
E-commerce has dominated our lives in the current digital era, and many of us rely on it to fulfill our everyday shopping demands. The risk of business logic problems, which can impact user experience and the general security of these websites, has increased along with the growth of e-commerce platforms.
Business logic faults are weaknesses in the software that governs how an e-commerce website processes orders, makes payments, and ships products. Attackers may take advantage of these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, including customer information and payment information, or to change the functioning of the website for their own benefit.
We’ll look at the various kinds of business logic errors that can happen on e-commerce websites in this blog post, as well as their possible effects. To maintain the security and dependability of e-commerce websites, we will also go over recommended methods for locating and addressing these problems.
Table of Content
Define Business Logic Flaws
Business logic flaws are mistakes or weaknesses that occur as a result of how an e-commerce website handles user input. Business logic flaws are created by mistakes in the website’s design and functionality, as opposed to technical vulnerabilities, which are brought on by problems with the code or software. Bypassing security safeguards, stealing confidential information, or making illicit purchases are all possible with these weaknesses.
Examples of Business Logic Flaws
- Price Manipulation – To make money, e-commerce websites need to control their prices. Attackers may be able to manipulate prices to get deals, discounts, or even free goods by taking advantage of weaknesses in business logic. Modifying the website’s code or taking advantage of security holes in the payment gateway are two ways to accomplish this.
- Account Takeover – Several e-commerce websites let customers set up accounts to save personal data like payment information and shipping addresses. Business logic weaknesses can be used to hijack these accounts, giving attackers access to confidential data and the ability to make transactions using the victim’s account.
Business Logic Flaws are Difficult to Find
Because they sometimes involve the unique business rules and procedures of an organization, business logic errors can be challenging to locate and may not always be obvious or simple to spot using conventional testing techniques. A few explanations are as follows:
- Complexity – Business logic flaws arise due to the complex interactions between systems, processes, and rules within an organization. This complexity can make it difficult to identify where the error is occurring.
- Non-Technical Nature – These flaws are not related to technical issues like coding or database problems, but rather stem from errors in the underlying business rules or assumptions. Because of this, technical teams that may not be as familiar with the business domain may find it challenging to identify and address them.
- Limited Visibility – Business logic flaws may not immediately manifest symptoms or error messages, making them challenging to spot. Instead, they could lead to unexpected or improper behavior that users or stakeholders might not detect until it poses serious issues.
- Variability – It might be challenging to recreate and test for business logic mistakes consistently because they may only happen in specific circumstances or scenarios.
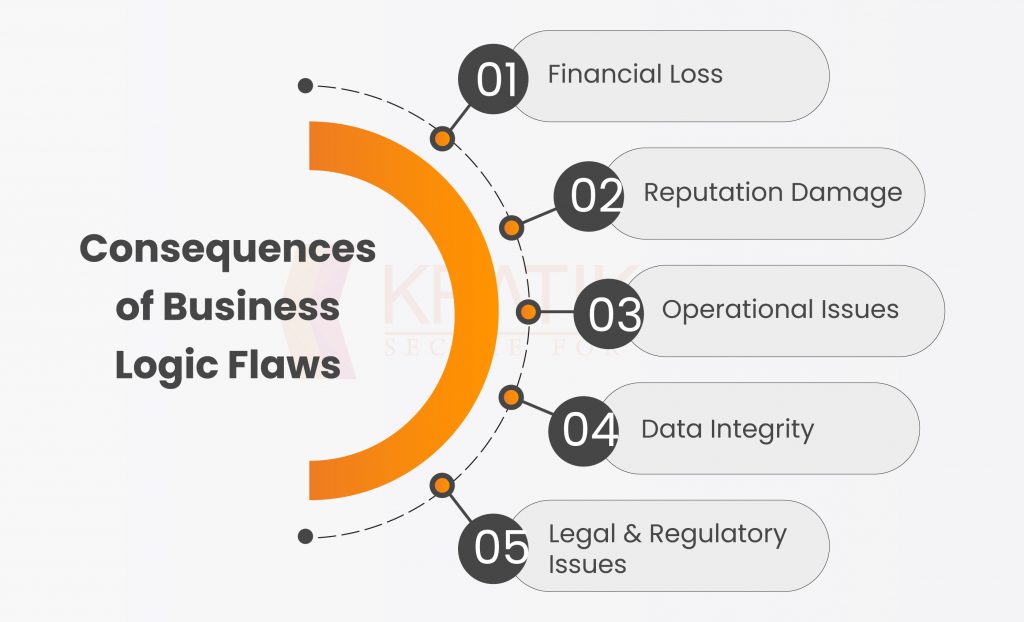
Consequences of Business Logic Flaws
Business logic flaws can have serious consequences for an organization. Here are some of the potential impacts of such flaws –
- Financial Loss – One of the most obvious consequences of business logic errors is financial loss. If the errors affect critical processes such as billing or payment processing, it could result in significant revenue loss for the company. Additionally, the cost of fixing the errors could be high.
- Reputation Damage – This can lead to customer dissatisfaction, which in turn can harm the company’s reputation. Negative reviews and word-of-mouth can deter potential customers from doing business with the company in the future.
- Operational Issues – Business logic errors can lead to operational issues such as delays, errors, and inefficiencies. This can negatively impact productivity and the ability of the company to deliver products or services on time.
- Data Integrity – They can also impact the integrity of the company’s data. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to poor decision-making, and can also compromise the security and privacy of sensitive information.
- Legal and Regulatory Issues – Business logic errors that result in non-compliance with legal or regulatory requirements can lead to fines, lawsuits, and other legal problems.
Kratikal’s Role
Business logic flaws are weaknesses in an application’s or system’s design or logic that could be used by attackers to their advantage. These defects are especially hazardous since they may be hard to find and may not be fixed by more conventional security measures like firewalls or antivirus software.
Businesses must thoroughly test and validate their systems and applications, use safe coding techniques, and maintain ongoing security monitoring in order to overcome business logic issues. In order to defend against new attacks and vulnerabilities, it is essential for businesses to stay current with the best practices and security risks. Kratikal, CERT-IN EMPANELLED ORGANIZATION provides the best solution and techniques in safeguarding security breaches.
The efficacy of a company’s cybersecurity measures ultimately depends on a number of variables, including the unique dangers they face, their level of risk tolerance, and the money they have available to invest in security measures. Businesses should adopt a comprehensive strategy for cybersecurity that addresses both organizational and technical security issues, and they should regularly review and update their security protocols as necessary.


