail and e-Commerce.
Financial Impact of Cyberattacks on SMBs
- Cost per Breach: One analysis found the median cost of a cyber incident for a small business is around $8,300, yet another report put the average breach cost for an SMB at about $200,000 when considering major losses. 60% of small businesses that suffer a major cyberattack go out of business within six months and as noted earlier nearly 20% of attacked SMBs end up closing or bankrupt.
- Ransom Payments and Recovery: Many SMBs do pay (about half of victims, as noted), but paying a ransom of even ~$25,000, roughly a typical demand, is a huge hit for a small firm. Only ~17% of small businesses have cyber insurance coverage to help absorb these costs.
- Downtime and Business Disruption: About 50% of SMBs report it took 24+ hours to recover normal operations after their most recent attack. In fact, 51% of small businesses said their website (or critical systems) were knocked offline for 8–24 hours due to a cyber incident.
- Wider Impact – Customers & Reputation: In surveys, nearly 40% of small businesses said they lost important data as a result of an attack, and 29% reported losing clients or contracts because of the incident. According to the Identity Theft Resource Center, 42% of SMBs reported a revenue loss after a breach, and 32% said they lost customer trust as a direct consequence.
- Comparative Impact: The Verizon DBIR noted that 95% of SMB security incidents cost between $826 and $653,587 – a huge range, but even the high end is a rounding error for a Fortune 500, whereas it could be fatal for a 50-person business.
Cybersecurity for Small Business – How To Approach Effective Security?
The nature of cybersecurity you need must align with your nature of business and organizational goals. Here’s the basic yet compulsory guide that you as a young business can prefer to outshine in your domain without worrying about the malicious cyber actors in the long run. Here’s cybersecurity for SMBs simplified:
Establish a Strong Security Foundation
- Secure Leadership and Culture: Effective cybersecurity starts at the top. You as a security leader must develop a security-first mindset among your employees and allocate optimum resources to security. In India, leadership should also be aware of local cyber laws and guidelines that make cybersecurity a governance issue.
- Assess Risks and Assets: Start with a risk assessment. This will help you:
- Identify your critical assets.
- Evaluate threats to them.
- Determine where data resides and who has access.
- Harm that could occur if each asset were compromised.
- Prioritize what to protect first and inform your security strategy.
Furthermore, regarding cybersecurity for small business in India, CERT-In (India’s Computer Emergency Response Team) has defined 15 elemental cyber defense controls for MSMEs as a baseline to protect critical data and ensure legal compliance. The SMBs in India are, therefore, advised to assess their security along these baseline controls. Cybersecurity companies like Kratikal help implement these frameworks as well as conduct internal audit.
- Develop Security Policies and Procedures: Draft simple, clear security policies for your business. These should cover areas like acceptable use of IT, data handling, incident response plans, and access control rules. Moreover, you need to ensure policies align with any regulatory requirements.
- Compliance and Legal Awareness: Different industries and regions impose cybersecurity obligations. Globally, you need to be mindful of laws like GDPR for customer data privacy and other sectoral rules. Indian small businesses should be aware of regulations like the IT Act amendments and sector-specific guidelines like RBI cybersecurity frameworks for finance.
If navigating compliance is challenging, consider affordable programs like “Kratikal for Startups” which offer expert guidance to make startups compliant at competitive prices.
Cybersecurity for Small Businesses – Essential Measures
Every small business should implement core security measures to establish a baseline defense. Here is a checklist of key cybersecurity practices applicable to any SMB, whether a tech startup or a local retail shop, with brief on global best practices and Indian context:
Firewalls and Network Security
- Deploy a firewall at your network perimeter and enable host-based firewalls on devices. This is done to filter traffic and block unauthorized access
- Properly configure your firewall to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. It can stop hackers by blocking malicious sites or connections.
- Ensure your Wi-Fi networks are secure. Use strong encryption like WPA2/WPA3 instead of outdated WEP and set a strong router admin password.
- Segregate a guest Wi-Fi network from your internal network for visitors or customers.
- Regularly update firewall firmware and review rules to keep defenses current.
Endpoint Protection (Antivirus/Anti-Malware)
- Install reputable antivirus or endpoint protection software on all computers and devices.
- Software should be kept up-to-date to detect the latest viruses, spyware, ransomware, and other malware.
- Only use licensed software versions to ensure you receive vendor support and regular security updates.
- Do not disable built-in OS security features like Windows Defender or macOS Gatekeeper) without a good reason. This is because they add layers of protection.
