In an era of escalating cyber threats and strict regulatory expectations, your organization must not only secure their systems but also prove they are secure. This is where automated vulnerability scanning becomes invaluable. By continuously probing your IT asset inventory for weaknesses, automated vulnerability scanners like AutoSecT help maintain a strong security posture while providing tangible evidence for compliance with frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), SOC 2, and others. Why not explore how automated vulnerability scanning platforms and tools can align with these frameworks, enabling CISOs, compliance officers, and IT professionals to bridge the gap between technical security measures and compliance obligations?
Table of Contents
Automated Vulnerability Scanning – The Need for Mapping Compliance Frameworks
In most organizations today, vulnerability scans are fully automated, with minimal human intervention during the scanning process. Security teams configure scan schedules and scopes, and the tools then flag any findings for review. This automation drastically improves scalability and consistency as scans can cover thousands of assets across an enterprise regularly, something that would be impractical manually.
There is no doubt that vulnerability exploitation remains one of the most common cyber-attack vectors. By catching and fixing weaknesses before attackers do, organizations reduce the risk of incidents. Indeed, the Center for Internet Security (CIS) ranks continuous vulnerability management including frequent automated scanning as a critical cybersecurity practice for organization like yours. Moreover, many industry regulations explicitly or implicitly require regular vulnerability scanning as part of security due diligence. For instance, PCI-DSS mandates quarterly scans for any systems handling credit card data.
This brings us to the conclusion that automated scanning is both a cornerstone of good security hygiene and a key component in meeting various compliance benchmarks.
An Effective Vulnerability Scanning Tool – AutoSecT
There are many vulnerability scanning tools available, ranging from open-source utilities to enterprise-grade platforms. One among them is AutoSecT.
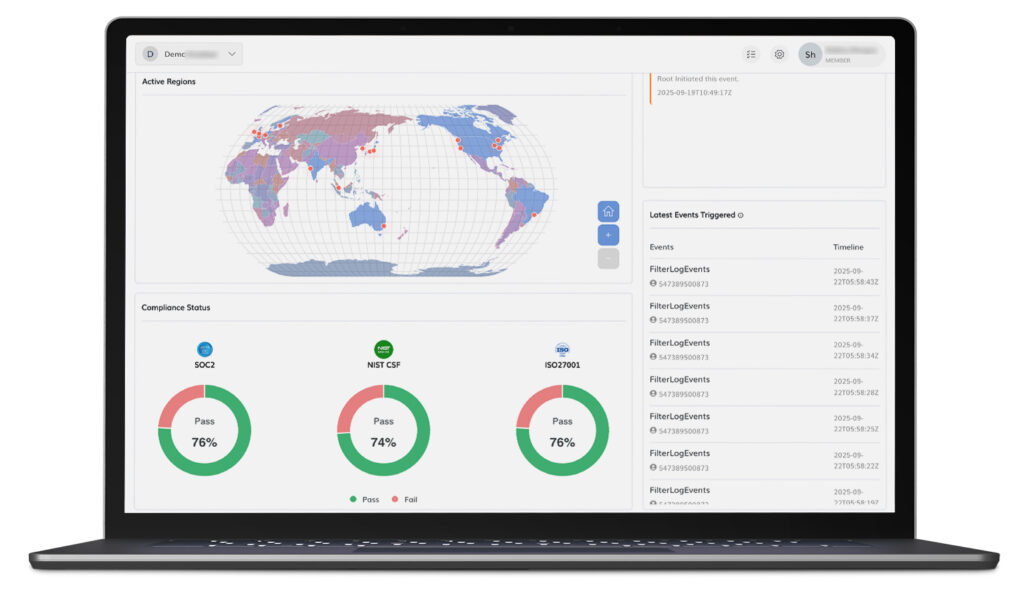
Speaking of facts, managing cloud security and compliance can be complex, with multiple frameworks, standards, and regulatory requirements to track. AutoSecT simplifies this process by automatically mapping discovered vulnerabilities to your organization’s compliance frameworks, ensuring you always have a clear view of your security posture. Each vulnerability detected across your cloud environment, whether in AWS, Azure, or GCP, is analyzed, categorized, and linked to relevant compliance standards. This mapping is then visually represented on an intuitive dashboard, allowing security and compliance teams to quickly identify high-risk areas, prioritize remediation, and demonstrate adherence to auditors or stakeholders.
By integrating vulnerability management directly with compliance tracking, AutoSecT not reduces manual effort and human error and empowers organizations to maintain a robust, audit-ready cloud environment while continuously mitigating risks before they escalate into costly breaches.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
How Automated Vulnerability Scanning Aligns with Framework Controls
Let us break down how automated vulnerability scanning contributes to compliance with each framework’s specific controls or domains. By understanding these mappings, organizations can directly link scanning activities to compliance requirements, thus, turning technical findings into evidence of control effectiveness.
ISO 27001
Within ISO 27001, automated vulnerability scanning primarily supports the controls related to risk management and technical security. Here are the key areas it impacts:
Annex A 8.8 – Management of Technical Vulnerabilities:
- Identify and remediate vulnerabilities promptly using automated scans.
- Reports guide fixes like patching or configuration changes.
- Providing scan results and proof of remediation demonstrates compliance during ISO 27001 audits.
Annex A 18.2.3 – Technical Compliance Review:
- Ensures systems comply with security configuration standards.
- Automated vulnerability scanners help by detecting deviations from benchmarks, such as weak SSH ciphers, automatically highlighting non-compliance and supporting adherence to 18.2.3.
Other Controls:
- Scanning supports multiple ISO 27001 controls beyond vulnerability management.
- Integrates with SIEMs to aid logging and monitoring (A.12.4.1)
- Identifies misconfigured or default accounts for access control reviews (A.9.2.3)
- Detects code vulnerabilities for secure development (A.14.2.1)
- Scans reveal deviations from secure baselines (A.18.2.3)
- Automate discovery of known vulnerabilities (A.12.6.1), providing actionable evidence to demonstrate compliance across technical controls.
Risk Assessment and Treatment (Clause 6 & 8 in ISO):
- ISO 27001 requires a risk assessment (Clause 6.1) and risk treatment plan.
- Vulnerability scan findings turn theoretical risks into concrete issues with measurable severity
- Makes assessments evidence-based and strengthens the organization’s overall security posture.
Continuous Improvement (Clause 10 & PDCA):
- ISO 27001’s PDCA cycle relies on regular monitoring and improvement.
- Automated vulnerability scanning supports the “Check” phase by measuring control effectiveness and the “Act” phase by informing corrective actions.
- Tracking high-severity findings over time turns scan trends into clear evidence of continuous improvement, in line with Clauses 9.1 and 10.2.
NIST CSF
Under the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, automated vulnerability scanning plays a role in fulfilling outcomes across multiple functions:
- Identify (ID) Function – Risk Management Strategy & Asset Management: An up-to-date asset inventory and understanding of the business environment are essential. Scans reveal vulnerabilities on critical systems, helping prioritize risks (ID.RA) and guide mitigation strategies (ID.RM) to protect operations, assets, and reputation.
- Protect (PR) Function – Maintenance & Protective Technology: NIST CSF emphasizes secure maintenance (PR.MA-2) and protective technology (PR.PT). Regular vulnerability scanning supports these activities by identifying outdated systems and required patches, ensuring software remains updated and security controls are effective (aligned with PR.IP-12).
- Detection (DE) Function – Security Continuous Monitoring: Automated vulnerability scanning is central to DE.CM-8, helping identify and address system vulnerabilities promptly. A structured scanning covering relevant systems regularly and integrating results into organizational awareness fulfills this CSF subcategory. Scans also support DE.CM-7 and DE.CM-1 by detecting unauthorized software and devices on the network, enhancing continuous monitoring.
- Respond/Recover Functions: While focused on response and recovery, scanning results support these functions. Discovering high-risk or actively exploited vulnerabilities can trigger incident analysis (RS.AN) and mitigation (RS.MI), such as applying patches proactively to reduce risk and strengthen organizational resilience.
SOC 2
For SOC 2, recall that it’s less about specific technical measures and more about showing the auditor that your controls meet the criteria. Here’s how scanning maps to those criteria:
- Security Category (Common Criteria CC1-CC9): Automated vulnerability scanning primarily supports CC7 (System Operations) and CC6 (Logical & Physical Access). Scans directly address CC7.1 by identifying new vulnerabilities and risky configuration changes, and also aid CC7.2 by detecting anomalies or unauthorized systems, helping organizations meet SOC 2 requirements effectively.
- CC7.1 Evidence: Auditors expect a clear vulnerability management process for CC7.1. Providing recent scan results along with proof of remediation demonstrates active identification and resolution of security issues, directly satisfying the criterion and showing a mature SOC 2 Security posture.
- Other Criteria: If your SOC 2 report includes additional principles, automated vulnerability scanning still helps:
- For Availability, scans can uncover weaknesses (like potential DoS vulnerabilities or single points of failure due to unpatched systems) that might impact uptime. Fixing those contributes to resilient, highly available systems.
- For confidentiality, scanning finds issues that could lead to data leaks or unauthorized access (e.g., an open port with a known exploit), thus helping protect confidential data.
- For Processing Integrity, while less directly related, maintaining systems free of known bugs can ensure they process data correctly and are not tampered with.
- For Privacy, scanning can identify vulnerabilities that might expose personal data, thus supporting privacy commitments.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
In The End
Automated Vulnerability Scanning turns security work into proof of compliance. By finding and fixing weaknesses fast and mapping each fix to ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and SOC 2, your organization stays safer and audit-ready at the same time. AutoSecT makes this simple: scan, see the gaps, link them to controls, and track remediation. Start with a clear schedule, focus on high-risk assets, and show your results. That’s how you turn checks into confidence and compliance into a continuous habit.
FAQs
- What is Automated Vulnerability Scanning in compliance?
It’s the use of tools, platforms, and programs to detect security weaknesses and map them to frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and SOC 2, keeping systems secure and audit-ready.
- How does Automated Vulnerability Scanning support ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and SOC 2?
Scans align with ISO 27001 Annex A 8.8, NIST CSF DE.CM-8, and SOC 2 CC7.1, providing reports that prove compliance and guide quick remediation.
- Why should organizations use tools like AutoSecT for compliance mapping?
AutoSecT links vulnerabilities to framework controls, offers dashboards across AWS, Azure, and GCP, and simplifies compliance tracking and audits.
Reference: https://www.iso.org/standard/27001; https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.29.pdf









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *