
In a time of swift technological progress and more global connectivity, protecting sensitive financial data has become critical for businesses. System Audit Report commonly known as SAR, acts as a vital strategy that secures against the complex web of problems. These issues have been brought about by threats to money laundering, geopolitical unpredictability, and the pressing requirement for safe payment gateways.
This blog aims to highlight the intricate relationship between organizations and SAR compliance. We will also look at its potential for managing geopolitical risks, fortifying financial sectors, and enhancing IT governance.
What is SAR Compliance Audit?
System Audit Report compliance scrutinizes a financial institution’s systems, practices, and processes meticulously to ensure adherence to all legal requirements for identifying, investigating, and disclosing suspicious activity. The purpose of the audit is to evaluate how well the organization’s SAR program works to identify and stop financial crimes such as money laundering and terrorism financing.
The data centers can quickly retrieve backup copies. Spreading data over different locations represents an ongoing trend in data storage technologies. Any organization handling payment data, from fintech firms enabling transactions among peers to internationally accessible gateway operators for international cash transfers, needs to acquire the appropriate license. This makes a SAR audit necessary.
As per the recommendations released by the RBI on April 6, 2018, payment companies that have their payment system servers located outside of India are required to set up these servers within India. These servers would hold data related to the citizens of India. In accordance with the Payment and Settlement Act of 2007, the order stipulates that all payment system providers under the jurisdiction of the Reserve Bank of India shall transfer their payment systems to India.
Within the RBI’s data localization requirements, the NPCI and RBI have provided a thorough checklist for every information maintained in India. Defined as the System Audit Report criteria, this checklist lists the different domains that need to be taken into account while auditing payment systems.
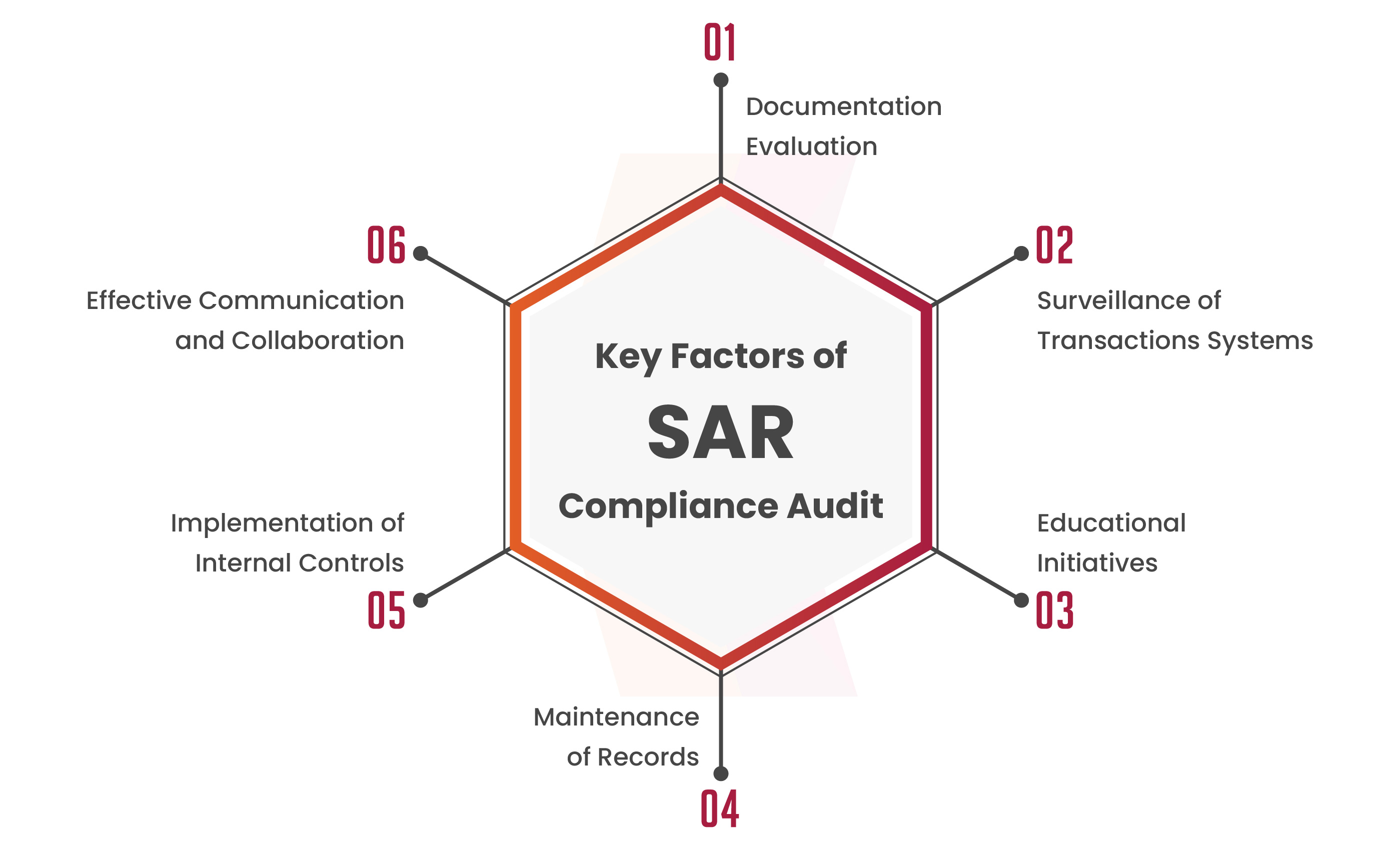
Key Aspects of System Audit Report
Documentation Review: Examining policies, procedures, and documentation related to the institution’s SAR program.
Transaction Monitoring Systems: Assessing the effectiveness of systems in place to monitor and flag potentially suspicious transactions.
Training Programs: Evaluating the training programs for employees involved in identifying and reporting system vulnerabilities.
Recordkeeping: Ensuring proper recordkeeping of SARs and related documentation.
Internal Controls: Reviewing internal controls to identify and mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and financial crimes.
Communication and Collaboration: Assessing communication and collaboration mechanisms with law enforcement and regulatory authorities.
Geopolitical Risks and SAR Implementation
Organizations face the challenging task of protecting sensitive data in the face of geopolitical unpredictability worldwide. System Audit Report is a strategic requirement that offers a strong defense against potential threats resulting from geopolitical instability. SAR has become a vital tool in protecting financial data. This data should be protected from unwanted access and potential breaches as the world struggles with shifting alliances. The data must be secure from economic swings, and unanticipated geopolitical events.
Book a Free Consultation with our Cyber Security Experts

SAR Compliance in the Financial Sector
In order to stop money laundering and other illegal financial activities, it is important for the financial industry to be a System Audit Report Compliant.
- It is necessary for the financial institutions to follow SAR requirements. This is because they play a key role in preserving the integrity of the world financial system.
- SAR requirements require quick identification, investigation, and reporting of any transactions or activities. This raises suspicions of potential financial crimes or money laundering.
- It is imperative to implement robust monitoring systems and provide personnel with training. This is done to identify potential red flags of questionable conduct.
- Some examples of these warning signs include large or odd transactions, frequent cash deposits, or patterns that deviate from a customer’s known financial behavior.
- Following SAR regulation not only satisfies legal requirements but also supports larger national and international efforts by law enforcement to combat financial crime.
- Failing to report suspected activities might have major consequences, including fines from the authorities and reputational damage.
To maintain the trust of the public, regulators, and clients, financial institutions must constantly be alert. One must be secure from emerging financial threats and must follow SAR compliance rules. Additionally, they have to take a leading role in the worldwide fight against financial crime.
Why is SAR needed by Organisations?
In times of geopolitical crisis, localization of SAR (System Audit Report) data is essential. This is to protect the financial and personal data of native individuals. Organizations can create a barrier to protect confidential information. This can help to stop illegal access by localizing SAR data, particularly in times of increased global instability.
Additionally, SAR helps organizations boost their security against threats related to anti-money laundering (AML). Organizations are able to detect and prevent unlawful transactions by identifying and looking into suspicious financial activities. This owes to the extensive insights that SAR provides. This proactive strategy supports the general security of the financial system and complies with legal standards.
Another important factor in protecting payment gateways is the comprehensive application of SAR requirements. Following SAR principles enables organizations to set up thorough procedures for identifying and reporting potentially fraudulent activity. This helps in strengthening user confidence and the resilience of payment systems.
Moreover, the implementation of SAR practices serves to improve payment service provider IT governance. It ensures a strong structure for keeping an eye on, evaluating, and reacting to questionable behavior in the field of financial transactions. This improves the cybersecurity posture overall and promotes accountability and compliance in the handling of financial data.
SAR is essentially necessary for organizations to protect themselves from geopolitical risks, fight money laundering threats, adhere to laws governing secure payment gateways, and support IT governance in the financial services industry.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the significance of SAR for businesses is highlighted by its function in reducing geopolitical risks, blocking attempts to launder money, ensuring safe payment gateways, and improving IT governance. Kratikal, a CERT-In empanelled auditor is an asset on the path to a SAR compliance audit as companies work to overcome these obstacles. With its comprehensive solutions and cybersecurity knowledge, Kratikal helps organizations strengthen their defenses, negotiate the challenges of SAR implementation, and secure the protection of financial data in a constantly changing environment.