“Remember that antivirus is reactive, finding and removing malware that got in, whereas firewalls proactively block threats at the door – you need both.”
Secure Configuration and Patch Management:
- Keep all software and systems updated with the latest patches. About 60% of breaches involve unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Enable automatic updates wherever possible for operating systems, applications, and plugins. Don’t forget network devices like routers – these may require manual firmware updates.
- Remove or disable any software, services, or user accounts you don’t need. Avoid using pirated or unauthorized software, besides legal issues, they often carry malware or miss critical security patches.
Access Control and Identity Management
- Implement strong access controls to ensure only authorized people can reach sensitive data and systems.
- Follow the principle of least privilege. Each employee should have the minimum access rights needed for their job.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign permissions based on roles/responsibilities, which prevents casual access to critical resources.
Enforce a Robust Password Policy
- Ensure every password is strong and unique with at least 8 – 12 characters with a mix of letters, numbers, symbols and change default credentials on all devices.
- Educate staff not to reuse passwords or share them.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on important accounts (email, admin logins, banking, etc.). This is because MFA can block the vast majority of unauthorized login attempts even if passwords are leaked.
- Using a password manager can help employees maintain unique, complex passwords without the hassle.
- Have a process to promptly revoke access for departing employees or contractors and to review user access rights periodically.
Data Backup and Recovery
- Regular backups are a lifesaver if you suffer a ransomware attack or data loss incident.
- Schedule automatic backups of important files and databases at least daily or weekly.
- Use the 3-2-1 rule for backups: keep multiple copies (at least three), on two different media (e.g. cloud storage and external drive), with at least one offsite or offline copy.
- Storing backups offline is critical. This protects them from being encrypted by ransomware that might spread through your network.
- Encrypt backup files and ideally all sensitive data at rest so that even if backup media are stolen, the data is unreadable.
- Test your backups periodically by attempting restorations. An untested backup might fail when you need it most, so verify you can recover critical systems from your backups.
Employee Security Awareness Training
- Your employees can be the weakest link or the first line of defense.
- Many breaches originate from employees being tricked or making errors.
- Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training to educate staff on threats like phishing, social engineering, and safe internet use.
- Train them to recognize suspicious emails or links and to report incidents immediately.
- Emphasize good practices like using strong passwords and securing their devices.
- Establish clear policies on handling customer data and avoiding shadow IT.
Threat Monitoring and Incident Response
- Implement basic threat monitoring so you can detect problems early.
- At minimum, enable logging on critical systems and network devices.
- Regularly review logs or use tools to alert on unusual activity.
- Continuously monitor network activity and privileged user actions to catch suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts. It’s recommended to deploy centralized monitoring solutions that can analyze logs and network traffic for threats in real-time.
Cybersecurity for Small Business – VAPT
A vulnerability assessment systematically identifies security flaws in your networks, systems, or applications, and provides a prioritized list of issues to fix. A penetration test goes a step further! Skilled ethical hackers emulate real attacks to find out if vulnerabilities can be exploited and what damage could result. Conducting VAPT helps you discover and fix weaknesses proactively, reducing the risk of data breaches, financial loss, and reputation damage.
Structure of VAPT
Generally, a Vulnerability Assessment (VA) comes first, followed by a Penetration Test (PT). The VA uses automated scanners like AutoSecT and manual analysis to identify known vulnerabilities across your IT infrastructure. You get a report listing these vulnerabilities, often with a risk rating and remediation steps. The PT uses creative techniques to actively exploit some of those vulnerabilities in a controlled manner, to see what an attacker could achieve.
Both are complementary – VA gives breadth, PT gives depth.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
We have come to the end of this article. We have shared the risks and also provided you a detailed checklist on cybersecurity for small business. This is all you need to secure your SMBs from the evergrowing sophisticated attacks.
FAQs
- Why is cybersecurity for small businesses important?
Cybersecurity protects small businesses from data breaches, financial loss, and closure. With nearly 1 in 5 SMBs shutting down after a major attack, security is essential for survival and growth.
- What are the most common cyber threats to small businesses?
Small businesses face ransomware, malware, and human error, which cause most breaches. Industries like finance, healthcare, and retail are frequent targets due to valuable customer data.
- How can small businesses protect themselves from cyberattacks?
They can safeguard by using firewalls, MFA, backups, and employee training. Regular VAPT testing and initiatives like Kratikal for Startups help close security gaps affordably.









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *